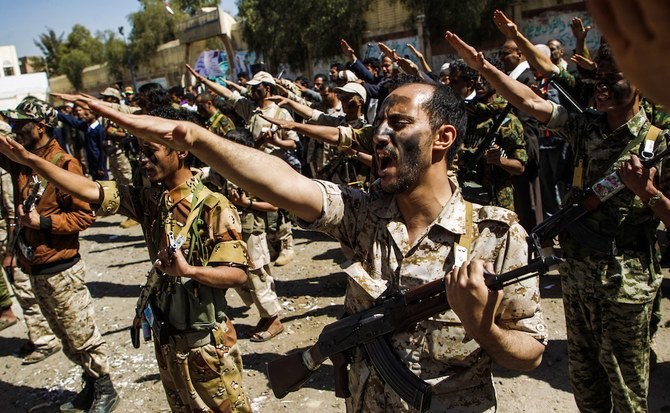
LONDON: Joe Biden, the newly inaugurated US president, is using his first days in office to review many of his predecessor’s policies and executive orders. How his administration handles its strategic inheritance, particularly with regard to Iran and its proxies, notably the Yemeni Houthi militia, could well shape the Arab region’s opinion of his nascent presidency.
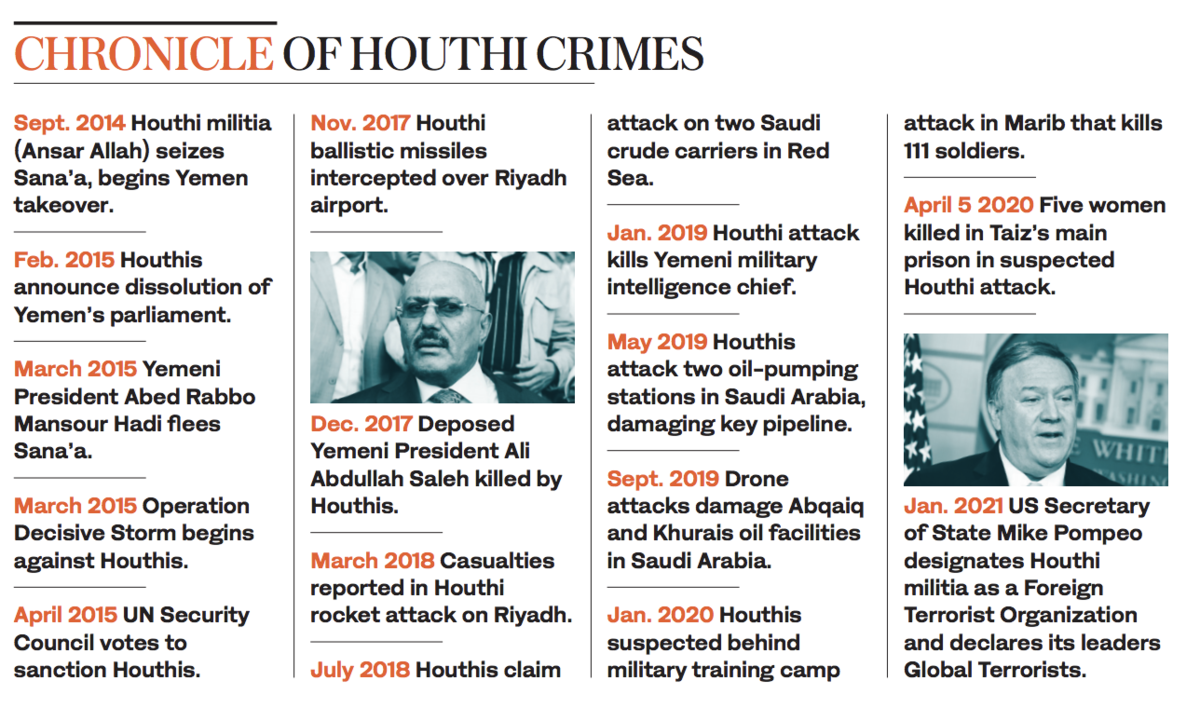
On Jan. 10, Mike Pompeo, the outgoing secretary of state, announced the State Department would designate the Houthis (also known as Ansar Allah) as a “Foreign Terrorist Organization.” Three Houthi leaders — Abdul Malik Al-Houthi, Abdul Khaliq Badr Al-Din Al-Houthi and Abdullah Yahya Al-Hakim — were declared Specially Designated Global Terrorists with effect from Jan. 19.
“The designations are intended to hold Ansar Allah accountable for its terrorist acts, including cross-border attacks threatening civilian populations, infrastructure, and commercial shipping,” Pompeo said.
“The designations are also intended to advance efforts to achieve a peaceful, sovereign and united Yemen that is both free from Iranian interference and at peace with its neighbors.”
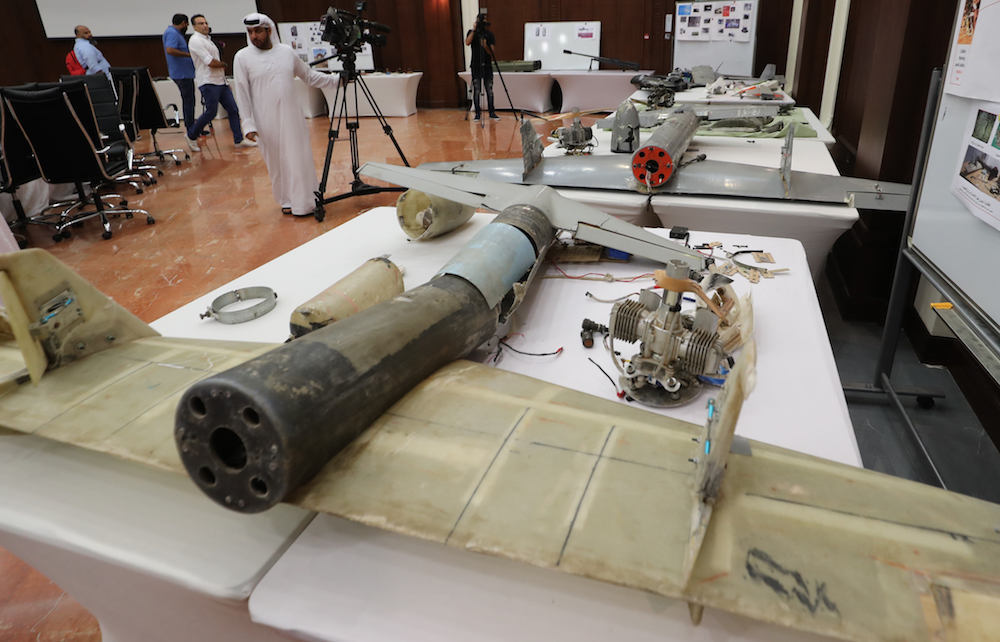

A picture taken on June 19, 2018 shows debris of Iranian-made Ababil drones displayed Abu Dhabi, which the Emirati armed forces say were used by Houthi rebels in Yemen in battles against the coalition forces led by the UAE and Saudi Arabia. (AFP/File Photo)
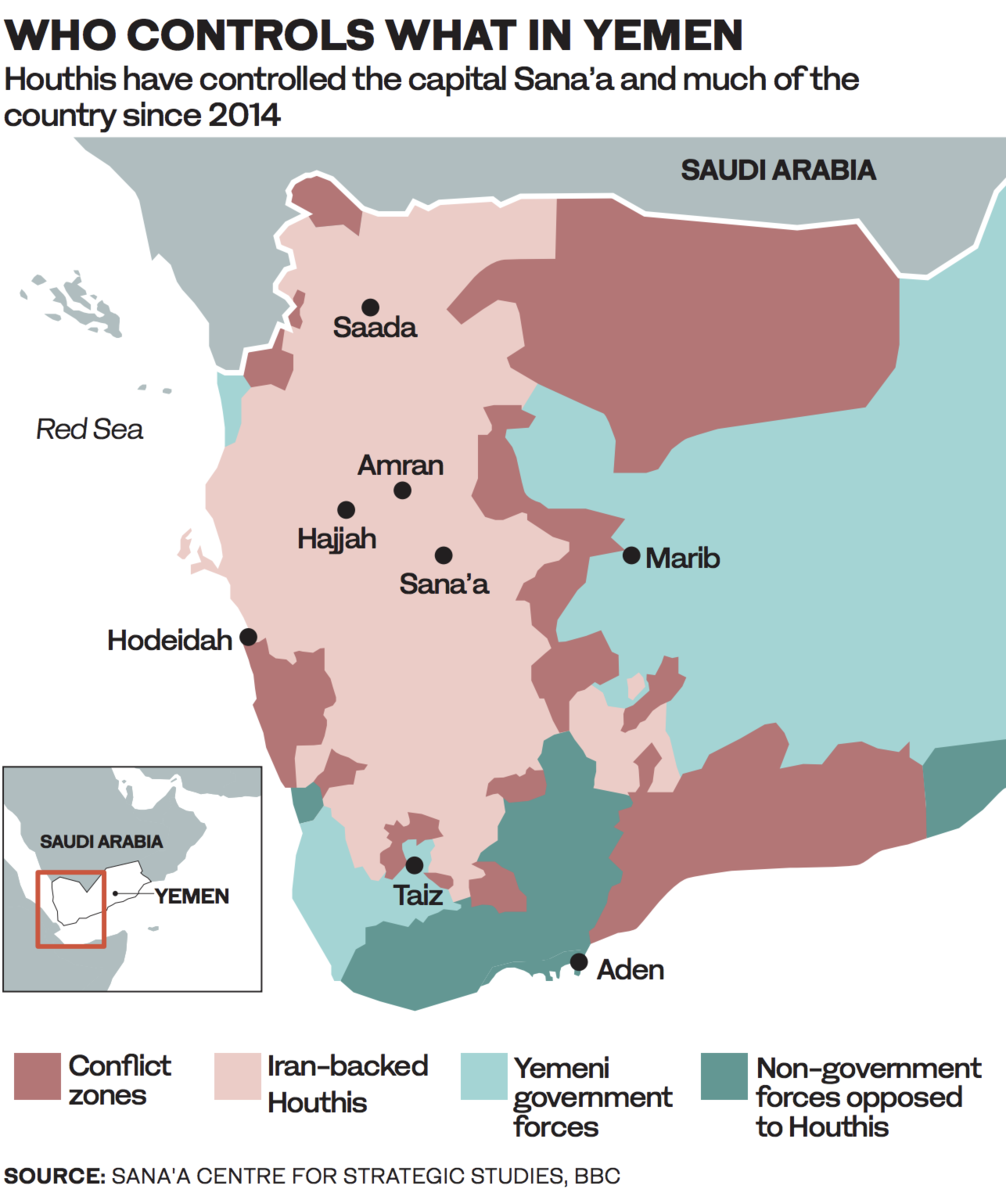
One reason why the Trump administration was able to achieve a lot in the Middle East was probably its readiness to call a spade a spade. The war in Yemen escalated in 2015 when the Iran-backed Houthis overthrew the UN-recognized government of President Abed Rabbo Mansour Hadi. A coalition of Arab states, backed by the US, Britain and France, launched a military campaign to restore the legitimate government to power.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Since then, repeated attempts to reach a peace settlement have foundered, with the militia’s representatives failing to attend UN-brokered talks in Geneva in Sept. 2018 and its combatants willfully ignoring the terms of the Stockholm and Riyadh agreements.
An April 2020 ceasefire announced by the coalition at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic quickly fell apart when the Houthis resumed cross-border drone and missile strikes targeting Saudi Arabia.
For the Yemeni government, any peace agreement with the Houthis would be contingent on the militia breaking its ties with Tehran — a development that is highly unlikely at present.
Iran’s support for the Houthis has been an open secret since long before the Houthi takeover of Sana’a in 2015. It has caused the brutal war to rage on unabated and one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises to fester.
The conflict, now in its sixth year, has left 112,000 dead and 24 million in dire need of humanitarian assistance.
The Houthis have repeatedly targeted civilian population centers in Yemen and Saudi Arabia. Most recently, 27 people were killed when a Houthi missile targeting ministers of the newly established Yemeni government struck Aden’s international airport on Dec. 30.
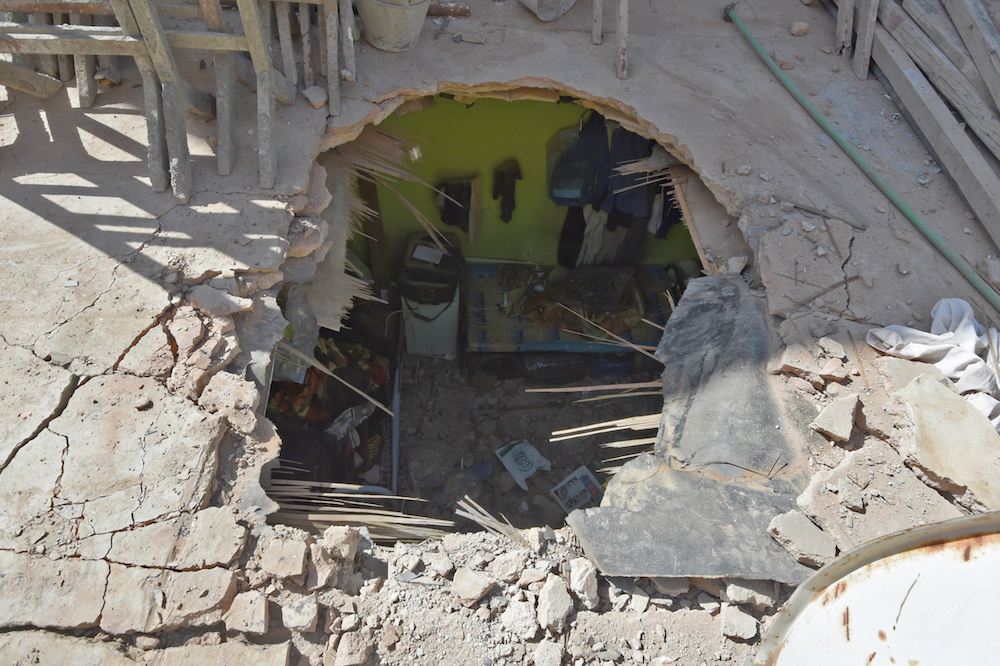

A picture taken March 26, 2018 in Um Al-Hammam district in Riyadh shows the pierced ceiling of a home hit by falling shrapnel from Houthi missiles that were intercepted over the Saudi capital. (AFP/File Photo)
In April last year, five women were killed in a suspected Houthi strike on a prison in the city of Taiz — an act forcefully condemned by aid groups. Houthi missiles have even hit civilian facilities in Riyadh, including its international airport in Nov. 2017.
The group has also routinely targeted Saudi Arabia’s oil infrastructure. A July 2018 attack hit two Saudi crude carriers on the Red Sea while a May 2019 strike on two oil-pumping stations near Riyadh damaged a key pipeline.
The most damaging of all Houthi-claimed attacks was a Sept. 2019 drone and missile strike on Saudi Arabia’s Abqaiq and Khurais oil facilities, which sent shockwaves through the global crude market.
Although the Houthis claimed responsibility, investigators suggested the strike involving Iranian-supplied hardware may have originated from the north.
Biden’s foreign-policy team may also recall three attacks on the US navy in 2016 when he was Barack Obama’s vice president — by a militia whose actions matched the notorious words of its slogan “Death to America. Death to Israel. Curse on the Jews.”
The USS Mason was targeted on Oct. 9, 2016, by two missiles fired from Houthi-controlled territory while deployed near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait off the coast of Yemen. The projectiles failed to cause any damage.
Three days later, the Mason was targeted again, with one missile falling short while the other was intercepted. USS Nitze, which was also deployed to the region, retaliated the following day, destroying three radar sites in Houthi-held territory.
On Oct. 15, the Mason was targeted a third time, this time in the Red Sea. All five anti-ship cruise missiles were neutralized or intercepted.

Houthi leader Abdul-Malik Al-Houthi delivers a speech in he Yemeni capital Sanaa on November 9, 2019. (AFP/File Photo)
Given this behavior, it is surprising that the Houthis did not land the terrorist designation then, although historians would probably chalk it up to the Obama administration’s wish to preserve the 2015 Iran nuclear accord at any cost.
Foreign military vessels have not been the only targets. The Houthis have launched repeated attacks on ports and ships in recent years, routinely planting marine mines in the southern Red Sea and in the Bab Al-Mandab Strait in the path of commercial shipping.
The militia has also repeatedly rebuffed UN pleas to allow an inspection team to enter the FSO Safer, a 45-year-old oil tanker abandoned off the port of Hodeidah with 1.1 million barrels of crude on board, to conduct urgent repairs. In an extraordinary session, the UN expressed fears on July 15, 2020, of “catastrophe” if the vessel ruptured into the Red Sea.
Pompeo’s boss, Donald Trump, had pursued a policy of “maximum pressure” against Tehran, withdrawing the US from the Obama-era nuclear deal and reimposing sanctions on Iran.

Members of displaced Yemeni families who fled battles between government forces and Houthi fighters near the Hodeidah airport share a meal on the balcony of of a school used as temporary housing inside the city. (AFP/File Photo)
The strategy was matched by a zero-tolerance approach to Iranian influence in Yemen, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and Palestine, as well as to its role in harboring leaders and operatives of Al-Qaeda.
Almost all the findings of an Arab News-YouGov pan-Arab survey conducted in late 2020 suggest that Biden would be wise to shed the Obama administration baggage. The most popular response (53 percent) was that Obama left the region worse off, with another 58 percent saying Biden should distance himself from Obama-era policies.
With Houthi attacks on civilian targets triggering condemnations from inside and outside Yemen and prompting calls for more pressure on the leadership, the State Department’s “terrorist” designation gives Biden valuage leverage for future negotiations both with the Houthis and their patrons in Tehran.
-------------------
Twitter: @RobertPEdwards














