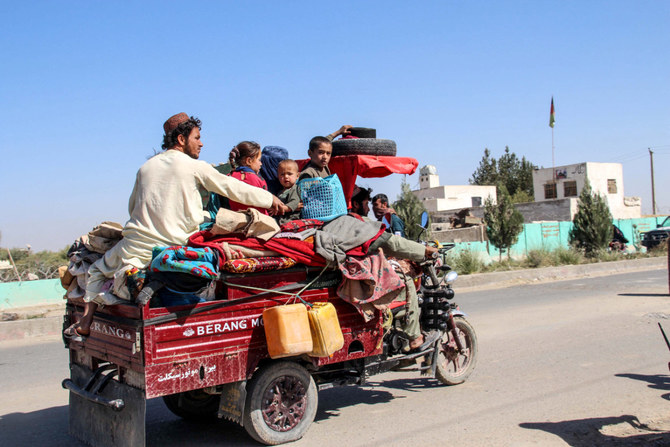
KABUL: The skeletal remains of an armored car, destroyed by the Taliban just hours earlier, smoldered in the middle of the highway, about 30km west of the Afghan capital, Kabul. It was a stark reminder of just how far the insurgents had advanced in recent months.
Further down the highway, locals helped themselves to coils of barbed wire and barriers that were originally installed to protect Afghan government forces. They had abandoned their hilltop outpost just days earlier.
This scene is a familiar one these days in war-torn Afghanistan, particularly in rural areas where army positions have fallen like dominoes to an emboldened Taliban since the withdrawal of US-led forces began in May.
The group has made spectacular gains, seizing scores of districts and vital border crossings from government forces, depriving the government in Kabul of millions of dollars in much-needed customs revenue.
Even urban centers such as Herat, Lashkar Gah and Kandahar are feeling the heat, with scores of civilians caught in the crossfire as Afghan forces and tribal militias attempt to hold off a multipronged Taliban assault.
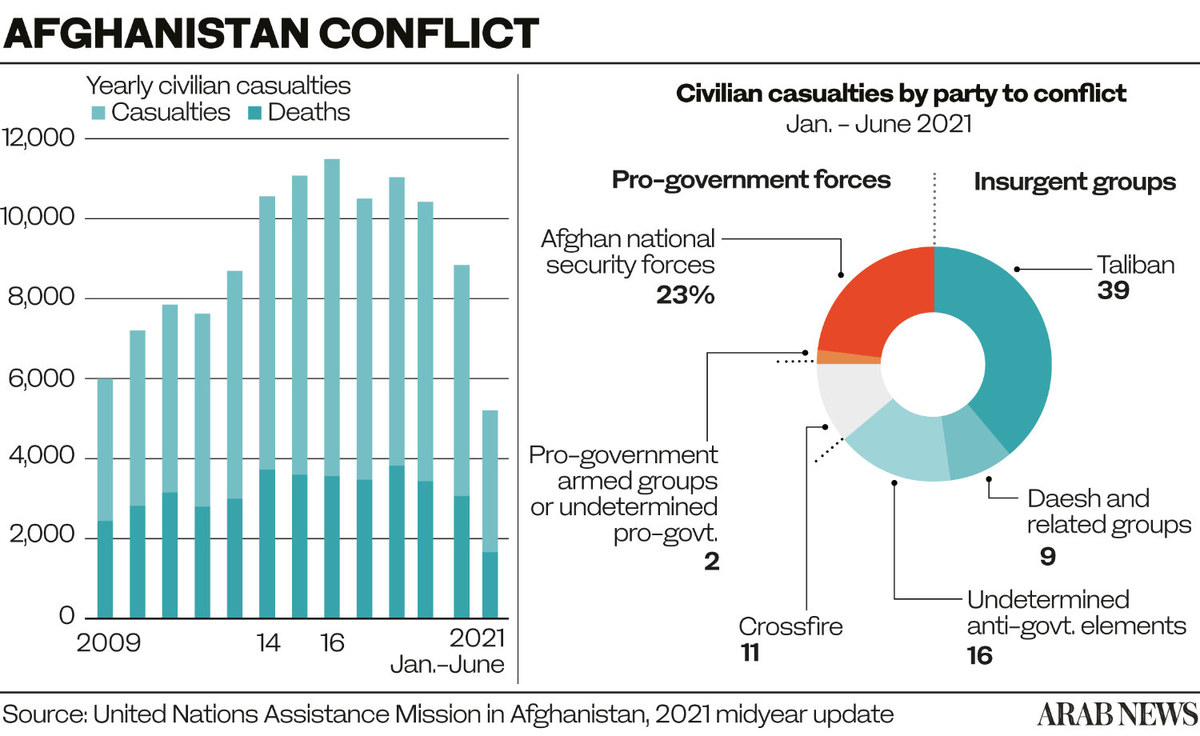
At least four people were killed and 20 wounded on Tuesday night during a coordinated attack in Kabul that targeted the country’s defense minister and other politicians. After the assault, hundreds of civilians took to the city’s streets chanting “Allahu Akbar” (“God is great”) to express their support for the Afghan security forces and opposition to the Taliban.
The state’s continued territorial losses have eroded public faith in an already weak, divided and corruption-plagued administration that depended on foreign firepower and generosity to remain afloat.
To support its beleaguered Afghan allies, the US recently resumed airstrikes in the hope of curbing Taliban advances. However, this vital support is due to end on Aug. 31, when the withdrawal of foreign forces will conclude, and the government will be left to fend for itself.
If the US-brokered talks between the Taliban and the government of President Ashraf Ghani fail to deliver a peaceful settlement, the ongoing civil war is expected to intensify. Many analysts predict the Afghan government will collapse within six months of the US departure, and are talking about the Taliban’s return to power as a matter of course.
But some expect the Taliban to tread more carefully than it did in 1996 when it wrested power from the fractured Mujahideen government that had emerged from the ruins of the 1979-89 Soviet-Afghan War.
Rather than risk a repeat of the isolationism that was cynically exploited by Al-Qaeda, which was in search of a safe haven from which to plot the Sept. 11, 2001 attacks, a Taliban “emirate” might instead seek international legitimacy to secure financial support and avoid being strangled in its infancy.
Torek Farhadi, who was an adviser to Afghanistan’s first post-9/11 president, Hamid Karzai, believes one of the top priorities for Taliban leaders and their predominantly Pashtun support might be to embrace the country’s other ethnic minorities, among them Tajiks, Uzbeks and Hazaras, to prevent a further mass exodus.
“If the Taliban brutalizes ethnic minorities in Afghanistan, as they did the last time around, and if as a result of this intra-Afghan violence they send refugees out of the country, then all neighboring countries will sour on a Taliban-led Afghanistan,” he told Arab News.
“The Taliban has promised to let a broader cross-section of the Afghan population govern with them this time around.”

Despite the increasing odds of total military victory, the group may seek a more moderate approach to ruling than in the 1990s. (AFP)
Another top priority might be to “drastically curb the metastasizing of corruption from the top of the Afghan administration,” Farhadi said
Indeed, a Taliban victory might actually end Afghanistan’s bureaucratic dysfunction, bring its ungoverned areas under centralized control, enhance the investment environment and even improve regional ties, he added.
“Personal security would improve when it comes to private citizens traveling by car or by bus from one city to another,” he said. “In city neighborhoods, the average population and shopkeepers would feel much more secure and petty crime would disappear.
“This will lead to possible reductions in the price of food and other essentials, as the links between borders and markets would become safe and efficient, while commercial transit would not endure the current racketeering system.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
“Consequently the Taliban’s ties with neighbors are expected to become friendlier, which would also have positive effects on commerce, cross-border trade and markets.”
Of course, the Taliban would have to work incredibly hard to convince the international community it has softened its puritanical stance on such matters as the rights of women.
“The Taliban have said this time they will allow women and girls to go outside the house for work and education but the memories of 1996-2001, when they asked all women to stay home, still haunt us,” Farhadi said.
“We live by these memories because the Taliban’s past practices deprived a generation of women of an education. These would not be acceptable now. Past experience makes us fearful about Taliban rule, although we don’t have proof of what their future governance would look like. But undoubtedly, women would lose the most under a strict Taliban system.”
Freedom of the press and artistic expression would also no doubt suffer under the Taliban’s narrow interpretation of Islam, Farhadi said.
The justice system, though, “would be much more effective than the current regime, where courts are corrupt and slow. However, by international standards the Taliban’s religion-based justice system would be classified as expeditious and harsh.”
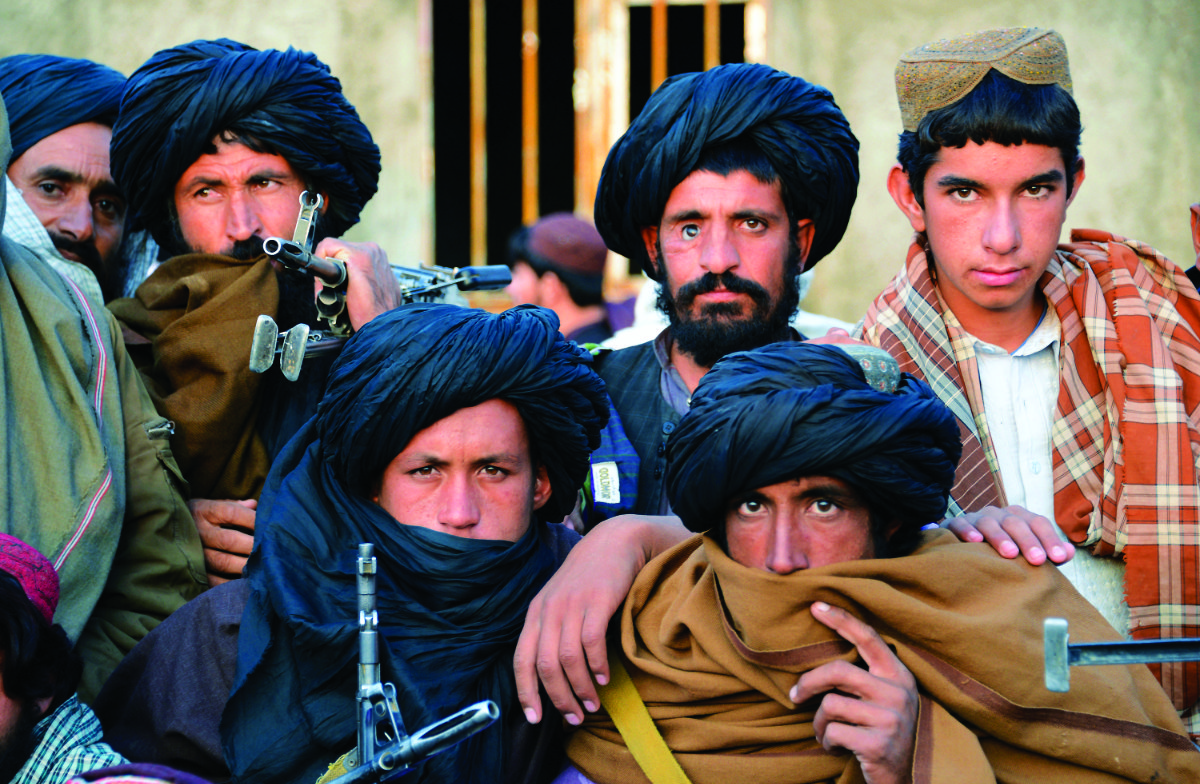

Taliban fighters have retaken control of great swathes of the country as US-led forces withdraw from Afghanistan. (AFP)
Trafficking in drugs — a widespread problem in Afghanistan — might also be reduced significantly as the Taliban has pledged to eradicate the country’s opium-production and smuggling networks.
“This would be welcome news for Afghanistan’s neighbors,” Farhadi said.
Tameem Bahiss, an analyst specializing Afghan and Pakistani affairs, believes the Taliban view drugs “as a bargaining chip to use in return for international legitimacy. If they believe counternarcotics can make them a legitimate player, they would be willing to take action.”
He remains skeptical, however, of the idea that the Taliban has somehow changed its ways.
“It is too early for us to claim that the Taliban has changed,” he said. “The primary reason is that they are still an insurgent group who are there to challenge the writ of the government.”
Said Azam, an Afghan analyst based in Canada, said a Taliban government is likely to bear many ideological similarities to its 1996-2001 incarnation, but could become more moderate over time out of necessity.
He believes Taliban 2.0 would continue to employ its rigid interpretation of Islam domestically, but deal with the wider world in a manner that is compatible with more moderate sensibilities.
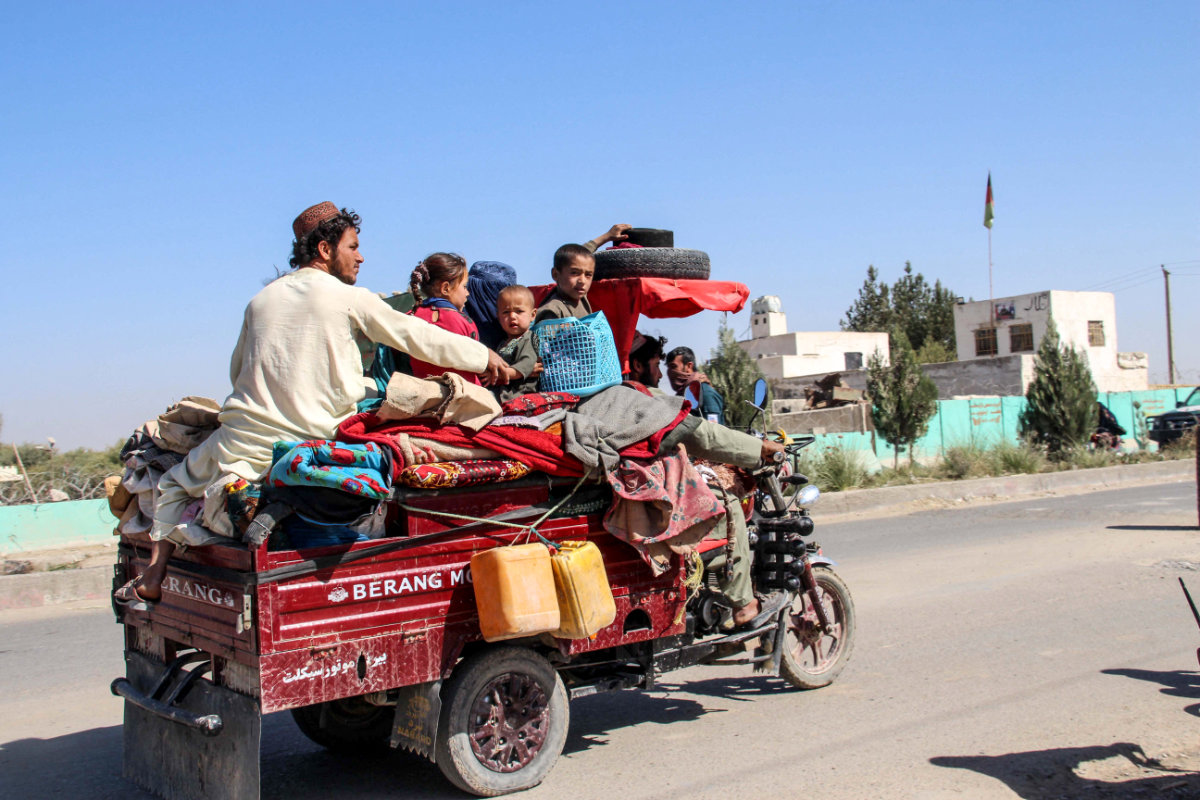

Tens of thousands of people in southern Afghanistan have fled their homes following days of heavy fighting between the Taliban and security forces in the past months. (AFP file photo)
“A new Taliban regime might have similarities with their pre-9/11 administration, still using Islam and Sharia law as a means of justifying their rule over the country,” he told Arab News. “But in regional and international affairs, they will inevitably take a nationalistic position.
“A combination of these two elements — their desire to rule and their need to act from a nationalistic position — will direct the Taliban to accept a more inclusive and, at the same time, more liberal approach to governance, civil liberties, women’s and children’s rights, as well as the rights of ethnic and religious minorities.”
It is also notable, Azam said, that Taliban leaders do not appear to be insisting on a monopoly on political power, preferring instead to lead “a more inclusive administration.”
As far as the US is concerned, assurances from the Taliban that Afghanistan will never again become a sanctuary from which terrorists can plot attacks remains the overriding objective.
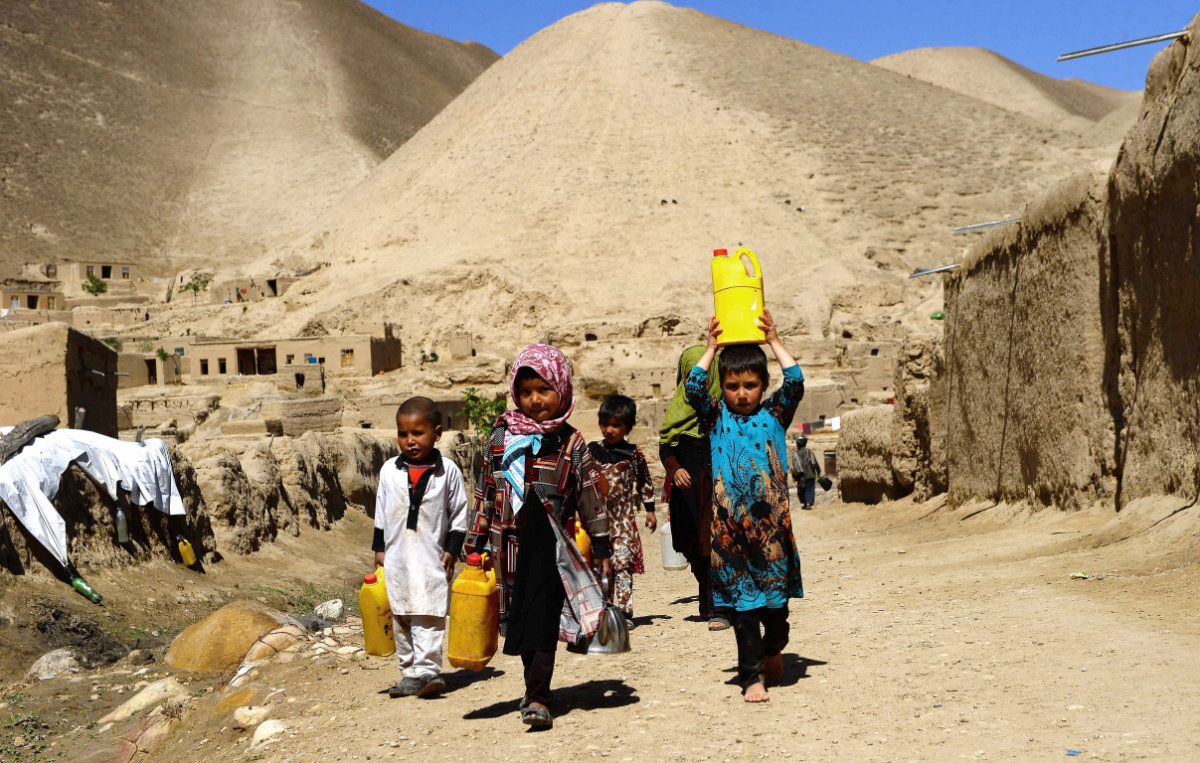

Tens of thousands of Afghan children have been forced to live in refugee camps as a result of the fighting between government troops and the Taliban. (AFP file)
Taliban leaders “have consistently stated they will not allow any group to use Afghan soil,” said Bahiss, highlighting the group’s opposition to Daesh, which is known locally as the Islamic State in Khorasan Province (ISKP ).
“The Taliban’s fight against ISKP shows they are willing and able to fight groups that do not accept their supremacy,” he added.
Ahmad Samin, a former adviser to the World Bank, said Taliban leaders are conscious of the risks of finding themselves once again universally shunned on the international stage.
“A full military takeover of Afghanistan by the Taliban is more than unlikely and, if it happens, it will result in a pariah state,” he told Arab News. “It seems that the Taliban also know this fact; hence they will not go for full military victory.
“If the Taliban want to be part of the future government, they need to soften their stance regarding the role of women, education and personal freedoms. They need to back up their promises with actions that prove they have changed and that they are ready to live peacefully with the rest of the world.”
___________
• Twitter: @sayedsalahuddin



















