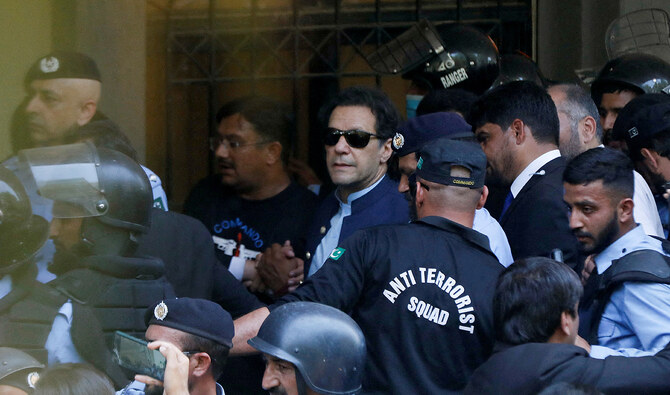ISLAMABAD: UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy recently assured a fellow parliamentarian that there have been “no recent indications” from Pakistani authorities that they intend to try former prime minister Imran Khan in a military court, reiterating that he had the right to a fair trial and due process.
Protesters linked to Khan’s Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party attacked and damaged government and military buildings on May 9, 2023, after his brief arrest that day in a land graft case. Hundreds of PTI followers and leaders were arrested following the riots. The military has also initiated trials of at least 103 people accused of involvement in the violence.
The development raised fears among Khan supporters of his possible trial by a military court, prompting the former prime minister to file a petition in the Islamabad High Court against it. The petition was dismissed by the court in September after the government said it had not decided whether or not it wanted to try the former premier.
Pakistan’s military spokesperson in September hinted at Khan’s possible military trial, saying that though the matter was sub judice, using military personnel for personal or political gains invites legal action.
In response to an Oct. 16 letter penned by Labour legislator Kim Johnson, Lammy assured him that the UK government engages regularly “at a senior level” with Pakistan on the country’s political situation.
“We have no recent indications from the Pakistani authorities that they intend to try Imran Khan in a military court, but my officials continue to monitor the situation closely,” Lammy wrote in a letter to Johnson dated Nov. 11.
The UK official said he has raised concerns about the potential use of military courts to try civilians, including Khan. Lammy added that such courts can lack transparency and independent scrutiny, making it difficult to assess their compliance with international standards.
“While Pakistan’s judicial processes are a domestic matter, we have been very clear that the Pakistani authorities need to act in line with their international obligations and with respect for fundamental freedoms, including the right to a fair trial, due process and humane detention,” he wrote.
“This applies to Imran Khan as it does to all Pakistan’s citizens.”
Lammy said he remains concerned by restrictions on freedom of expression and assembly in Pakistan, including those in relation to political opposition.
“In our engagements with the authorities, we continue to underline that the freedom to hold and express views without censorship, intimidation or unnecessary restriction is a cornerstone of democracy,” he said.
Khan’s close aide, Sayed Zulfikar Bukhari shared Lammy’s letter on social media platform X.
“Respect for free and fair elections, and the rule of law, underpinned by an independent judiciary, are the bedrock of a democracy,” Bukhari wrote. “Pakistanis continue to struggle for theirs.”
Khan, arguably Pakistan’s most popular politician, was ousted from office after a parliamentary no-trust vote in April 2022 and has since waged an unprecedented campaign of defiance against the country’s powerful military and Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif-led government.
Khan’s party says the military and his political rivals rigged the Feb. 8 general election to form the Sharif-led government. Both deny the charge.
No indication from Pakistan on trying Imran Khan in military court — UK foreign secretary
https://arab.news/2bdmn
No indication from Pakistan on trying Imran Khan in military court — UK foreign secretary

- UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy says Khan, like other Pakistani prisoners, has right to fair trial and due process
- Pakistan’s military has initiated trials of at least 103 Khan supporters accused of attacking military installations last year
Pakistan announces national Islamic scholarship competition focused on youth

- Contest invites books, essays, poetry in multiple languages, with awards for men and women
- Best entries to be published digitally and in print, submissions due by March 31
ISLAMABAD: Pakistan’s Ministry of Religious Affairs on Wednesday announced a nationwide competition for books, poetry and academic papers focused on Islamic scholarship, as part of efforts to promote religious discourse addressing modern social challenges, particularly among younger generations.
The annual competition will cover works on Seerat — the biography and teachings of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) — as well as Na’at, a traditional form of devotional poetry praising the Prophet, alongside broader Islamic research and literary contributions published in Pakistan and abroad.
“Ministry of Religious Affairs ... remains committed to addressing contemporary challenges through the guidance of the Seerat-e-Tayyaba (the life of the Prophet Muhammad), describing the national competition as an important step toward promoting Islamic teachings in society,” the ministry said in a statement.
“The initiative serves as an effective platform to encourage writers and researchers working on Seerat and Islamic subjects.”
For 2026, the ministry has set the central theme for Seerat research papers as “Protection, development and character-building of the younger generation in the light of the life of the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him).”
Officials said the focus aims to encourage scholarly engagement with issues such as ethics, social responsibility and education in a rapidly changing society.
The competition will award separate cash prizes and certificates to male and female writers at national and provincial levels, while selected research papers will be published in both digital and printed formats, the statement said.
According to the ministry, works published in national, regional and foreign languages will be eligible, with eight dedicated categories covering Seerat authors and Na’at poets. Separate categories have also been introduced for women writers, journals and magazines, expanding participation beyond individual book authors.
The ministry said the competition is intended to strengthen Islamic literary traditions while encouraging new voices to engage with religious subjects in a contemporary context.
The deadline for submission of books and research papers is March 31, 2026, it added.