PESHAWAR: Privately, Afghan Taliban leaders say they have made enough sacrifices for the sake of Al-Qaeda, despite publicly never conceding they ever harbored the group, its former leader Osama bin Laden, or that Afghanistan was used to prepare the 9/11 attacks and other operations.
They also argue that they lost power in Afghanistan resisting the US invasion after the 9/11 attacks, as the Bush administration launched a vengeful assault in October 2001 to destroy Al-Qaeda and oust the Taliban from power for harboring Osama bin Laden.
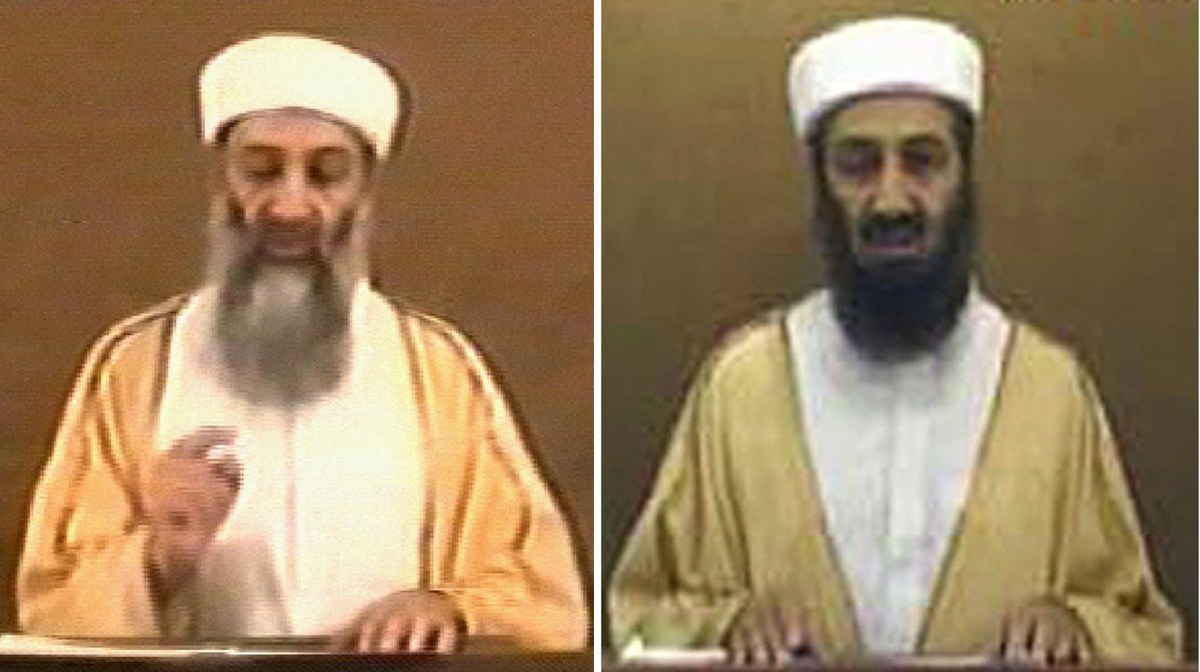

A frame grab (L) taken 29 October 2004 from a videotape aired by Al-Jazeera news channel shows Al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden. (FileAFP)
The gap between the positions that the Taliban has adopted privately and publicly shows that the Islamist group, founded by Mullah Mohammed Omar, does not want to take responsibility for the attacks — its denials meant to argue that the Taliban was, in fact, an unwitting victim when the US invaded Afghanistan.
The jury is still out on whether the Taliban remains associated with Al-Qaeda 20 years on. However, the US as well as the UN continues to claim that the Taliban has not cut its ties, providing names of Al-Qaeda members and affiliates who have died in different provinces of Afghanistan while fighting alongside the Taliban.
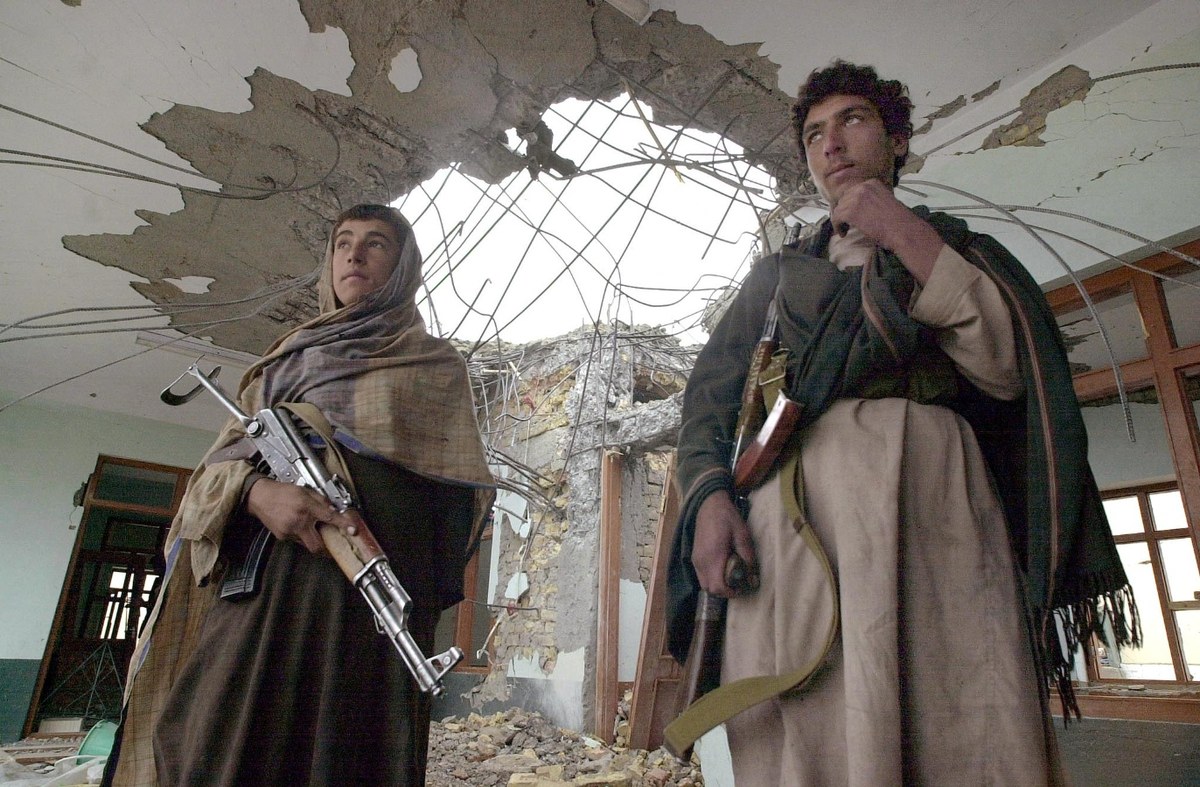

Fighters loyal to Kandahar Governor Gul Agha stand in the wreckage of former Taliban leader Mullah Mohammad Omar's compound, 14 December 2001. (File/AFP)
The Taliban has denounced the claims as propaganda, and issued blanket denials. This reaction is not surprising given that, under the terms of the Taliban-US Doha peace agreement of Feb. 29, 2020, the group must dissociate itself from Al-Qaeda.
From the outset, the Taliban had a nebulous and controversial relationship with Al-Qaeda, with conflicting views over whether the former or the latter controlled the other. The general Western viewpoint was that Al-Qaeda funded and managed the Taliban, but Taliban leaders disputed this claim and argued that they were in power in Afghanistan and, naturally, called the shots.
The relationship was rather strange because the Taliban were Afghans, known for their fighting skills and a reputation for successfully resisting invaders, including three superpowers (Britain, the Soviet Union and the US). Al-Qaeda members, meanwhile, were mostly Arabs belonging to different countries, inspired by various causes and pulled to Afghanistan by the call of war.
Curiously, the first meeting between Bin Laden and the Taliban leadership took place in an environment of suspicion. It was held in Jalalabad just a few days before the fall of Kabul to the Taliban for the first time on Sept. 26, 1996. A Taliban delegation, led by one of their commanders, Mullah Mohammad Sadiq, who had lost his son battling the Mujahideen in Logar province a few days before, was sent to Bin Laden’s house on the outskirts of Jalalabad city to meet him and find out more about his future plans.
They were unsure if Bin Laden would stay put in Jalalabad, leave Afghanistan or accompany the Afghan Mujahideen trying to escape after facing defeat by the Taliban. The Taliban fighters had just captured the city, and were on their way to Kabul.
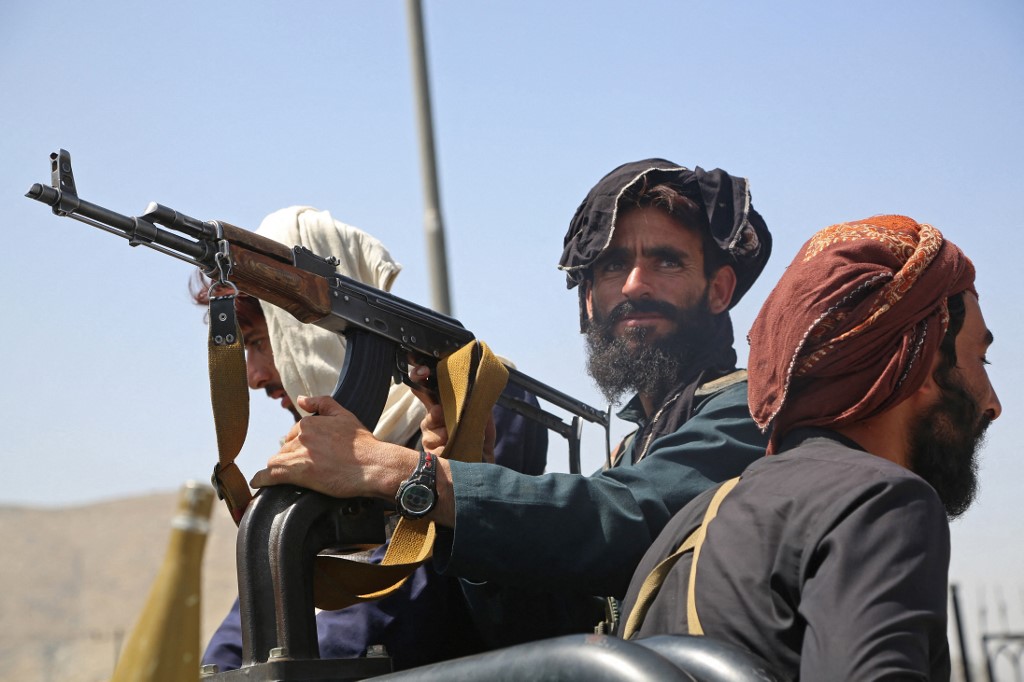

Taliban fighters stand guard in a vehicle along the roadside in Kabul on August 16, 2021, after a stunningly swift end to Afghanistan's 20-year war. (File/AFP)
I was a witness to the conversation between Mullah Sadiq, Mullah Mohammad Rabbani, the deputy leader of the Taliban at the time, and Mullah Borjan, the top Taliban military commander, to frame a unified Taliban position ahead of negotiations with Bin Laden.
All expressed their reservations about his intentions and decided to take a firm stand before deciding to let the Al-Qaeda head stay in areas controlled by the Taliban. Eventually, the issue was resolved when he gave an assurance that he would stay loyal to the Taliban and accept Mullah Omar as the Ameer-ul-Momineen. Soon afterwards, he pledged allegiance to Mullah Omar, which was conveyed to the Taliban chief through an interview I had conducted.
The Taliban supreme leader was called the Ameer-ul-Momineen (the commander of the faithful) because he had the final authority on every issue concerning the group. He was accountable to none; every member was answerable to him. His decisions had to be obeyed; disobeying him amounted to a sin.
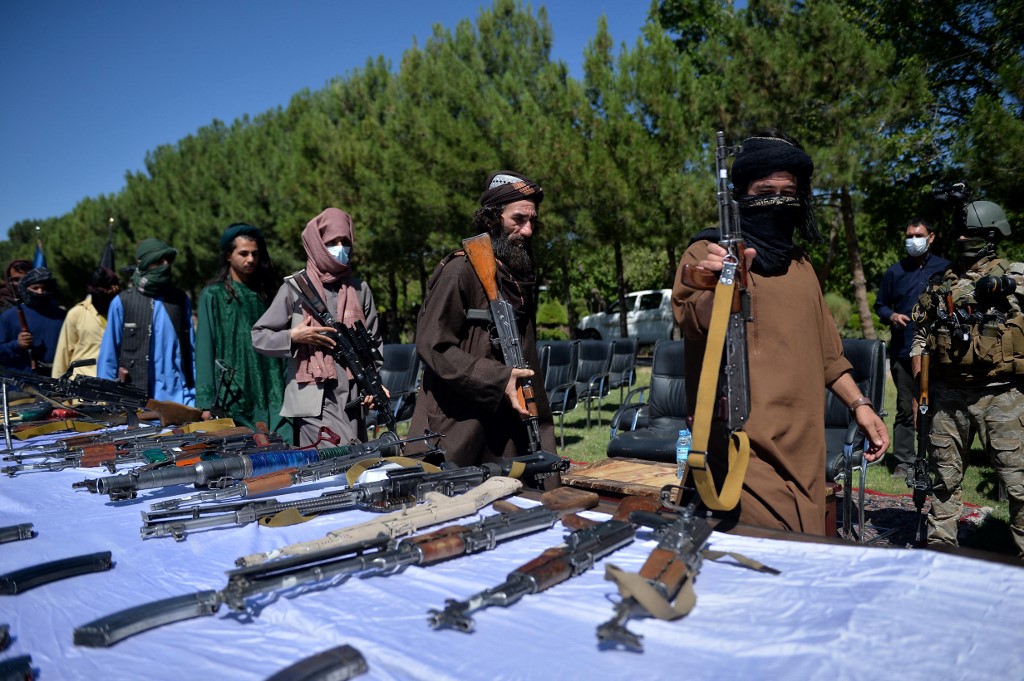

Taliban fighters put down their weapons as they surrendered to join the Afghanistan government during a ceremony in Herat on 24, 2021. (File/AFP)
If there is a common factor that has kept both the Taliban and Al-Qaeda strong and relevant, it is their ability to survive in a united way as militant groups. Otherwise, both might have split not once, but many times over.
In hindsight, the Taliban’s decision, when it emerged as a movement in the autumn of 1994 in Kandahar, to have a supreme leader proved crucial in keeping the flock together. In Osama bin Laden, Al-Qaeda too had a resourceful founder.
For 27 long years, the Taliban has remained largely united despite the fact that its members were drawn to it from rival Afghan Mujahideen groups. Its leaders resisted political and monetary temptations to defect or launch separate wars on Mujahideen factions and US-led NATO forces.
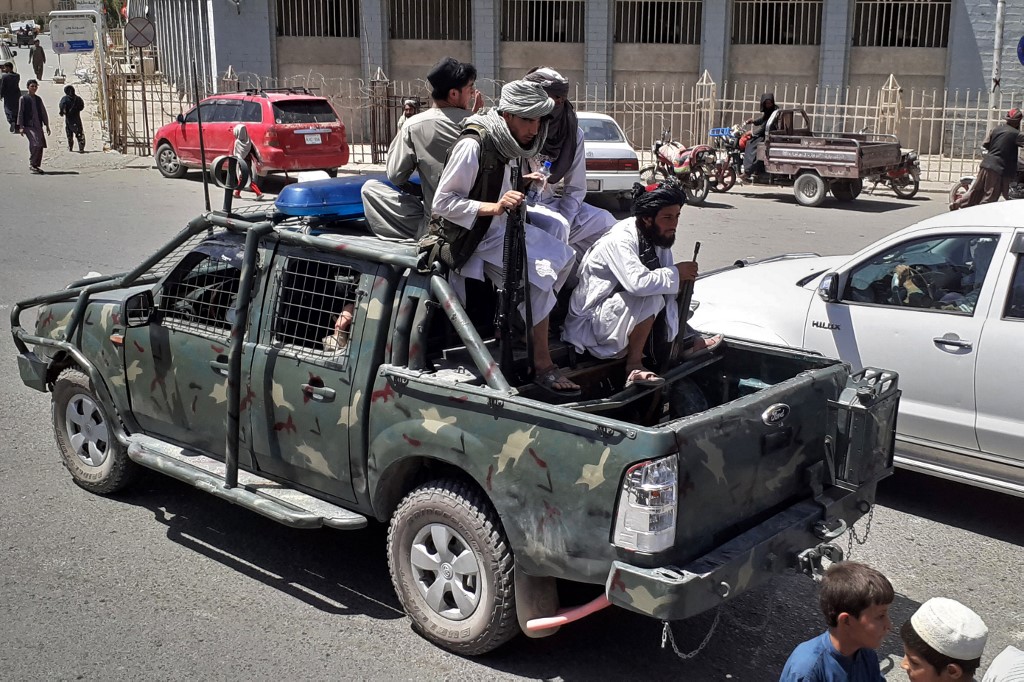

Taliban fighters are pictured in a vehicle of Afghan National Directorate of Security (NDS) on a street in Kandahar on August 13, 2021. (File/AFP)
Though there have been a few minor splits in the group, including one led by Mullah Mohammad Rasool, none was big enough to weaken it and cause its collapse.
So far, the Taliban has had three supreme leaders, including Mullah Omar, a semi-literate village cleric from Kandahar, who was the founder and remained the supreme leader until his death in 2016. His leadership was unchallenged as long as he was alive and even his death was kept secret for nearly two years as other Taliban figures feared the group might splinter once the supreme leader was gone.
The other two supreme leaders were Mullah Akhtar Mohammad Mansoor, a controversial military commander who was killed in a US drone strike in Pakistan’s Balochistan province, and Shaikh Haibatullah Akhundzada, a respected religious scholar who has led the Taliban to their biggest military victory to date — the capture of the entire country.
Mullah Omar, as we know, refused to hand over Bin Laden to the US after the 9/11 attacks. Tremendous pressure was brought to bear on him, including the threat of an American invasion of Afghanistan, but none of this was enough to make him change his mind.
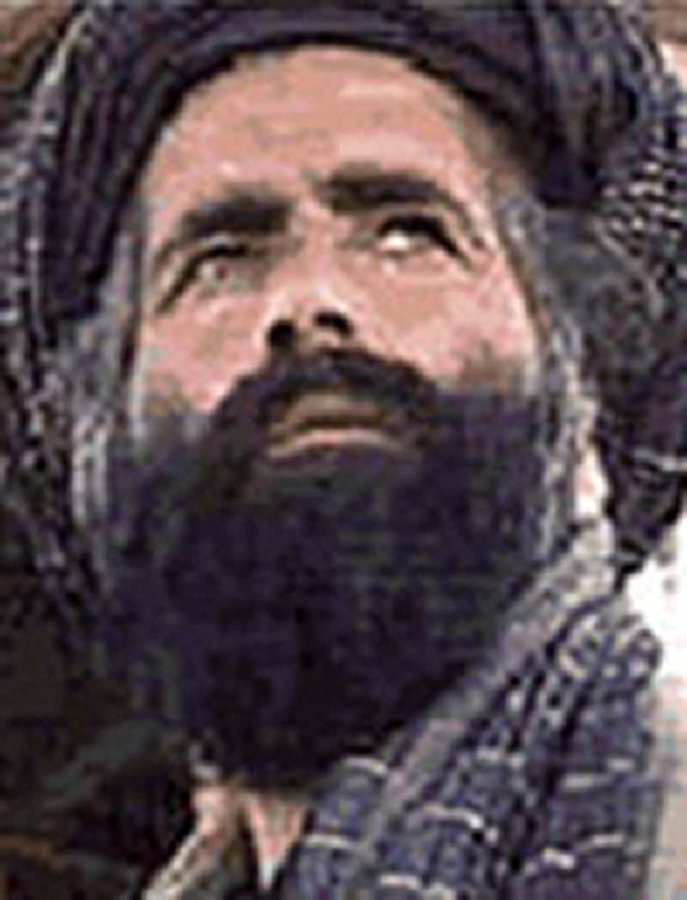

This undated photo obtained July 30, 2015 courtesy of the US State Department shows Mullah Omar. (File/AFP)
The Pakistan government, which was close to the Taliban, also applied pressure on the group through Pakistani religious scholars and the military’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) to hand over Bin Laden to the US or Saudi Arabia. Once again, the efforts did not succeed.
The Taliban was defeated in a few weeks as its fighters had no protection from American air power. However, they did not suffer many casualties. They merely retreated, melting into the rural population.
When the Americans invaded, Al-Qaeda decided to go to Tora Bora on the border with Pakistan. The Americans came to know Bin Laden was there in December 2001, and bombed heavily.
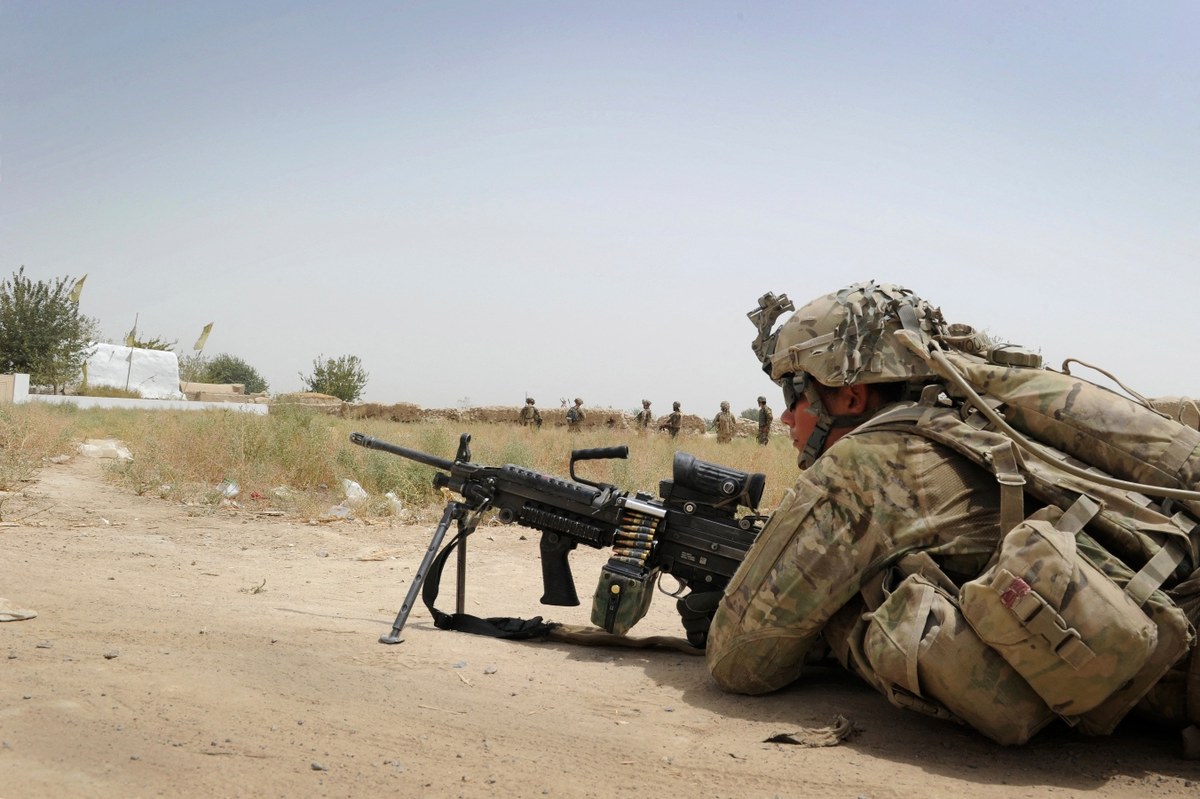

A US soldier armed with an M249 light machine gun takes position on a dirt road while troops from Battle Company, 1-32 Infantry Battalion, 3rd Brigade Combat Team and Afghan National Army soldiers approach Mullah Omar mosque. (File/AFP)
The chain of events thus culminated in the US invasion, the collapse of the Taliban regime and the deaths of scores of Taliban fighters. Mullah Omar made it clear that Islamic teachings did not allow him to betray and deliver a fellow Muslim, even if the man had a $10 million price on his head.
Twitter: @rahimyusufzai1












