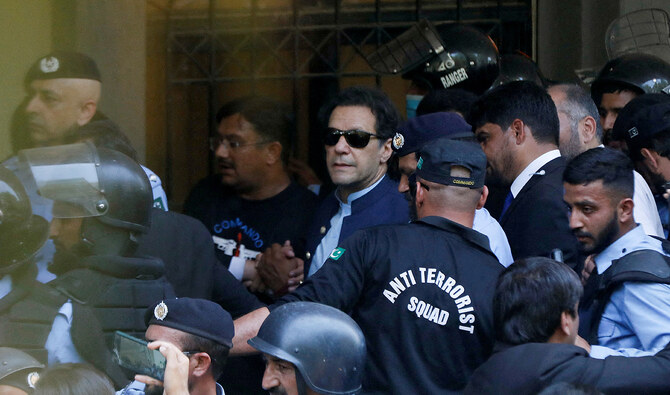ISLAMABAD: UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy recently assured a fellow parliamentarian that there have been “no recent indications” from Pakistani authorities that they intend to try former prime minister Imran Khan in a military court, reiterating that he had the right to a fair trial and due process.
Protesters linked to Khan’s Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party attacked and damaged government and military buildings on May 9, 2023, after his brief arrest that day in a land graft case. Hundreds of PTI followers and leaders were arrested following the riots. The military has also initiated trials of at least 103 people accused of involvement in the violence.
The development raised fears among Khan supporters of his possible trial by a military court, prompting the former prime minister to file a petition in the Islamabad High Court against it. The petition was dismissed by the court in September after the government said it had not decided whether or not it wanted to try the former premier.
Pakistan’s military spokesperson in September hinted at Khan’s possible military trial, saying that though the matter was sub judice, using military personnel for personal or political gains invites legal action.
In response to an Oct. 16 letter penned by Labour legislator Kim Johnson, Lammy assured him that the UK government engages regularly “at a senior level” with Pakistan on the country’s political situation.
“We have no recent indications from the Pakistani authorities that they intend to try Imran Khan in a military court, but my officials continue to monitor the situation closely,” Lammy wrote in a letter to Johnson dated Nov. 11.
The UK official said he has raised concerns about the potential use of military courts to try civilians, including Khan. Lammy added that such courts can lack transparency and independent scrutiny, making it difficult to assess their compliance with international standards.
“While Pakistan’s judicial processes are a domestic matter, we have been very clear that the Pakistani authorities need to act in line with their international obligations and with respect for fundamental freedoms, including the right to a fair trial, due process and humane detention,” he wrote.
“This applies to Imran Khan as it does to all Pakistan’s citizens.”
Lammy said he remains concerned by restrictions on freedom of expression and assembly in Pakistan, including those in relation to political opposition.
“In our engagements with the authorities, we continue to underline that the freedom to hold and express views without censorship, intimidation or unnecessary restriction is a cornerstone of democracy,” he said.
Khan’s close aide, Sayed Zulfikar Bukhari shared Lammy’s letter on social media platform X.
“Respect for free and fair elections, and the rule of law, underpinned by an independent judiciary, are the bedrock of a democracy,” Bukhari wrote. “Pakistanis continue to struggle for theirs.”
Khan, arguably Pakistan’s most popular politician, was ousted from office after a parliamentary no-trust vote in April 2022 and has since waged an unprecedented campaign of defiance against the country’s powerful military and Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif-led government.
Khan’s party says the military and his political rivals rigged the Feb. 8 general election to form the Sharif-led government. Both deny the charge.
No indication from Pakistan on trying Imran Khan in military court — UK foreign secretary
https://arab.news/2bdmn
No indication from Pakistan on trying Imran Khan in military court — UK foreign secretary

- UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy says Khan, like other Pakistani prisoners, has right to fair trial and due process
- Pakistan’s military has initiated trials of at least 103 Khan supporters accused of attacking military installations last year
Peace can only prevail if Afghanistan renounces support for ‘terrorism’— Pakistan defense chief

- Pakistan’s chief of defense forces visits South Waziristan district bordering Afghanistan
- Pakistan says has killed 481 Afghan Taliban operatives since clashes began last Thursday
ISLAMABAD: Pakistan’s Chief of Defense Forces Field Marshal Syed Asim Munir said on Wednesday that peace with Afghanistan can only prevail if Kabul renounces support for “terrorism” and “terrorist” organizations, the military’s media wing said as the two countries remain locked in conflict.
Fighting between the two neighbors, the worst in decades, broke out last Thursday night after Afghan forces attacked Pakistan’s military installations along their shared border. Afghanistan said its attacks were in response to earlier airstrikes by Pakistan against alleged militant hideouts in its country.
Pakistan accuses Afghanistan of sheltering militant outfits such as the Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) on its soil who have launched attacks against Pakistani civilians and security forces in recent years. Kabul denies the allegations.
Munir visited Wana town in Pakistan’s South Waziristan district to review the security situation and troops’ operational preparedness at the Afghan border, the Pakistani military’s media wing said in a statement.
“The Field Marshal reiterated that peace could only prevail between both sides if the Afghan Taliban renounced their support for terrorism and terrorist organizations,” the Inter-Services Public Relations (ISPR) said.
The military chief said the use of Afghan soil by militant outfits to launch attacks against Pakistan was unacceptable, vowing that “all necessary measures” would be taken to neutralize cross-border threats.
During the visit, Munir was briefed by military commanders about ongoing intelligence-based operations and measures being taken by the military to manage the border with Afghanistan.
He was also briefed about “Operation Ghazab Lil Haq” or “Wrath for the Truth,” the name Pakistan has given to its military operation against Afghan forces, the ISPR said.
The Pakistani military chief spoke to troops deployed in the area, praising their vigilance, professional conduct and high morale, the ISPR said.
Pakistan’s Information Minister Attaullah Tarar said on Wednesday that the military has killed 481 Taliban operatives, injured more than 690 and destroyed 226 Afghan checkposts since clashes began.
Arab News has been unable to verify claims by both sides about the damages they claim to have inflicted on each other.
Afghanistan has signaled it is open for dialogue but Pakistan rejected the offer, saying it would continue its military operations till its objectives were achieved.
Since the conflict began, diplomatic efforts have intensified with several countries, including global bodies such as the European Union and United Nations, urging restraint and calling for talks.
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan told Pakistani Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif that Ankara would help reinstate a ceasefire, the Turkish Presidency said on Tuesday, as other countries that had offered to mediate have since been hit by the conflict in the Gulf.