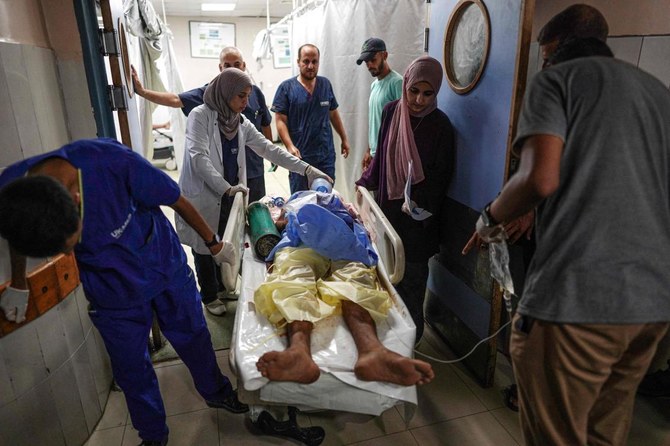
DEIR AL-BALAH: An Israeli airstrike on a school-turned-shelter in southern Gaza killed at least 25 Palestinians on Tuesday, as heavy bombardment in the north forced the closure of medical facilities in Gaza City and sent thousands fleeing in search of increasingly elusive refuge.
Israel’s new ground assault in Gaza’s largest city is its latest effort to battle Hamas militants regrouping in areas the army previously said had been largely cleared.
Large parts of Gaza City and urban areas around it have been flattened or left a shattered landscape after nine months of fighting. Much of the population fled earlier in the war, but several hundred thousand Palestinians remain in the north.
“The fighting has been intense,” said Hakeem Abdel-Bar, who fled Gaza City’s Tuffah district to the home of relatives in another part of the city. He said Israeli warplanes and drones were “striking anything moving” and that tanks had moved into central districts.
The strike at the entrance to the school killed at least 25 people, according to an Associated Press reporter who counted the bodies at Nasser Hospital in Khan Younis. Hospital spokesperson Weam Fares said the dead included at least seven women and children and that the toll was likely to rise.
Earlier airstrikes in central Gaza killed at least 14 people, including a woman and four children, according to two hospitals that received the bodies. Israel has repeatedly struck what it says are militant targets across Gaza since the start of the war nine months ago.
The military blames civilian deaths on Hamas because the militants fight in dense, urban areas, but the army rarely comments on individual strikes, which often kill women and children. The Israeli army said the airstrike near the school and reports of civilian casualties were under review, and claimed the strike targeted a Hamas militant who took part in the Oct. 7 attack on Israel.
There was also no immediate word on casualties in Gaza City. Families whose relatives were wounded or trapped were calling for ambulances, but first responders could not reach most of the affected districts because of the Israeli operations, said Nebal Farsakh, a spokesperson for the Palestinian Red Crescent.
“It’s a dangerous zone,” she said.
After Israel on Monday called for an evacuation from eastern and central parts of Gaza City, staff at two hospitals — Al-Ahli and the Patients Friends Association Hospital — rushed to move patients and shut down, the United Nations said. Farsakh said all three medical facilities run by the Red Crescent in Gaza City had closed.
Scores of patients were transferred to the Indonesian Hospital in northern Gaza, which itself was the scene of heavy fighting earlier in the war. “We do not know where to go. There is no treatment and no necessities for life,” said Mohammad Abu Naser, who was being treated there. “We are dying slowly.”
The Israeli military said Tuesday that it told hospitals and other medical facilities in Gaza City they did not need to evacuate. But hospitals in Gaza have often shut down and moved patients at any sign of possible Israeli military action, fearing raids.
The Episcopal Church in the Middle East, which operates Al-Ahli, said the hospital was “compelled to close by the Israeli army” after the evacuation orders and a wave of nearby drone strikes on Sunday.
In the past nine months, Israeli troops have occupied at least eight hospitals, causing the deaths of patients and medical workers along with massive destruction to facilities and equipment. Israel has claimed Hamas uses hospitals for military purposes, though it has provided only limited evidence.
Only 13 of Gaza’s 36 hospitals are functioning, and those only partially, according to the United Nations’ humanitarian office.
Israel’s campaign in Gaza, triggered by Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack, has killed or wounded more than 5 percent of Gaza’s 2.3 million Palestinians, according to the territory’s Health Ministry. Nearly the entire population has been driven from their homes. Many have been displaced multiple times. Hundreds of thousands are packed into sweltering tent camps.
The UN humanitarian office said the exodus in Gaza City was “dangerously chaotic,” with people instructed to flee through neighborhoods where fighting was underway.
“People have been observed fleeing in multiple directions, not knowing which way may be safest,” the agency said in a statement. It said the largest UN bakery in the city was forced to close, and that the fighting had blocked aid groups from accessing warehouses.
Maha Mahfouz, a mother of two, said she fled twice in the past 24 hours. She first rushed from her home in Gaza City to a relative’s house in another neighborhood. When that became dangerous, she fled Monday night to Shati, a decades-old refugee camp that has grown into an urban district where Israel has carried out repeated raids.
She described vast destruction in the areas targeted in the latest raids. “The buildings were destroyed. The roads were destroyed. All has become rubble,” she said.
The Israeli military has said it had intelligence showing that militants from Hamas and the smaller Islamic Jihad group were regrouping in central Gaza City. Israel accuses Hamas and other militants of hiding among civilians. In Shijaiyah, a Gaza City neighborhood that has seen weeks of fighting, the military said it had destroyed 6 kilometers of Hamas tunnels.
Hamas has warned that the latest raids in Gaza City could lead to the collapse of negotiations for a ceasefire and hostage-release deal.
Israel and Hamas had appeared to narrow the gaps in recent days, with the US, Egypt and Qatar mediating.
CIA Director William Burns met Tuesday with Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi in Cairo to discuss the negotiations, El-Sisi’s office said. More talks were to be held Wednesday in Qatar, where Hamas maintains a political office.
But obstacles remain, even after Hamas agreed to relent on its key demand that Israel commit to ending the war as part of any agreement. Hamas still wants mediators to guarantee that negotiations conclude with a permanent ceasefire.
Israel has rejected any deal that would force it to end the war with Hamas intact. Hamas on Monday accused Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of “putting more obstacles in the way of negotiations,” including the operations in Gaza City.
Hamas’ cross-border raid on Oct. 7 killed 1,200 people in southern Israel, most of them civilians, according to Israeli authorities. The militants took roughly 250 people hostage. About 120 are still in captivity, with about a third said to be dead.
Israel’s bombardment and offensives in Gaza have killed more than 38,200 people and wounded more than 88,000, according to the territory’s Health Ministry, which does not distinguish between combatants and civilians in its count.
Airstrike kills 25 in southern Gaza as Israeli assault on Gaza City shuts down medical facilities
https://arab.news/gprzt
Airstrike kills 25 in southern Gaza as Israeli assault on Gaza City shuts down medical facilities

- Heavy bombardment in the north meanwhile forced the closure of medical facilities in Gaza City and sent thousands fleeing in search of increasingly elusive refuge
- Large parts of Gaza City and urban areas around it have been flattened or left a shattered landscape after nine months of fighting
How Gaza’s shattered fishing industry deepened the enclave’s food security crisis

- Once a pillar of local food security, Gaza’s fishing sector has been reduced to a fraction of its prewar capacity
- UN agencies warn the destruction of boats and ports has deepened aid dependence and worsened protein shortages
DUBAI: Gaza’s fishing industry — once a critical source of food, income and affordable protein — has been largely destroyed as a result of Israel’s war with Hamas, worsening the Palestinian enclave’s food security crisis.
According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, fishing activity in Gaza now stands at less than 10 percent of prewar levels following the widespread destruction of boats, ports and equipment, combined with prolonged maritime closures enforced under Israel’s naval blockade.
UN and human rights organizations estimate that up to 72 percent of Gaza’s fishing fleet has been damaged or destroyed, alongside near-total devastation of related infrastructure, including landing sites, storage facilities and repair workshops.

The remaining vessels are small, damaged skiffs capable of operating only meters from shore.
Ramzy Baroud, a journalist, author and editor of The Palestine Chronicle, said the destruction of Gaza’s fishing sector must be understood as part of a deliberate policy aimed at preventing Palestinians from developing independent food-producing systems.
Baroud says Israel had pursued a strategy since 1967 to foster Palestinian dependency — first on the Israeli economy, and later on humanitarian aid entering Gaza through Israeli-controlled crossings — leaving the population permanently vulnerable to economic collapse.
“This vulnerability is functional for Israel, as it allows the Israeli government and military to leverage their control over Palestinian lives through political pressure in pursuit of concessions,” he told Arab News.
Palestinians were prevented from developing local industry through restrictions on imports and exports, while much of Gaza’s arable land was seized or turned into military targets, he said.
“Likewise, the fishing sector was deliberately crippled through direct attacks on fishermen, including arrests, live fire, confiscation of equipment, and the sinking or destruction of boats,” he added.
FAO has documented widespread destruction across Gaza’s coastal fishing areas.
“In Gaza’s fishing areas now lie broken boats, torn nets, and ruined infrastructure, standing in stark contrast to the once-vibrant industry that supported thousands of fishers for generations,” Beth Bechdol, FAO deputy director-general, said in a statement.
Before the war, more than 4,000 registered fishermen worked along Gaza’s 40-kilometer coastline, supporting tens of thousands of family members and contributing to local food security in an enclave heavily dependent on imports.
Today, the majority have been stripped of their livelihoods, as access to the sea has become sporadic, dangerous, or entirely prohibited.
For decades, fishing off Gaza was restricted to shifting maritime zones — typically between three and 12 nautical miles offshore — often tightened or closed entirely during periods of escalation.
Since October 2023, when the Israel-Hamas conflict began, humanitarian organizations say there have been extended periods of total maritime closure, effectively banning fishing and depriving Gaza’s population of one of its few remaining sources of local food production.
Baroud said the assault on Gaza’s fishing sector was not a by-product of war, but part of a deliberate strategy that intensified during the conflict.
“For Gaza, the sea represents freedom,” he said. “All of Gaza’s other borders are controlled by Israel, either directly or indirectly.”
Israel had consistently worked to deny Palestinians access to the sea, he said. And despite commitments under the Oslo Accords to allow fishing up to 20 nautical miles offshore, those provisions were never honored.
“The assault on Gaza’s fishing sector is therefore not incidental,” Baroud said. “It is about severing Palestinians from one of the few spaces not entirely enclosed by walls, checkpoints, and military control.”
Israel has generally rejected or not accepted accusations that it is unlawfully targeting Gaza’s fishermen, framing incidents at sea as enforcement of security zones or as under investigation rather than deliberate attacks on civilians.
In past lethal incidents at sea highlighted by Human Rights Watch, the Israel Defense Forces have typically said boats “deviated from the designated fishing zone” and that forces fired after warnings were ignored.
According to FAO, rebuilding Gaza’s fishing sector will be impossible without a fundamental change in access and security conditions.
“For Gazans, the sea was not just a source of food, but a source of livelihood and identity,” Bechdol said.
“FAO can assist to help rebuild Gaza’s fishing industry. But for this to happen, peace must first be established and fishers must be allowed to operate their boats and cast their nets without fear of harm.”
Ciro Fiorillo, head of the FAO office for the West Bank and Gaza, said the agency is primed to offer assistance once the security situation improves.
“FAO is ready to restart projects, replenish damaged boats and equipment, and inject emergency funds as soon as these key fishing inputs for production are allowed to enter the Strip, a sustained ceasefire is in place, and access to the sea is restored,” Fiorillo said in a statement.
Since the Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas-led attack on southern Israel triggered the Israeli military assault on Gaza, much of the enclave has been flattened, tens of thousands killed, and some 90 percent of the population displaced.
Even since the ceasefire came into effect with the exchange of hostages and prisoners in October last year, pockets of violence have continued and humanitarian needs remain dire. The collapse of fishing has only compounded an already catastrophic food crisis.
The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs has repeatedly warned that the destruction of food-producing systems — including agriculture, fisheries and markets — has pushed Gaza toward famine, with households facing extreme shortages of protein and calories.
With farmland destroyed, livestock killed and imports severely restricted, fish was once among the few foods that could still be sourced locally.
Its near disappearance has driven prices beyond reach for most families and increased dependence on limited humanitarian aid.
“This is about denying Palestinians access to life itself — to survival,” said Baroud.
The destruction of fishing forces Palestinians into deeper dependence on humanitarian aid that Israel itself controls, effectively weaponizing food rather than allowing Palestinians to sustain themselves independently, he said.
Human rights groups documenting maritime enforcement report that fishermen attempting to operate — even close to the shore — face gunfire, pursuit, detention and arrest, contributing to a climate in which fishing has become a life-threatening activity rather than a livelihood.
According to rights monitors, the destruction of larger vessels has eliminated the possibility of reaching deeper waters, forcing the few remaining fishermen to operate in unsafe, shallow zones with damaged equipment, limited fuel and no protection.
Baroud said international law clearly obligates an occupying power to protect civilian livelihoods and ensure access to food and means of survival.
“The systematic targeting of fishermen — who are civilians engaged in subsistence activity — cannot be justified as a military necessity, especially when it results in starvation and famine,” Baroud said.
He said the Fourth Geneva Convention prohibits collective punishment, the destruction of civilian infrastructure and the targeting of livelihoods.
The Palestinian Centre for Human Rights has described the restriction of Gaza’s fishing sector as part of a broader assault on civilian survival systems, warning that the denial of access to the sea has direct implications for nutrition, employment and aid dependency.
Baroud said the recovery of Gaza’s fishing sector could not occur in isolation from the broader economy.
“Only a measure of real freedom for Palestinians — freedom of movement, access to land and sea, and the ability to import, export and produce independently — can allow Gaza’s industries and economy to recover,” he said.
Without ending the system of control governing Palestinian life, Baroud said, any discussion of reconstruction or recovery would remain hollow.
As famine warnings intensify, the fishing sector’s collapse stands as a stark example of how Gaza’s food system has fractured.
What was once a daily livelihood is now reduced to occasional, high-risk attempts to secure food.
With no functioning fleet and no safe access to waters, Gaza’s fishermen are operating at the edge of survival.