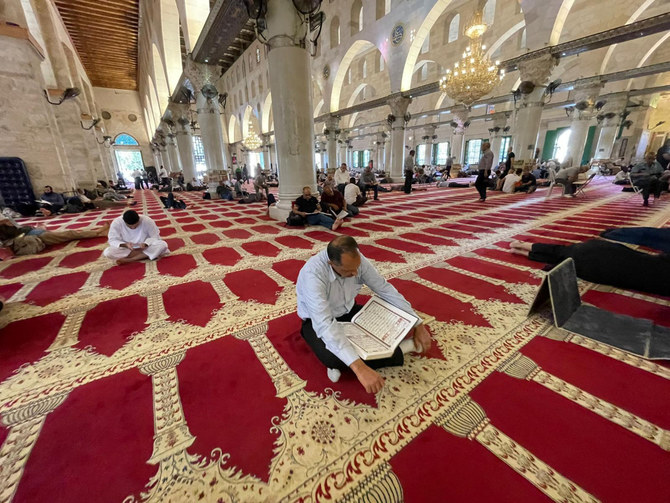
JERUSALEM: The last 10 days of the holy month of Ramadan are always special. In Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa Mosque they are unique — and charged.
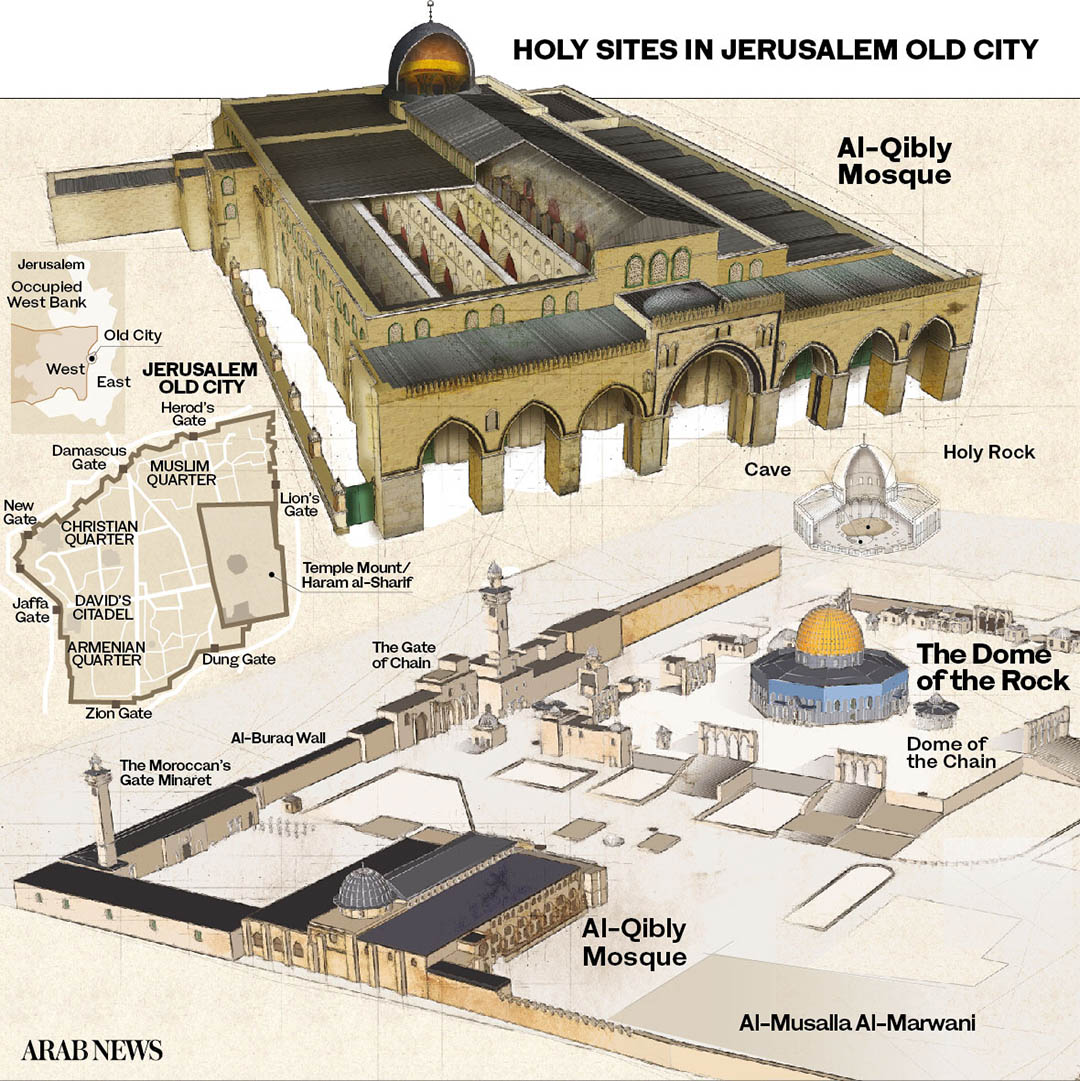
On May 10, Israeli police, firing tear gas and rubber bullets, stormed the Haram Al-Sharif, which houses both Al-Aqsa Mosque and the Dome of the Rock. More than 300 people were injured in the ensuing violence.
Before the unrest erupted there, Arab News spent four days in Jerusalem and talked to the faithful as they awaited Laylat Al-Qadr, the night of fate that falls on the 28th day of Ramadan and marks the date, according to Muslim scholars, when the Holy Qur’an was revealed.
Most worshippers stressed the spiritual dimension of their visits.
Mohammed Abdo, a laborer from Jerusalem’s Sur Baher neighborhood, said he liked to go to the mosque as often as possible but due to his work he usually visited for afternoon and evening prayers. “But my favorite is the dawn prayer. It feels very spiritual and heavenly,” he added.
Mustafa Abu Sway, a professor of Islamic studies at Al-Quds University and holder of the Ghazali chair, said he is almost always at Al-Aqsa Mosque for noon prayers. “I give daily lectures and the best time for these spiritual talks is just before the noon prayers.”
He noted that worshippers and students often have questions about life and look for solutions for daily issues.
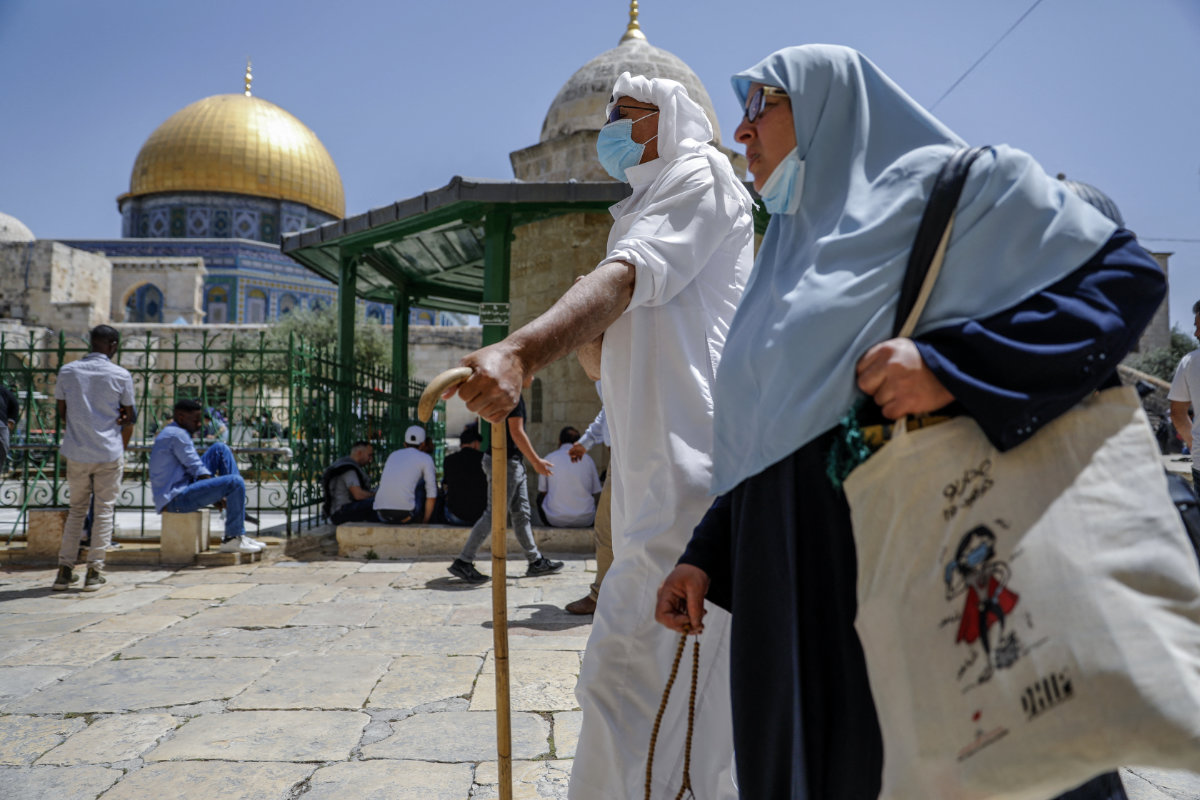

Palestinian worshippers arrive to pray outside the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem's Al-Aqsa Mosque compound on April 30, 2021. (Photo by AHMAD GHARABLI / AFP)
“We try and deal with how the Islamic faith has a direct influence on our behavior. Whether it is in personal relations, work ethics, or issues of the environment, we talk about all these issues during our discussions,” he added.
He pointed out that there was great interest in international academic circles in the doctrines and thinking of Al-Ghazali, an influential Islamic theologian and a famous preacher.
Getting to Al-Aqsa is not easy. The nearest parking lot for those coming from outside the Old City is several kilometers away. A fleet of electric carts carry older and disabled people, but the majority have to make the long walk on cobbled streets.
Some enter via the Damascus Gate to the north and make their way up the Khan Al-Zayt and the Suq Al-Wad, two ancient thoroughfares, to the higher ground of Haram Al-Sharif.
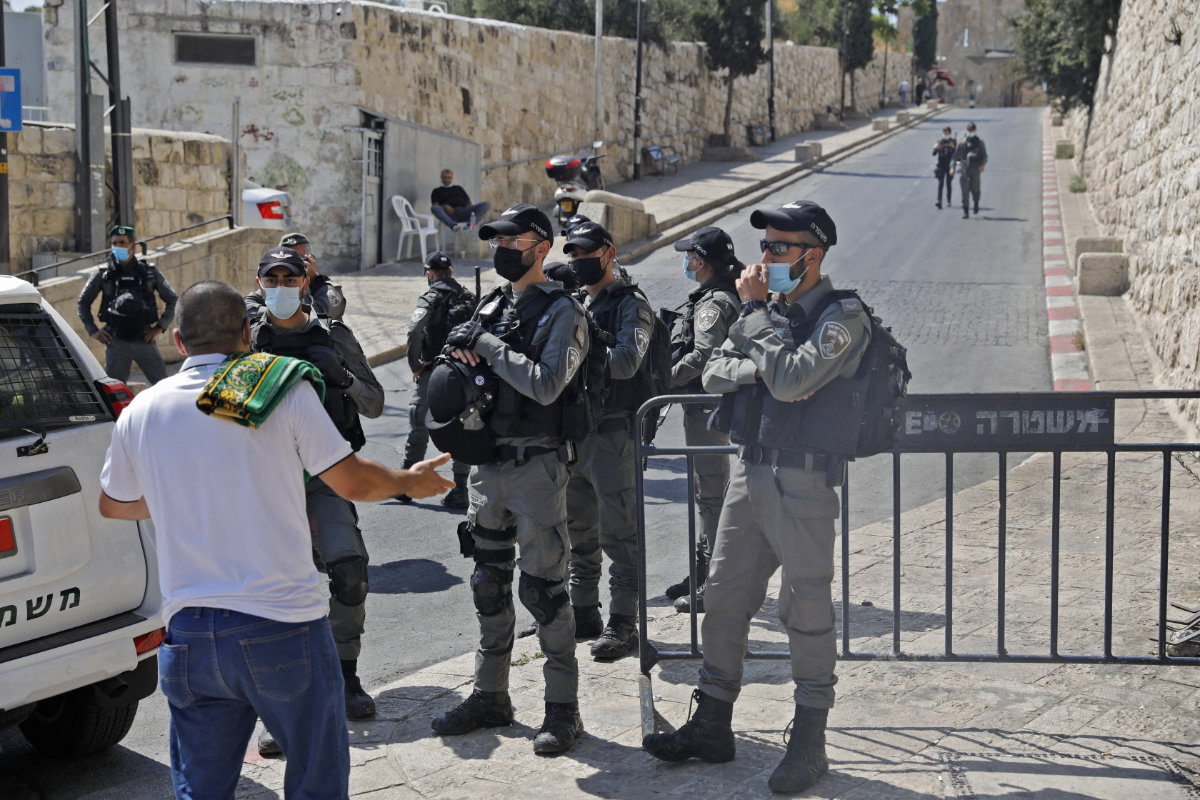

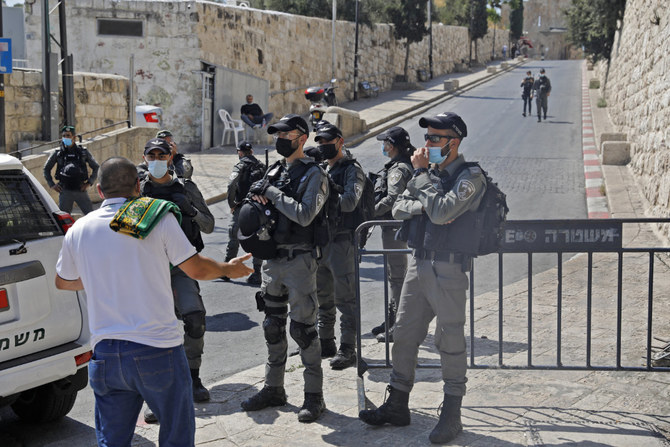
Israeli security forces stand guard on Sept. 25, 2020 in front of the Lion's Gate in Jerusalem to prevent worshippers from reaching the Al-Aqsa mosque compound amid COVID-19 restrictions. (AFP file photo)
Others come via Lion’s Gate in the city’s eastern wall. Once inside the compound, there are separate entrances for men and women in the Dome of the Rock mosque. Inside, a small wooden barrier divides the genders.
In the separate Al-Aqsa structure, the southern Al-Qibly is reserved for men while the part close to the Bab Al-Rahmeh, another prayer section, is divided with men on the right side and women on the left.
The whole compound, which forms an esplanade that dominates the Old City, is maintained by the Jordanian Ministry of Waqf. Jordan held the Old City and the West Bank until 1967.
During Ramadan, the Waqf sets up special areas for hundreds of worshippers to break their fast. Many come from out of town either from within the 1948 borders of Israel or from various parts of the West Bank.
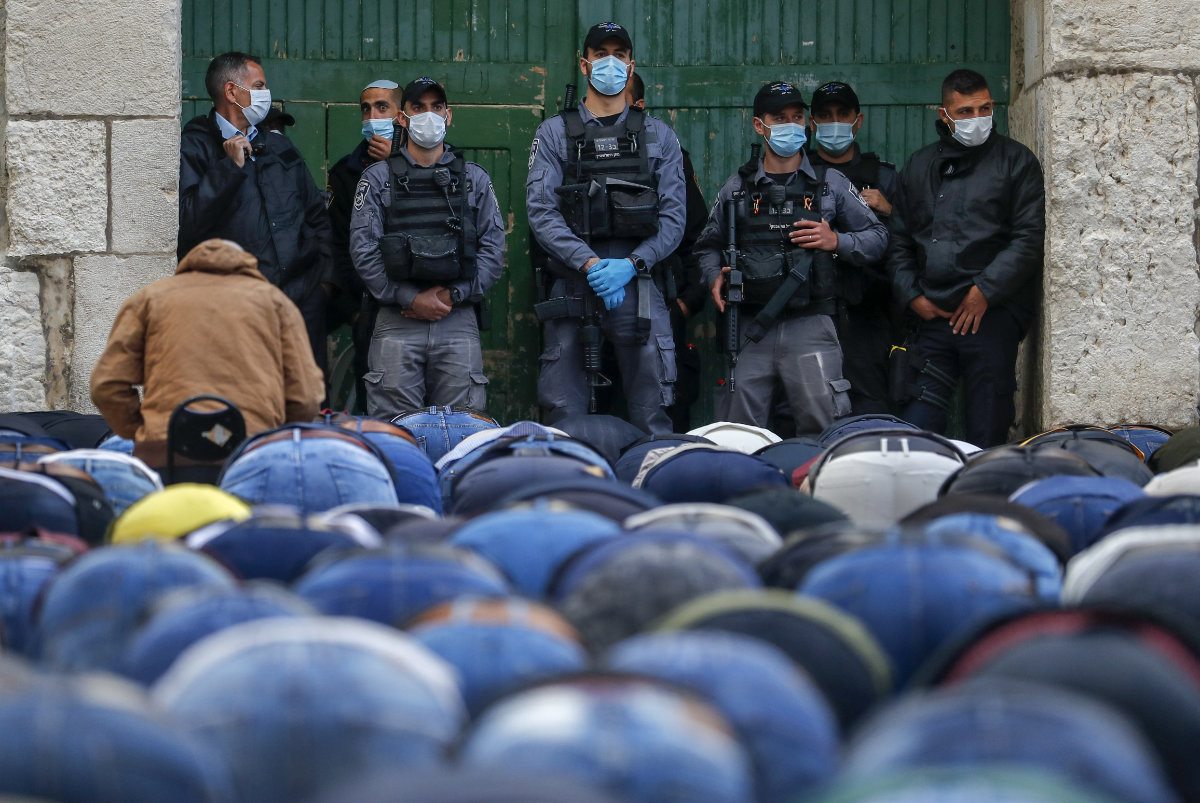

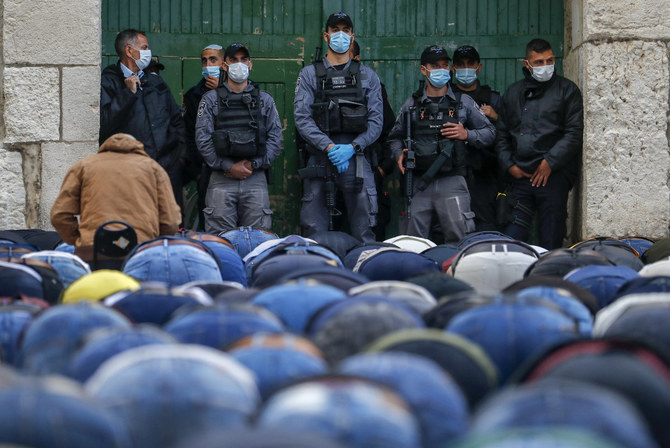
Israeli security forces keep watch as Palestinian worshippers attend the prayers of Eid al-Fitr outside the closed Aqsa mosque complex in Jerusalem on May 24, 2020. (AFP file photo)
This year and last, entering Israel from the West Bank has been further complicated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Only those who have been vaccinated have been able to obtain a permit to travel from the West Bank.
Before the May 10 incursion by the Israeli police into the Haram Al-Sharif, Israeli commanders had ordered the green-bereted border guards and plainclothes security to adopt a low profile.
At the beginning of the holy month, Israeli security forces cut off electricity to four minarets and blocked a plaza in front of the Damascus Gate, a major entrance to the Old City northwest of Al-Aqsa.
The commanders were trying to silence the call to prayer on the same evening as a Jewish remembrance event for fallen Israeli soldiers. On another date, they attempted to head off clashes between Palestinians and hardline Jewish protesters who shouted, “Death to Arabs.”
The atmosphere was further soured by attempts to evict Palestinian families in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood outside the Old City from buildings claimed by Jewish settlers. The US and EU appealed for calm.
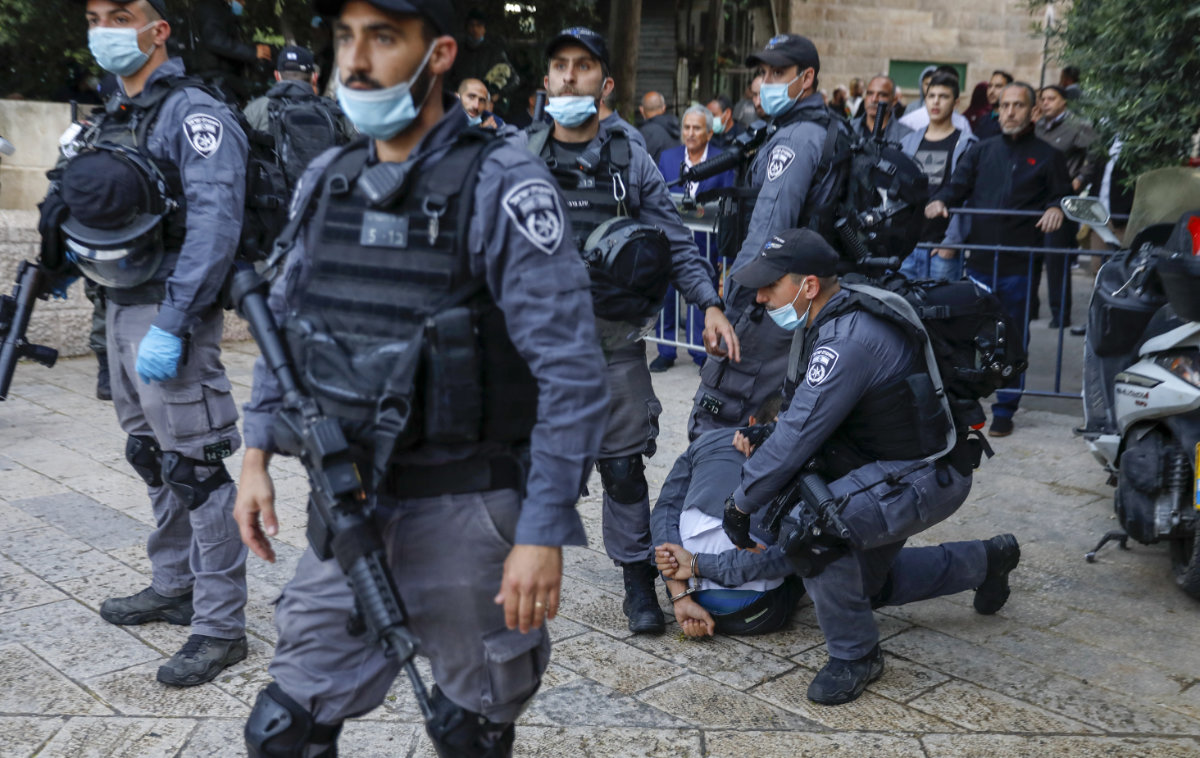

Israeli security forces detain a Palestinian who tried to break through a security barrier to enter the the closed Aqsa mosque complex in Jerusalem on May 24, 2020. (AFP file photo)
The mosque’s guards, who are employed by the Jordanian government, also kept a low profile as worshippers moved into and around the complex.
The Palestinian guards were monitoring visitors to ensure that they did not violate an agreement reached in 2014 in Amman between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, then US Secretary of State John Kerry, and King Abdullah of Jordan.
The unwritten understanding stated that only Muslims may pray in Al-Aqsa and the Dome of the Rock while all others may visit. The esplanade is, however, claimed by Jews to be the site of the First and Second Temples, which are sacred to the Jewish tradition. Israel claims the whole of Jerusalem as its undivided capital.

In Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa Mosque, the last 10 days of the holy month of Ramadan are always special. (Photo Credit: We One Agency, Jerusalem, Palestine)
The Waqf guards seek to head off attempts by hardline Jewish groups, such as the Temple Mount Faithful, who want to rebuild the third temple on the site. They may attempt to recite Jewish prayers as a sign of claiming sovereignty.
In the few hours separating the afternoon prayers from the evening prayers that follow the breaking of the fast or iftar, Al-Aqsa was quieter. Locals from the Old City returned to their homes to break the fast with their families, while outsiders were invited to a special corner of the mosque compound by various charities to share in a hot meal, drinks, and sweets.
Washing areas were available as well as drinking water for those who fasted through the day without drinking or eating.
In the evening, residents of the Old City came out of their houses to hold joint Taraweeh prayers with those who stayed in the mosque. Late evenings were spent in small and large group talks and religious studies.
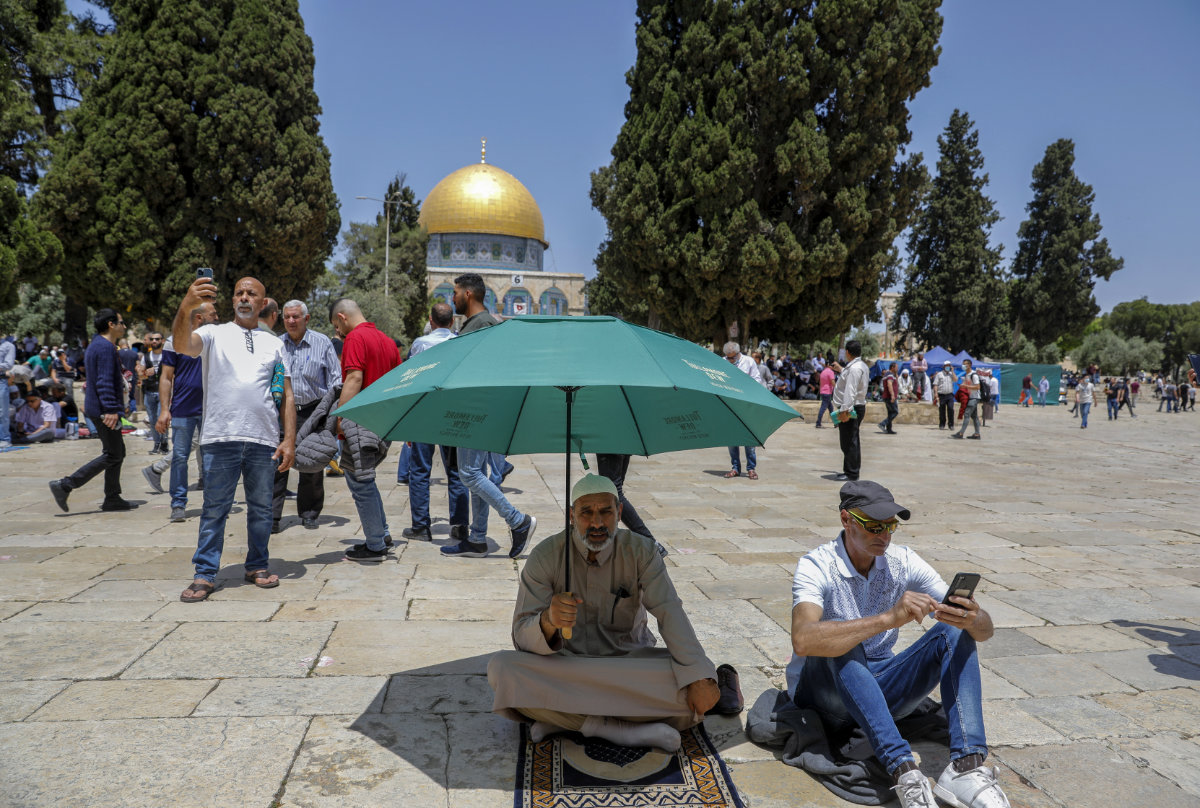

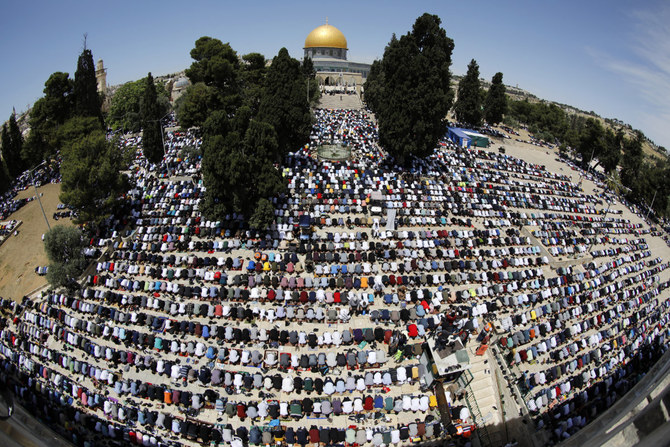
Palestinian worshippers gather outside Jerusalem's Al-Aqsa Mosque compound ahead of the third Friday prayers of the holy month of Ramadan, on April 30, 2021. (AFP file photo)
Some stayed up all night for the suhoor breakfast. Many slept before being awakened to partake in a light meal before the imsaq (the time of abstaining) as the sun rose.
Early risers returned to the mosque for the special time in the early morning hours for the dawn prayers.
Some do not have the luxury of being able to spend a night in the Haram Al-Sharif, in what is the third-holiest site in Islam.
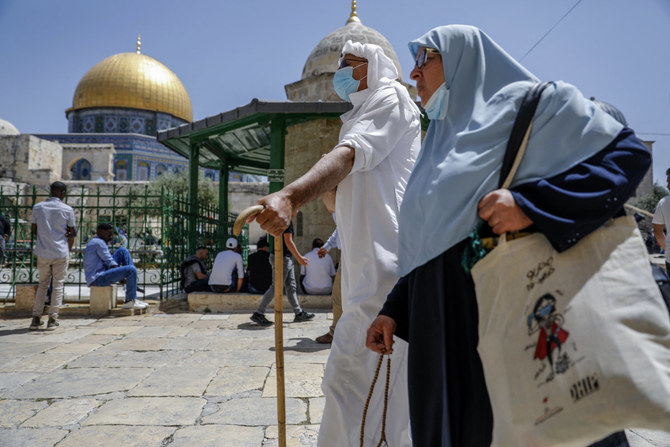
Nemeh Quteneh, from Beit Safafa, another district in east Jerusalem, was with her mother and aunt as they walked toward the Dome of the Rock, which houses the tip of Mount Moriah, for afternoon prayers.
She said: “My mother, Sufiana, can only come in the afternoon, but I prefer the early morning prayers. The air is calm and the quiet allows one to have that spiritual connection that this holy place allows.”
____________
• Twitter: @daoudkuttab




























