KARACHI: Pakistan’s central bank is expected to cut its key interest rate further at its policy meeting on Monday, with policymakers continuing their efforts to revive a fragile economy as inflation eases off recent record highs.
The central bank, the State Bank of Pakistan, has slashed the benchmark policy rate to 17.5% from an all time-high of 22% in three consecutive policy meetings since June, having last reduced it by 200 basis points in September.
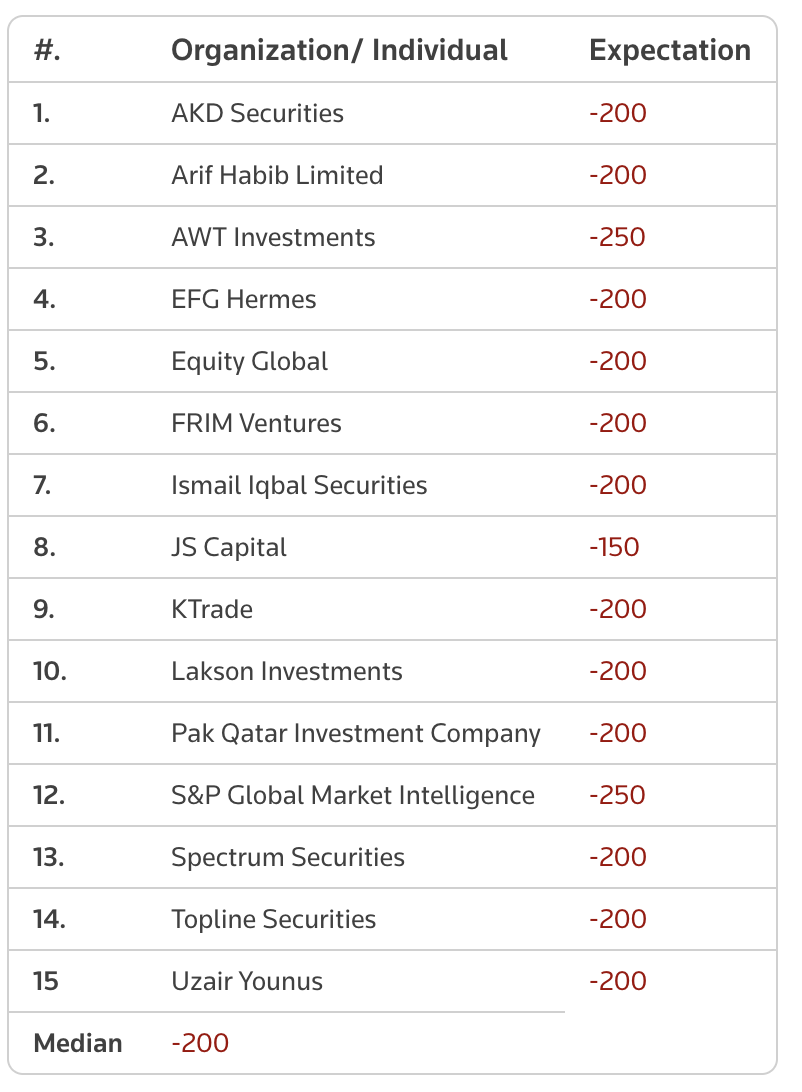
All 15 investors and analysts surveyed by Reuters expect the central bank to cut rates next week. Two expect a 150 bps cut, twelve predict a 200 bps reduction, and one forecasts a 250 bps cut.
Economic activity has stabilized since last summer when the country came close to a default before an eleventh hour bailout by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The IMF, which in September gave a boost to Pakistan’s struggling economy by approving a long-awaited $7 billion facility, said that the South Asian nation had taken key steps to restore economic stability with consistent policy implementation under the 2023-24 standby arrangement.
Advertisement · Scroll to continue
While the economy has started to gradually recover, and inflation has moved sharply down from a multi-decade high of nearly 40% in May 2023, analysts say further rate cuts are needed to bolster growth.
Mustafa Pasha, Chief Investment Officer at Lakson Investments, said rates must drop under 15% and hold below that for six months to have a material impact.
The IMF in its latest October report forecast Pakistan’s gross domestic product growth at 3.2% for the fiscal year ending June 2025, up from 2.4% in fiscal 2024.
The government expects annual inflation to have come in at 6-7% last month and slow further to 5.5-6.5% in November.
However, inflation could pick up again in 2025, driven by electricity and gas tariff hikes under the new $7 billion IMF bailout, and the potential impact of taxes on the retail and wholesale sector proposed in the June budget.
Ahmad Mobeen, senior economist at S&P Global Market Intelligence, said that while lower rates will offer some relief to the manufacturing sector, the benefits may be limited due to “elevated input costs, driven by high electricity and gas tariffs, combined with global supply and shipping constraints.”
The survey responses on Monday’s policy rate decision are listed below: