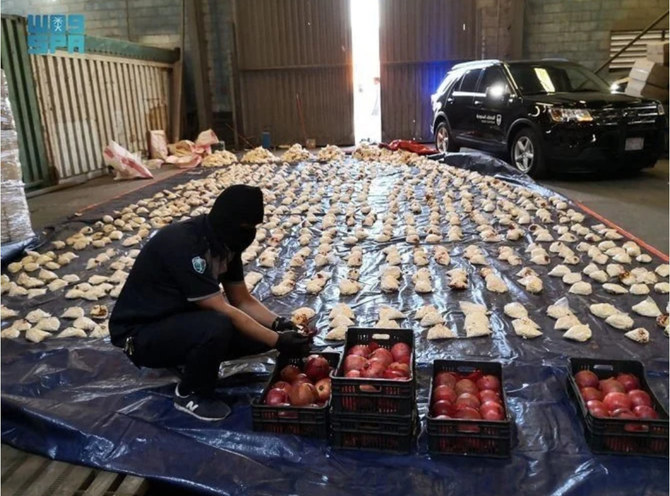
DUBAI: Lebanese fruits and vegetables are no longer welcome in Saudi Arabia after the Kingdom’s vigilant port authorities foiled an attempt to smuggle narcotics inside pomegranates.
Last month, Jeddah Islamic Port’s customs officers seized more than 5 million Captagon pills expertly hidden in a pomegranate consignment from Lebanon. Separately, amphetamine pills stashed in a pomegranate shipment from Lebanon were seized in Dammam’s King Abdulaziz Port.
The Kingdom responded to the incident by banning the import and transit of fruits and vegetables coming from Lebanon.
Waleed Al-Bukhari, Saudi Arabia’s ambassador to Lebanon, disclosed that there had been attempts to smuggle more than 600 million pills from Lebanon during the past six years.
 Deploring the economic impact of the drug bust and import ban, Michel Moawad, a Lebanese politician who resigned from parliament in protest over the Aug. 4, 2020, Beirut blast, said that farmers and legitimate importers are “today paying the price because of Captagon smugglers.”
Deploring the economic impact of the drug bust and import ban, Michel Moawad, a Lebanese politician who resigned from parliament in protest over the Aug. 4, 2020, Beirut blast, said that farmers and legitimate importers are “today paying the price because of Captagon smugglers.”
“What are we gaining by exporting missiles, militias and drugs?” he said. “What are our interests when we are hostile to Arabs and the international community, when we go fight in Yemen and other places?”
When Moawad demanded that Lebanon’s “soil must remain totally sovereign, without security strongholds, illegal weapons, missiles, military training camps for Houthis and no Captagon factories,” he did not have to explicitly name Hezbollah.
The failed attempt to smuggle the amphetamine pills into Saudi Arabia is most likely linked to the Iran-aligned Shiite group with an active military wing, an unnamed source told the Independent Persian.
The source pointed to Hezbollah’s reputed association with the smuggling of drugs, including Captagon pills manufactured in Syria, a charge the group strenuously denies.
The source added that Hezbollah, by virtue of its authority over both “legal and illegal” border checkpoints between Syria and Lebanon, has unchecked control over all drug-related operations.
Hezbollah officials and politicians have yet to comment on the accusations.
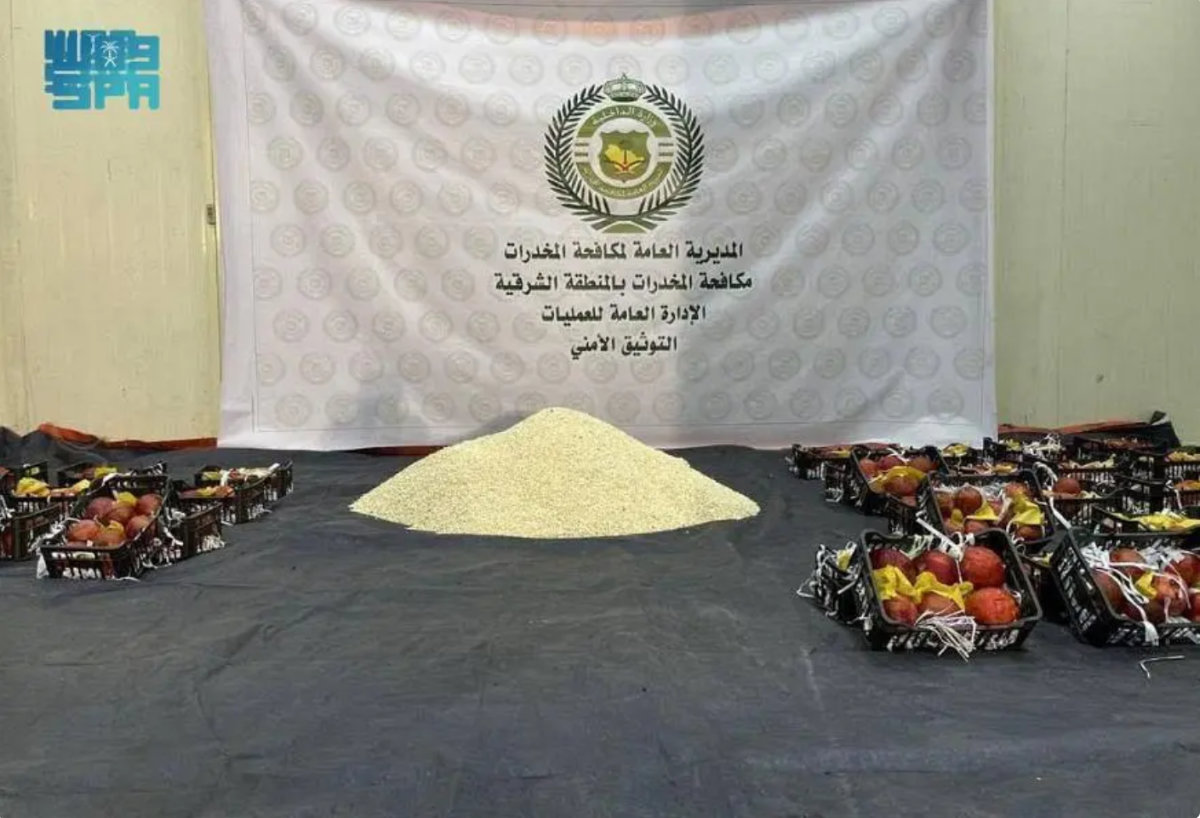

Captagon pills recovered by saudi anti-narcotics officers from a pomegranate shipment from Lebanon are put on display. (SPA)
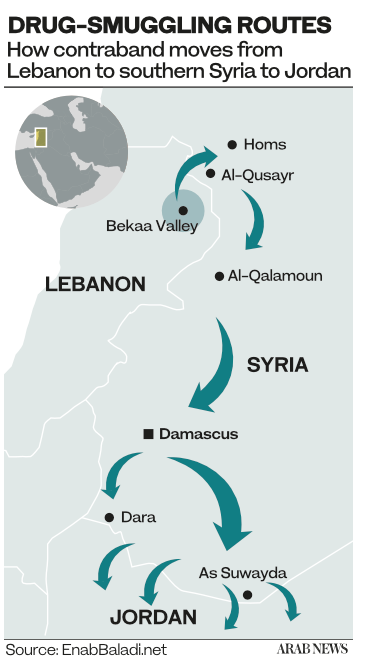
Lebanese security officials have arrested four people so far on suspicion of being connected with the seized cargo. Local news media reports speculated that the pomegranates came from Syria via either the Al-Masnaa border checkpoint or the northern border crossing of Al-Aboudeyye.
After the certificate of origin was changed from Syrian to Lebanese, the consignment was shipped to Saudi Arabia through Beirut’s port, which lacks scanning devices for detecting drugs. The Independent Persian cited the source as saying “the Captagon was produced in Syria, transported to Beirut then consigned to the Kingdom.”
Earlier in April, Greek authorities seized more than four tons of cannabis hidden in a shipment of dessert-making machines heading from Lebanon to Slovakia in the country’s main port of Piraeus, following a tip from the US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Greece’s authorities said that the street value of the drugs was estimated at $4 million and that Saudi Arabia’s drug enforcement agency assisted them in the case.
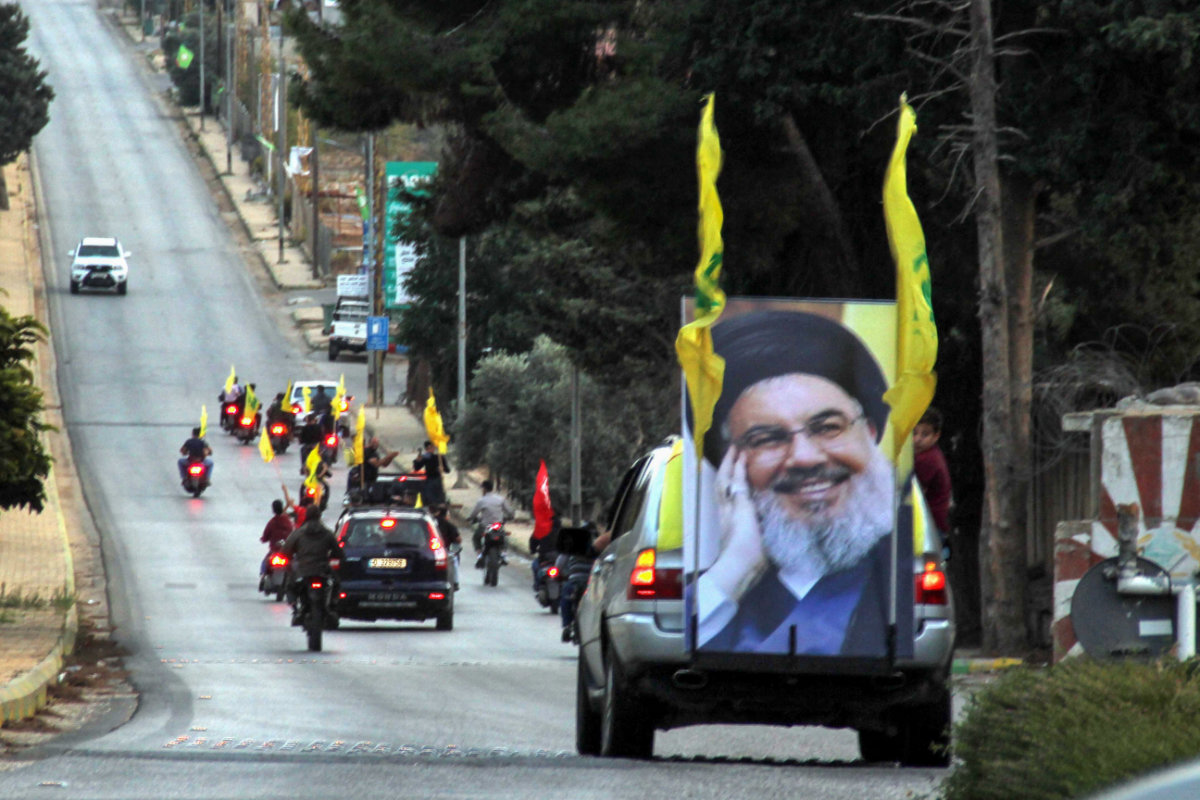

Supporters of the Shiite Hezbollah movement drive in a convoy in Kfar Kila on the Lebanese border with Israel on Oct. 25, 2019. (Photo by Ali Dia / AFP)
In January, the BBC aired a documentary that showed Italian police burning 85 million amphetamine pills, weighing 14 tons, that had been seized in June 2020. Italy’s financial crimes police said that the contraband came from the Syrian port of Latakia.
The origin of the contraband was initially thought to be Daesh but turned out to be Syria, according to the BBC’s documentary, which alleged that the Syrian regime and its ally, Hezbollah, are deep into the drug trade as a major source of funding.
The size of the haul indicated that the amphetamine pills were manufactured on a very large scale in proper factories, something that was evidently beyond the ability of Daesh given the loss of most of its territory. That left areas under the control of Syrian President Bashar Assad as the likely source of the pills.
The BBC’s report mentioned, however, that Captagon is produced illegally in Lebanon. The Italian authorities did not publicly announce a possible manufacturer of the pills but confirmed that they came from Latakia.
Illegal drug production is believed to have exploded in Syria during the civil war, emerging as a source of much-needed income for the Assad regime. The ruling clique and its foreign allies have used the proceeds from drug trafficking to evade sanctions imposed by the West.

Narcotics like Captagon pills and hashish are considered key sources of income for both Hezbollah and the Syrian regime. (AFP)
Amphetamine in Captagon is also known for its fear-inhibiting and stimulating effects, which have proved useful during protracted firefights in war-torn areas in the Middle East.
In the past few years, authorities in Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, the UAE and Jordan, among other countries, have seized enormous quantities of Captagon, often in shipments originating in Syria.
In a televised address in January, Hezbollah’s leader Hassan Nasrallah said that accusations about its involvement in amphetamine production had “no credibility.”
“Our position on drugs, of all kinds, is (clear). It’s religiously banned to manufacture, sell, buy, smuggle and consume. In some cases, the punishment could even be execution, according to Sharia laws,” he said.
However, US and European drugs agencies are convinced that Hezbollah profits from the drug trade. Europol, a European law enforcement agency, issued a report in 2020 cautioning that Hezbollah members were using European cities as a base for trading in “drugs and diamonds” and to launder the profits.
INNUMBERS
- 10,100 - Hashish packets seized on Syria-Jordan border in 2020.
- 4.1 million - Captagon pills seized on Syria-Jordan border in 2020.
- $4 million - Market value of drugs seized by Greece with Saudi help in April.
- $24 million - Lebanon’s annual fruit & vegetable trade with KSA until the ban.
- 85 million - Amphetamine pills seized in Italy in June 2020.
In 2018, the US State Department named Hezbollah among the top five global criminal organizations. Reports indicate that Hezbollah’s criminal operations have increased of late in response to Iranian directives to generate income as part of its efforts to dodge US sanctions.
For their part, police in Israel have accused Hezbollah of smuggling hashish into the country.
Lebanon is known to be one of the world’s top producers of cannabis, which is widely cultivated in areas considered strongholds of Hezbollah, notably Baalbek and Hermel.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Last year, the US State Department and Washington’s intelligence community said that there was ample evidence to support claims linking Hezbollah to criminal activities, including drug trafficking, in South America and Europe.
Since 2009, many Lebanese have been sanctioned by the US Treasury for their connection to organized crime, involving drug trafficking and money laundering. Many of those sanctioned were linked to Hezbollah.
Hezbollah has built strong connections with the tri-border area of Paraguay-Argentina-Brazil in South America, home to more than 5 million people of Lebanese origin. Local contacts are believed to facilitate and conceal Hezbollah’s drug-trafficking, money-laundering and terrorist-financing operations in this area.
Antoine Kanaan, editor in chief of Lebanon Law Review, says that there is little doubt that Hezbollah was behind the Captagon found in the consignment of pomegranates that reached Jeddah.
He said that pomegranate is not even commercially produced in Lebanon, adding that it is a secondary fruit crop whose cultivation is "restricted to plots of land as small as private orchards and gardens.
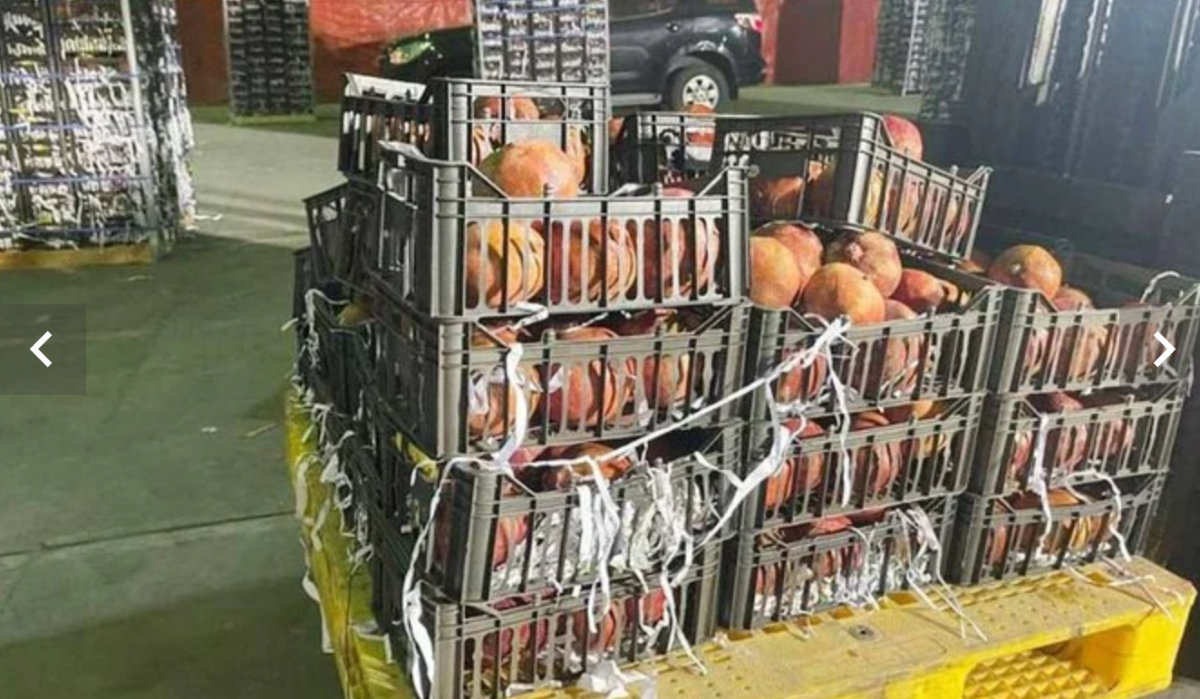

Pomegranates are among Lebanon's major agricultural export to Saudi Arabia. (SPA photo)
By contrast, Syria is well known for its pomegranate production, especially in areas such as Daraa, he told Arab News.
“That means that the pomegranates that went from Lebanon to Saudi Arabia originated in Syria,” said Kanaan, who believes that the Captagon was inserted into the fruits in Lebanon.
The amount of Captagon involved and the ingenuity of the plot confirm Hezbollah’s involvement, or at least consent and profit-sharing, according to Kanaan, who further noted that consensus governs everything in Lebanon, even drugs.
“I believe Hezbollah is the number one Captagon supplier in the region and there’s no way an independent Lebanese trader, or even the Syrian government, would have dared pull this off without involving Hezbollah,” he said.
As to why the drugs were sent to Saudi Arabia, Kanaan said: “It is possible but unlikely that they were headed for (Iran-backed Houthi) fighters in Yemen.”
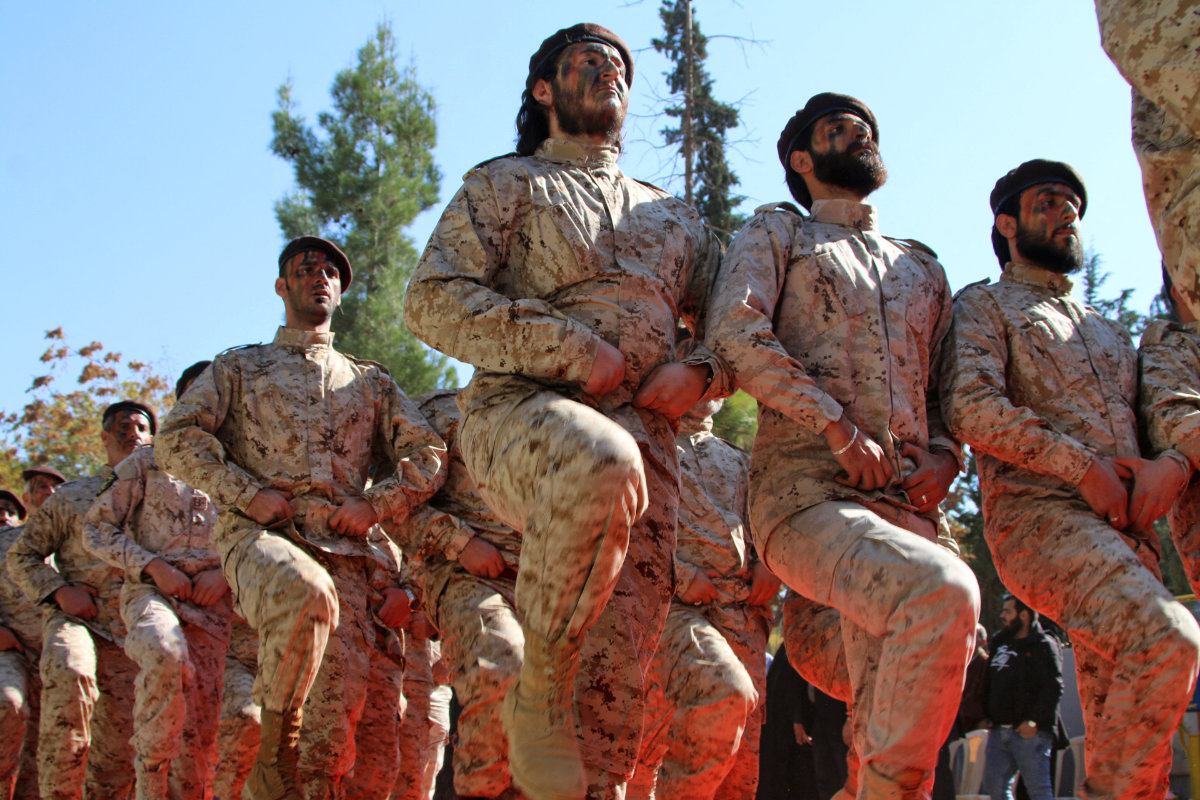

To sustain its paramilitary force, the Iran-backed Lebanese Shiite Hezbollah movement export drugs to countries it considers non-allies, such as Saudi Arabia. (AFP file photo)
Brig. Gen. Adel Machmouchi, a former chief of antinarcotics department at Lebanon’s Internal Security Forces, said that the drug bust in Jeddah has exposed Lebanon as one of the countries that does not cooperate with international drug-enforcement bodies.
In a TV interview over the weekend, he suggested that the Lebanese ministries and security bodies concerned should have “better and closer control” over areas — in Bekaa Valley and northern Lebanon — where illegal farming and production of drugs takes place.
He said that the government should transform those illegal businesses into legitimate, productive projects.
Machmouchi said that punishments “are not harsh enough to curtail crimes of producing, trafficking and smuggling drugs,” and should be made harsher to act as a deterrent.
He claimed there are about 20 factories used to produce Captagon pills in Lebanon. “Lebanese antinarcotics bodies should (join forces) with counterparts in Saudi Arabia and other GCC countries to be able to combat this crime and halt the process of using Lebanon as a launchpad to smuggle drugs,” Machmouchi said.























