LAHORE, Pakistan: For Pakistani police, reports of a college campus rape that went viral this month are “fake news” fomenting unrest. For protesting students, the social media posts offer a rare public reckoning with sexual assault.
But as the clashing accounts have spilled from the Internet and onto the streets, both sides agree the case has ignited a tinderbox of legitimate fears.
“Girls who go to campuses definitely feel threatened,” 21-year-old Khadija Shabbir told AFP at a Monday protest in eastern Lahore city that was swiftly dismantled by authorities.
Senior officer Syeda Shehrbano Naqvi is charged with probing the case police insist has been conjured from unverifiable online rumors.
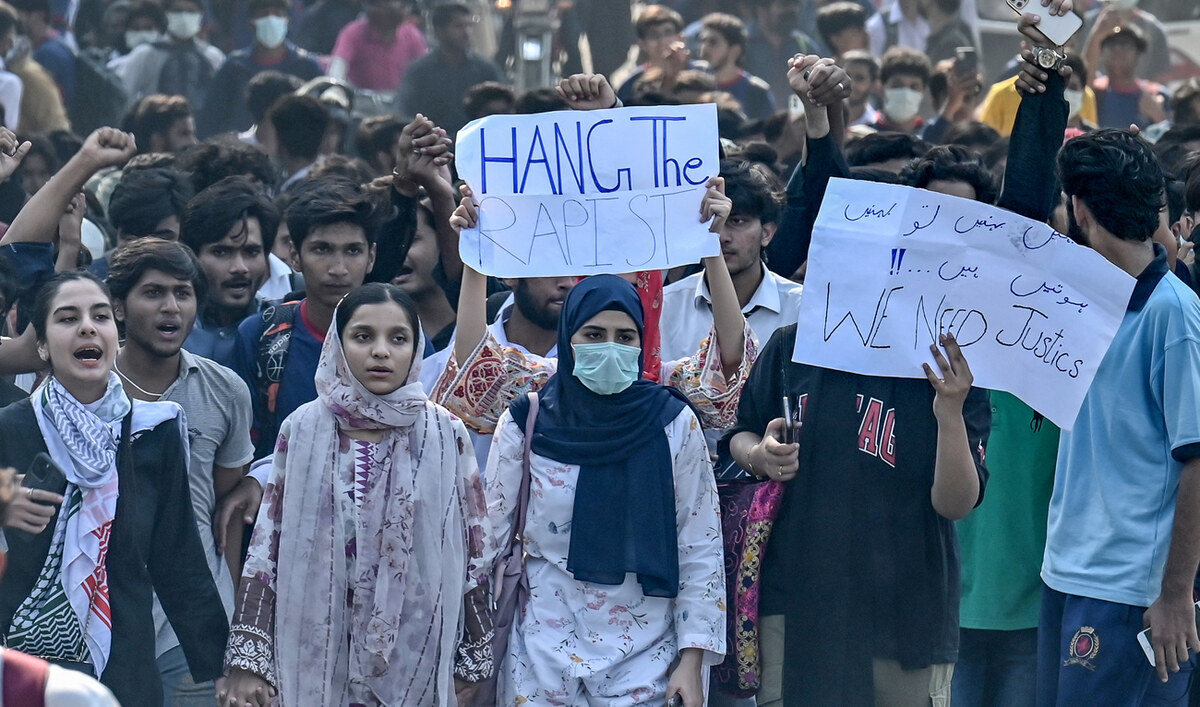
Students carry placards as they march during a demonstration to condemn the alleged rape of a female student in Lahore on October 16, 2024. (AFP)
But she admits it has struck a real chord on the issue of harassment in Pakistan, a patriarchal country where open discussion of abuse is taboo.
“All of us somewhere have experienced it,” she says. “It’s an extremely sensitive subject.”
It began earlier this month with a swirl of social media posts alleging a staff member had raped a woman in the basement of a Punjab College campus in Lahore.
When police and local media were unable to trace a victim, the local government and school administration dismissed the claims as a hoax.
But student protests broke out last Monday, escalating into unrest in Lahore and other cities later in the week that led to the arrests of at least 380 people over vandalism and arson.
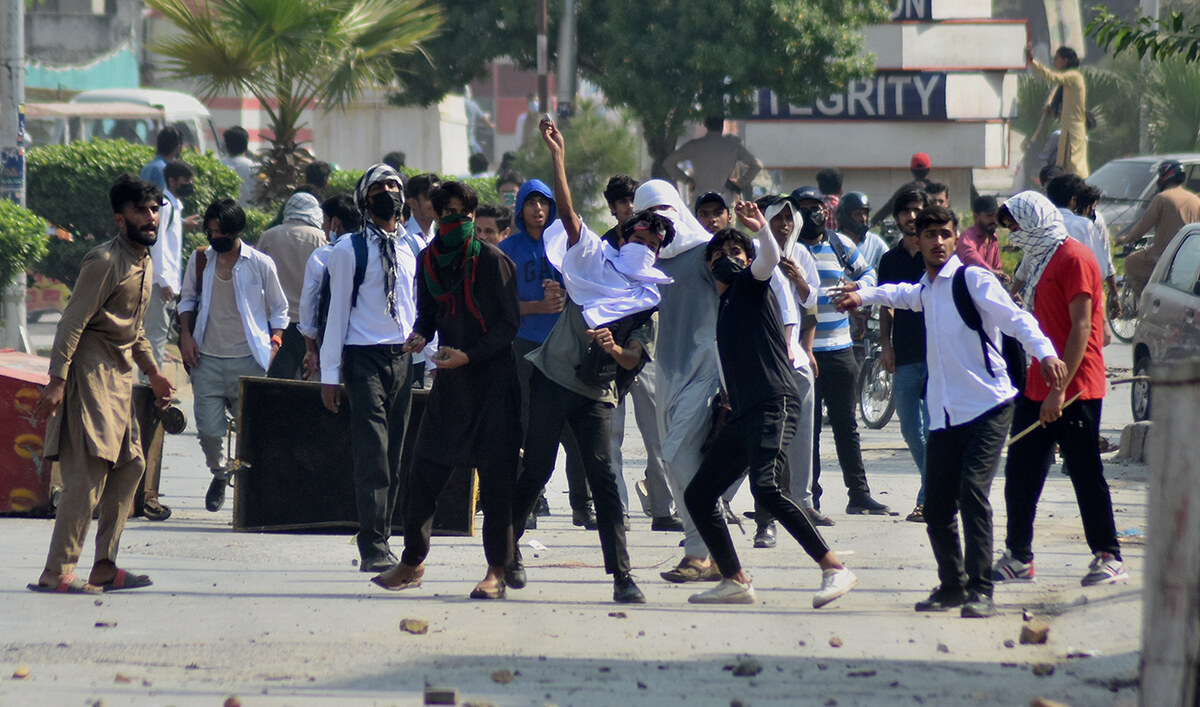

Students throw stones toward police during clashes as they protest over an alleged on-campus rape in Punjab, in Rawalpindi on October 17, 2024. (AP)
Educational institutes were shut across Punjab province last Friday — when protests are generally staged after prayers — and political gatherings were banned for two days, although officials gave no reason.
As a result, about 26 million children were out of school as well as many more university and college students in the country’s most populous province.
But students, banned from officially organizing in unions for the past four decades, have continued to come out this week.
“I haven’t seen it grow into a movement like this or this sort of anger or reaction from them before,” said Fatima Razzaq, a member of the Aurat March women’s rights group.
The Punjab government has a women-only police emergency line where they report receiving 1,300 calls daily from women concerned about their safety.
But with 80 percent of women saying they have been harassed in public places, according to the UN, there is little trust that authorities take the matter seriously.
Razzaq said “a deep-rooted frustration” is surfacing as a result.
While protesters’ opinions vary about the veracity of the rape claim that has sparked the movement, many cite their own experience as more pivotal in their decision to turn out.
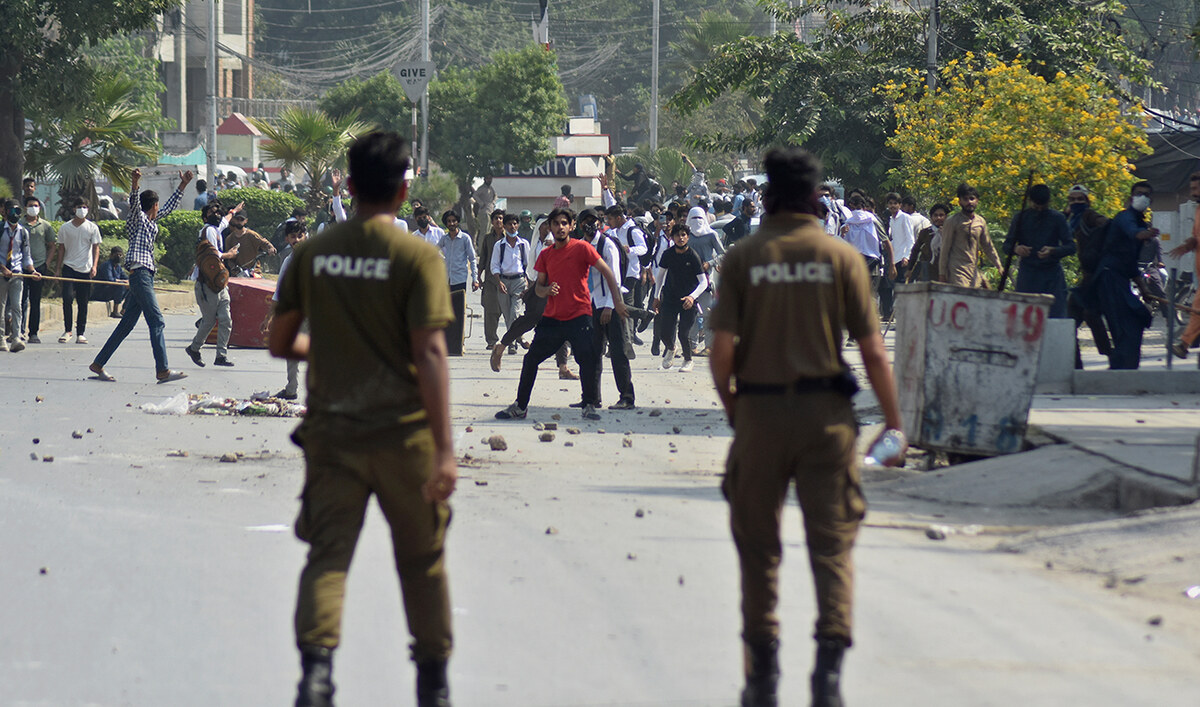

Students throw stones toward police during clashes as they protest over an alleged on-campus rape in Punjab, in Rawalpindi on October 17, 2024. (AP)
“A girl I know in my university committed suicide because she was being harassed,” student Amna Nazar told AFP.
“My professor keeps asking me out and calling me to his office,” said another University of the Punjab student, asking to remain anonymous. “This is something I do not want to do.”
On the campus where the crime is alleged to have happened, activists painted the walls with red hand prints and demands of “justice for the rape victim.” But it was quickly painted over.
“If we go and complain about an incident, we are told that nothing happened and we should stop talking about it,” said one female student at another university.
Lahore’s High Court has announced a new committee of judges to investigate campus sexual harassment, indicating authorities are conceding the protests have a point.
But the face-off between students and police is taking place amid a broader crackdown on dissent from political and ethnic activists across Pakistan.
Student social media pages and online chat groups created to mobilize protesters have disappeared and officials have pledged that those spreading misinformation will be prosecuted.

In this photograph taken on October 19, 2024, Syeda Shehrbano Naqvi, a Pakistani senior police officer, speaks during an interview with AFP at her office in Lahore. (AFP)
Naqvi — the police officer — said there was “less tendency of people to believe somebody in uniform” and that the confrontation had spiraled into the “state versus the students.”
Meanwhile, the women whose experiences with harassment have placed them at the center of the movement are finding themselves sidelined as the protests spill into violence often led by men.
As crowds of male students threw rocks at police in the city of Rawalpindi last week, officers returned fire with rubber bullets, and women fearing for their safety cowered away in side-streets.
Nevertheless, 19-year-old female student Inshai said: “We are standing up for our rights.”














