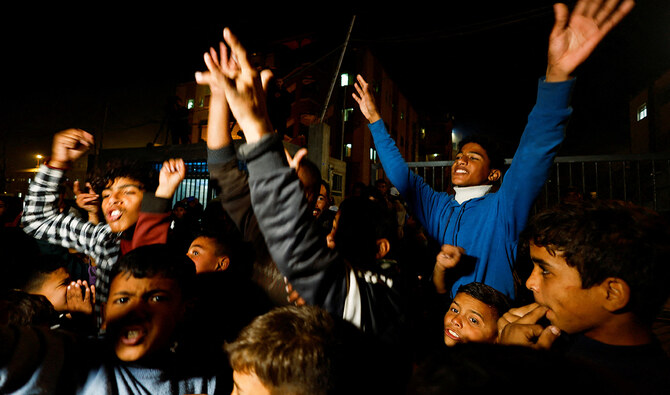DOHA: Israel and Hamas agreed to a ceasefire deal to pause the devastating war in the Gaza Strip, multiple officials announced Wednesday, raising the possibility of winding down the deadliest and most destructive fighting between the bitter enemies.
The deal, coming after weeks of painstaking negotiations in the Qatari capital, promises the release of dozens of hostages held by Hamas in phases, the release of hundreds of Palestinian prisoners in Israel and would allow hundreds of thousands of people displaced in Gaza to return to what remains of their homes. It also would flood badly needed humanitarian aid into a territory ravaged by 15 months of war.
Three officials from the US and one from Hamas confirmed that a deal had been reached, while the office of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said final details were still being ironed out.
All three US officials and the Hamas official requested anonymity to discuss the contours of the deal before the official announcement by mediators in Doha.
Netanyahu’s office said in a statement that it hoped “details will be finalized tonight.” Any agreement needs to be approved by Netanyahu’s Cabinet.
Once official, the deal is expected to deliver an initial six-week halt to fighting that is to be accompanied by the opening of negotiations on ending the war altogether.
Over six weeks, 33 of the nearly 100 hostages are to be reunited with their loved ones after months in in captivity with no contact with the outside world, though it’s unclear if all are alive.
It remained unclear exactly when and how many displaced Palestinians would be able to return to what remains of their homes and whether the agreement would lead to a complete end to the war and the full withdrawal of Israeli troops from Gaza — key Hamas demands for releasing the remaining captives.
Many longer-term questions about postwar Gaza remain, including who will rule the territory or oversee the daunting task of reconstruction after a brutal conflict that has destabilized the broader Middle East and sparked worldwide protests.
Hamas triggered the war with its Oct. 7, 2023, cross-border attack, which killed some 1,200 Israelis and took 250 others hostage. Israel responded with a fierce offensive that has killed over 46,000 Palestinians, according to local health officials, displaced an estimated 90 percent of Gaza’s population and sparked a humanitarian crisis.
More than 100 hostages were freed from Gaza in a weeklong truce in November 2023.
The US, along with Egypt and Qatar, have brokered months of indirect talks between the bitter enemies that finally culminated in this latest deal. It comes after Israel and the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah agreed to a ceasefire in November, after more than a year of conflict linked to the war in the Gaza.
Israel responded with a brutal air and ground offensive that has killed over 46,000 Palestinians, according to local health officials. They do not distinguish between civilians and militants but say women and children make up more than half of those killed.
UN and international relief organizations estimate that some 90 percent of Gaza’s 2.3 million people have been displaced, often multiple times. They say tens of thousands of homes have been destroyed and hospitals are barely functioning. Experts have warned that famine may be underway in northern Gaza, where Israel launched a major offensive in early October, displacing tens of thousands of residents.
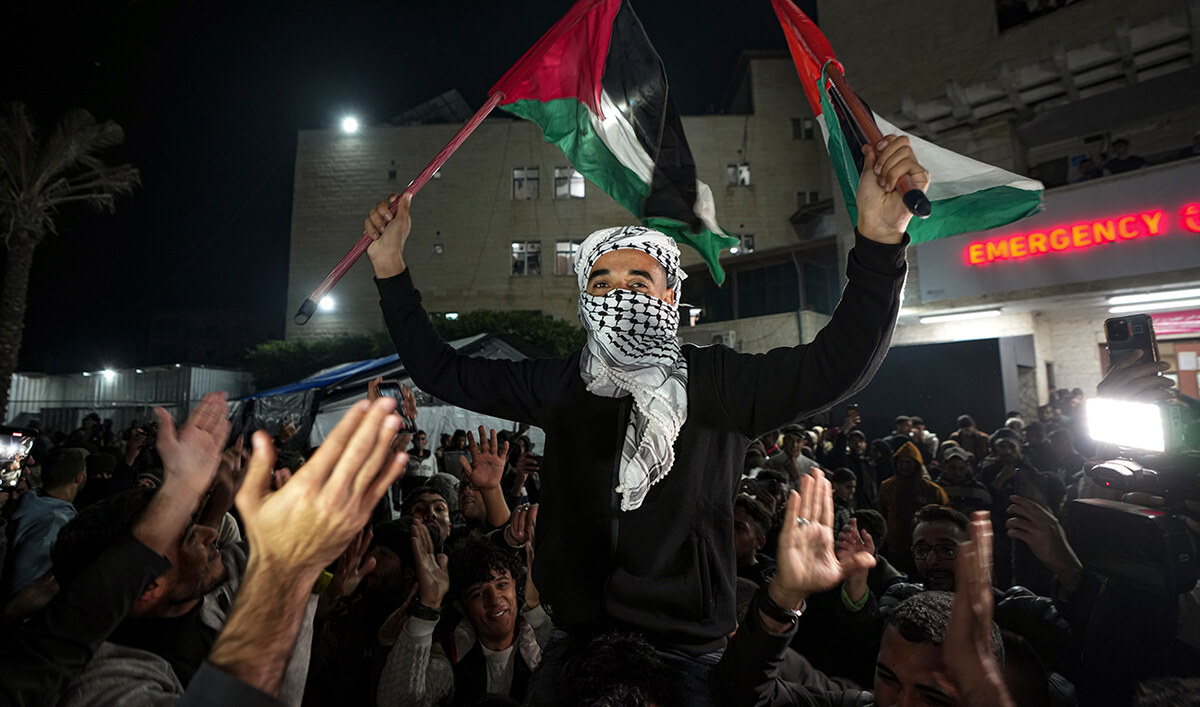

Palestinians celebrate the announcement of a ceasefire deal between Hamas and Israel in Deir Al-Balah, central Gaza Strip on January 15, 2025. (AP)
“The best day in my life and the life of the Gaza people,” Abed Radwan, a Palestinian father of three, said of the ceasefire deal. “Thank God. Thank God.”
Radwan, who has been displaced from the town of Beit Lahiya for over a year and shelters in Gaza City, said he will try to return to his hometown, and “rebuild my house, and rebuild Beit Lahiya.”
He spoke to AP over the phone. His voice has been overshadowed by celebrations. “People are crying here. They don’t believe it’s true.”
In Israel, hundreds of demonstrators gathered outside Israel’s military headquarters in Tel Aviv, calling for a deal to be completed. Many held posters of hostages held by Hamas, others hoisted candles in the air.
As the deal was announced, some people were unaware that it had gone through. Sharone Lifschitz, whose father Oded is being held in Gaza, told the AP by phone she was stunned and grateful but won’t believe it until she sees all the hostages come home.
“I’m so desperate to see them if by some miracle my father has survived,” she said.
US President Joe Biden, who has provided crucial military aid to Israel but expressed exasperation over civilian deaths, announced the outline of the three-phase ceasefire agreement on May 31. The agreement eventually agreed to followed that framework.
He said the first phase would last for six weeks and include a “full and complete ceasefire,” a withdrawal of Israeli forces from densely populated areas of Gaza and the release of a number of hostages, including women, older adults and wounded people, in exchange for the release of hundreds of Palestinian prisoners. Humanitarian assistance would surge, with hundreds of trucks entering Gaza each day.
The second and most difficult phase would include the release of all remaining living hostages, including male soldiers, and Israeli forces would withdraw from Gaza. The third phase calls for the start of a major reconstruction of Gaza, which faces decades of rebuilding from devastation caused by the war.
Hamas had been demanding assurances for a permanent end to the war and complete withdrawal of all Israeli forces from Gaza. Israel, meanwhile, has repeatedly said it would not halt the war until it destroys Hamas’ military and governing capabilities.
The various players have conducted months of on-again, off-again negotiations. But with Biden’s days in office numbered and President-elect Donald Trump set to take over, both sides had been under heavy pressure to agree to a deal.
Trump celebrated the soon-to-be-announced agreement in a posting on his Truth Social social media platform: “WE HAVE A DEAL FOR THE HOSTAGES IN THE MIDDLE EAST. THEY WILL BE RELEASED SHORTLY. THANK YOU!”
Hezbollah’s acceptance of a ceasefire in Lebanon after it had suffered heavy blows, and the overthrow of President Bashar Assad in Syria, were both major setbacks for Iran and its allies across the region, including Hamas, which was left increasingly isolated.
Israel has come under heavy international criticism, including from its closest ally, the United States, over the civilian toll. Israel says it has killed around 17,000 militants — though it has not provided evidence to support the claim. It also blames Hamas for the civilian casualties, accusing the group of using schools, hospitals and residential areas for military purposes.
The International Court of Justice is investigating allegations brought by South Africa that Israel has committed genocide. The International Criminal Court, a separate body also based in The Hague, has issued arrest warrants for Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, his defense minister and a Hamas commander for war crimes and crimes against humanity linked to the war.
Israel and the United States have condemned the actions taken by both courts.
Netanyahu also faced great domestic pressure to bring home the hostages, whose plight has captured the nation’s attention. Their families have become a powerful lobbying group with wide public support backed by months of mass protests urging the government to reach a deal with Hamas.
Israeli authorities have already concluded that more than a third of the roughly 100 remaining people held captive are dead, and there are fears that others are no longer alive. A series of videos released by Hamas showing surviving hostages in distress, combined with news that a growing number of abducted Israelis have died, put added pressure on the Israeli leader.
Hamas, a militant group that does not accept Israel’s existence, has come under overwhelming pressure from Israeli military operations, including the invasion of Gaza’s largest cities and towns and the takeover of the border between Gaza and Egypt. Its top leaders, including Yahya Sinwar, who was believed to have helped mastermind the Oct. 7, 2023, attack, have been killed.
But its fighters have regrouped in some of the hardest-hit areas after the withdrawal of Israeli forces, raising the prospect of a prolonged insurgency if the war continues.
Netanyahu has vowed to continue the war until Hamas’s military and governing capabilities are destroyed. But it has never been clear what that would entail or if it’s even possible, given the group’s deep roots in Palestinian society, its presence in Lebanon and the occupied West Bank, and its exiled leadership.
If the ceasefire takes hold, both sides face many difficult and unanswered questions.
As the war winds down, Netanyahu will face growing calls for postwar investigations that could find him at least partially responsible for the security failures of Oct. 7 — the worst in Israel’s history. His far-right governing partners, who opposed a ceasefire deal, could also bring down the coalition and push the country into early elections.
There is still no plan for who will govern Gaza after the war. Israel has said it will work with local Palestinians not affiliated with Hamas or the Western-backed Palestinian Authority. But it is unclear if such partners exist, and Hamas has threatened anyone who cooperates with Israeli forces.
The United States has tried to advance sweeping postwar plans for a reformed Palestinian Authority to govern Gaza with Arab and international assistance. As part of those plans, the US hope Saudi Arabia would normalize relations with Israel in return for US security guarantees and aid in setting up a civilian nuclear program.
But those plans depend on credible progress toward the creation of a Palestinian state, something Netanyahu and much of Israel’s political class oppose. Netanyahu has said Israel will maintain open-ended security control over Gaza as well as the occupied West Bank, territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war that the Palestinians want for their future state.
In the absence of a postwar arrangement with Palestinian support, Hamas is likely to remain a significant force in Gaza and could reconstitute its military capabilities if Israeli forces fully withdraw.