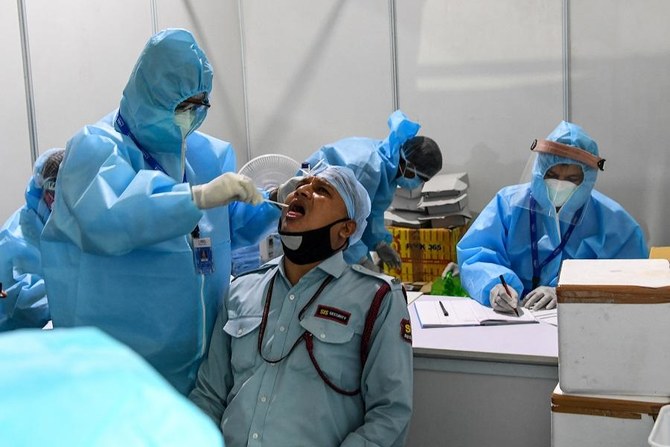
NEW DELHI: India’s new coronavirus infections hit a record peak for a fifth day on Monday as countries including Britain, Germany and the United States pledged to send urgent medical aid to help battle the crisis overwhelming its hospitals.
Infections in the last 24 hours rose to 352,991, with overcrowded hospitals in Delhi and elsewhere turning away patients after running out of supplies of medical oxygen and beds.
“Currently the hospital is in beg-and-borrow mode and it is an extreme crisis situation,” said a spokesman for the Sir Ganga Ram Hospital in the capital, New Delhi.
On Sunday, Prime Minister Narendra Modi urged all citizens to get vaccinated and exercise caution, while hospitals and doctors have put out urgent notices saying they were unable to cope with the rush of patients.
In some of the worst-hit cities, including New Delhi, bodies were being burnt in makeshift facilities offering mass services.
Television channel NDTV broadcast images of three health workers in the eastern state of Bihar pulling a body along the ground on its way to cremation, as stretchers ran short.
“If you’ve never been to a cremation, the smell of death never leaves you,” Vipin Narang, a political science professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the United States, said on Twitter.
“My heart breaks for all my friends and family in Delhi and India going through this hell.”
On Sunday, President Joe Biden said the United States would send raw materials for vaccines, medical equipment and protective gear to India. Germany joined a growing list of countries pledging to send supplies.
India, with a population of 1.3 billion, has a tally of 17.31 million infections and 195,123 deaths, after 2,812 deaths overnight, health ministry data showed, although health experts say the death count is probably far higher.
The scale of the second wave knocked oil prices on Monday, as traders worried about a fall in fuel demand in the world’s third-biggest oil importer.
RALLY BACKLASH
Politicians, especially Modi, have faced criticism for holding rallies attended by thousands of people, packed close together in stadiums and grounds, despite the brutal second wave of infections.
Several cities have ordered curfews, while police have been deployed to enforce social distancing and mask-wearing.
Still, about 8.6 million voters were expected to cast ballots on Monday in the eastern state of West Bengal, in the penultimate part of an eight-phase election that will wrap up this week.
Voting for local elections in other parts of India included the most populous state of Uttar Pradesh, which has been reporting an average of 30,000 infections a day.
Modi’s plea on vaccinations came after inoculations peaked at 4.5 million doses on April 5, but have since averaged about 2.7 million a day, government figures show.
Several states, including Maharashtra, the richest, halted vaccinations in some places on Sunday, saying supplies were not available.
Supply has fallen short of demand as the inoculation campaign was widened this month, while companies struggle to boost output, partly because of a shortage of raw material and a fire at a facility making the AstraZeneca dose.
Hospitals in Modi’s home state of Gujarat are among those facing an acute shortage of oxygen, doctors said.
Just seven ICU beds of a total of 1,277 were available in 166 private hospitals designated to treat the virus in the western state’s largest city of Ahmedabad, data showed.
“The problem is grim everywhere, especially in smaller hospitals, which do not have central oxygen lines and use cylinders,” said Mona Desai, former president of the Ahmedabad Medical Association.
India’s coronavirus crisis deepens as countries promise aid
https://arab.news/znty2
India’s coronavirus crisis deepens as countries promise aid

- Prime Minister Narendra Modi urged all citizens to get vaccinated and exercise caution
- President Joe Biden said the US would send raw materials for vaccines, medical equipment and protective gear to India
WHO appeals for $1 bn for world’s worst health crises in 2026

- The UN health agency estimated 239 million people would need urgent humanitarian assistance this year and the money would keep essential health services going
GENEVA: The World Health Organization on Tuesday appealed for $1 billion to tackle health crises this year across the world’s 36 most severe emergencies, including in Gaza, Sudan, Haiti and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The UN health agency estimated 239 million people would need urgent humanitarian assistance this year and the money would keep essential health services going.
WHO health emergencies chief Chikwe Ihekweazu told reporters in Geneva: “A quarter of a billion people are living through humanitarian crises that strip away the most basic protections: safety, shelter and access to health care.
“In these settings, health needs are surging, whether due to injuries, disease outbreaks, malnutrition or untreated chronic diseases,” he warned.
“Yet access to care is shrinking.”
The agency’s emergency request was significantly lower than in recent years, given the global funding crunch for aid operations.
Washington, traditionally the UN health agency’s biggest donor, has slashed foreign aid spending under President Donald Trump, who on his first day back in office in January 2025 handed the WHO his country’s one-year withdrawal notice.
Last year, WHO had appealed for $1.5 billion but Ihekweazu said that only $900 million was ultimately made available.
Unfortunately, he said, the agency had been “recognizing ... that the appetite for resource mobilization is much smaller than it was in previous years.”
“That’s one of the reasons that we’ve calibrated our ask a little bit more toward what is available realistically, understanding the situation around the world, the constraints that many countries have,” he said.
The WHO said in 2026 it was “hyper-prioritising the highest-impact services and scaling back lower?impact activities to maximize lives saved.”
Last year, global funding cuts forced 6,700 health facilities across 22 humanitarian settings to either close or reduce services, “cutting 53 million people off from health care.” Ihekweazu said.
“Families living on the edge face impossible decisions, such as whether to buy food or medicine,” he added, stressing that “people should never have to make these choices.”
“This is why today we are appealing to the better sense of countries, and of people, and asking them to invest in a healthier, safer world.”