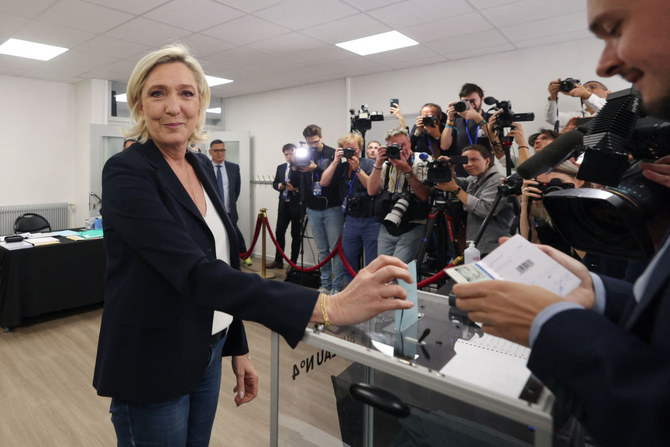
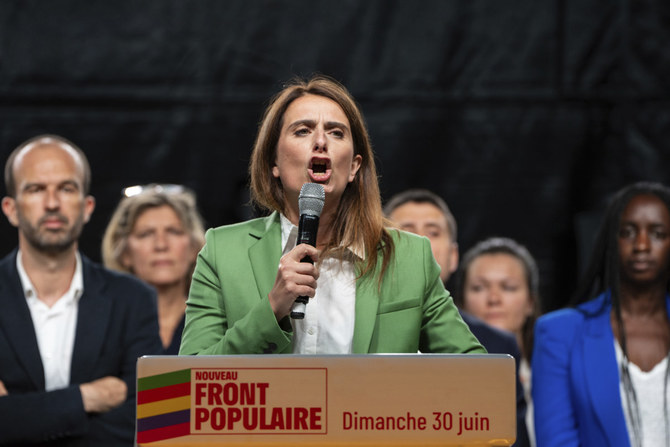
PARIS: French voters face a decisive choice on July 7 in the runoff of snap parliamentary elections that could see the country’s first far-right government since the World War II Nazi occupation — or no majority emerging at all.
Projections by polling agencies suggest the far-right National Rally stands a good chance of winning a majority in the lower house of parliament for the first time, but the outcome remains uncertain amid the complex voting system.
In Sunday’s first round, the National Rally arrived ahead with an estimated one-third of the votes. The New Popular Front coalition that includes center-left, greens and hard-left forces came out in second position, ahead of President Emmanuel Macron’s centrist alliance.
Here’s a closer look:
How does it work?
The French system is complex and not proportionate to nationwide support for a party. Legislators are elected by district.
Over 60 candidates who won at least 50 percent of Sunday’s vote have been elected outright.
In addition, the top two contenders, alongside anyone else who won support from more than 12.5 percent of registered voters, are qualified for the second round.

In many districts, three people made it to the second round, though some tactics to block far-right candidates have already been announced: The left-wing coalition said it would withdraw its candidates in districts when they arrived in third position in order to support other politicians opposed to the far right. Macron’s centrist alliance also said some of its candidates would step down before the runoff to block the National Rally.
This makes the result of the second round uncertain, despite polls showing that the National Rally party has a good chance to win an absolute majority, that is at least 289 out of the 577 seats.
The National Assembly, the lower house, is the more powerful of France’s two houses of parliament. It has the final say in the law-making process over the Senate, dominated by conservatives.
Macron has a presidential mandate until 2027, and said he would not step down before the end of his term.
What’s cohabitation?
If the National Rally or another political force than his centrist alliance gets a majority, Macron will be forced to appoint a prime minister belonging to that new majority.
In such a situation — called “cohabitation” in France — the government would implement policies that diverge from the president’s plan.
France’s modern Republic has experienced three cohabitations, the last one under conservative President Jacques Chirac, with Socialist Prime Minister Lionel Jospin, from 1997 to 2002.
The prime minister is accountable to the parliament, leads the government and introduces bills.
“In case of cohabitation, policies implemented are essentially those of the prime minister,” political historian Jean Garrigues said.
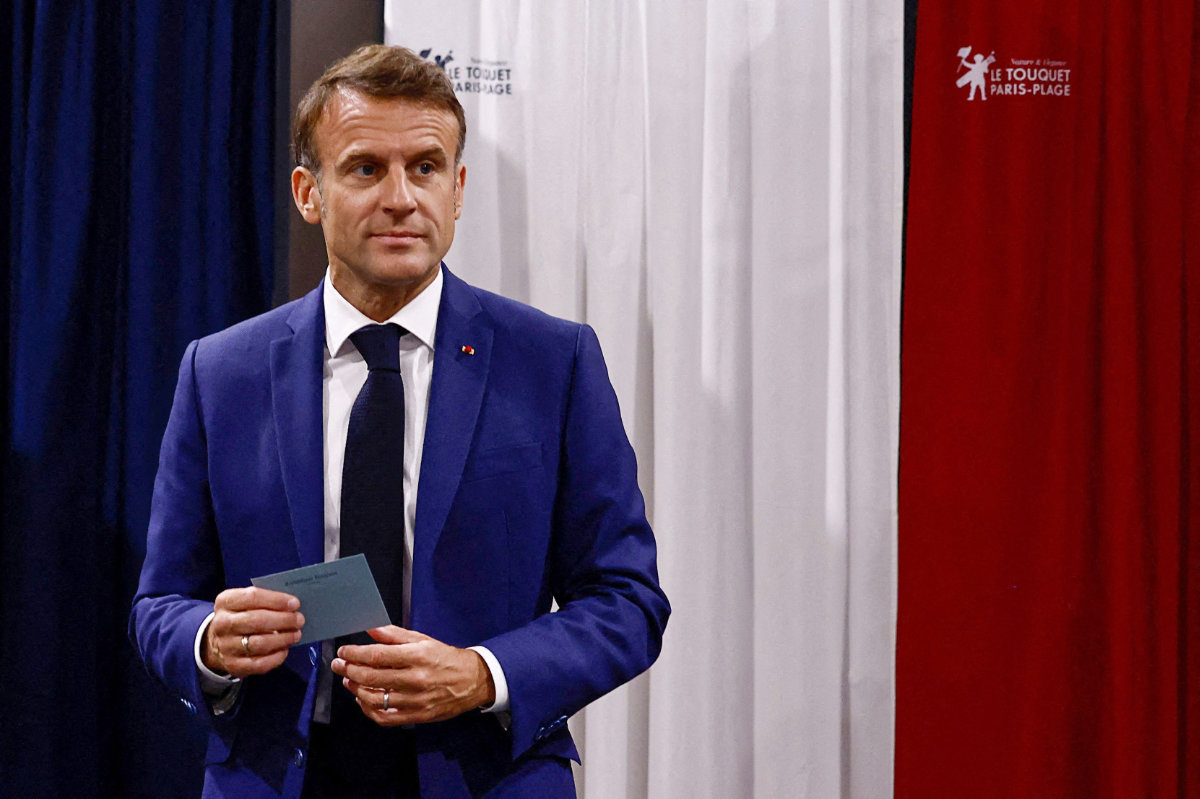

France’s President Emmanuel Macron leaves the polling booth prior to cast his vote at a polling station in Le Touquet, northern France on June 30, 2024. (POOL/AFP)
The president is weakened at home during cohabitation, but still holds some powers over foreign policy, European affairs and defense because he is in charge of negotiating and ratifying international treaties. The president is also the commander-in-chief of the country’s armed forces, and is the one holding the nuclear codes.
“It’s possible for the president to prevent or temporarily suspend the implementation of a certain number of the prime minister’s projects, since he has the power to sign or not sign the government’s ordinances or decrees,” Garrigues added.
“Yet the prime minister has the power to submit these ordinances and decrees to a vote of the National Assembly, thus overriding the president’s reluctance,” he noted.
Who leads defense and foreign policies?
During previous cohabitations, defense and foreign policies were considered the informal “reserved field” of the president, who was usually able to find compromises with the prime minister to allow France to speak with one voice abroad.
Yet today, both the far-right and the leftist coalition’s views in these areas differ radically from Macron’s approach and would likely be a subject of tension during a potential cohabitation.
According to the Constitution, while “the president is the head of the military, it’s the prime minister who has the armed forces at his disposal,” Garrigues said.
“In the diplomatic field also, the president’s perimeter is considerably restricted,” Garrigues added.

Jordan Bardella, president of the French far-right National Rally party, reacts on stage after partial results in the first round of the early French parliamentary elections in Paris on June 30, 2024. (REUTERS)
Far-right leader Jordan Bardella, who could becomes prime minister if his party wins the majority of the seats, said he intends “to be a cohabitation prime minister who is respectful of the Constitution and of the President of the Republic’s role but uncompromising about the policies we will implement.”
Bardella said that if he were to become prime minister, he would oppose sending French troops to Ukraine — a possibility Macron has not ruled out. Bardella also said he would refuse French deliveries of long-range missiles and other weaponry capable of striking targets within Russia itself.
What happens if there’s no majority?
The president can name a prime minister from the parliamentary group with the most seats at the National Assembly — this was the case of Macron’s own centrist alliance since 2022.
Yet the National Rally already said it would reject such an option, because it would mean a far-right government could soon be overthrown through a no-confidence vote if other political parties join together.
The president could try to build a broad coalition from the left to the right, an option that sounds unlikely, given the political divergences.
Prime Minister Gabriel Attal hoped Sunday to be able to have enough centrist lawmakers to build “a majority of projects and ideas” with other “Republican forces,” which may include those from the center-left and the center-right.

French Prime Minister Gabriel Attal delivers a speech in the courtyard of the Prime Minister’s residence in Paris on June 30, 2024. (AP)
Experts say another complex option would be to appoint “a government of experts” unaffiliated with political parties but which would still need to be accepted by a majority at the National Assembly. Such a government would likely deal mostly with day-to-day affairs rather than implementing major reforms.
If political talks take too long amid summer holidays and the July 26-Aug. 11 Olympics in Paris, Garrigues said a “transition period” is not ruled out, during which Macron’s centrist government would “still be in charge of current affairs,” pending further decisions.
“Whatever the National Assembly looks like, it seems that the Constitution of the 5th Republic is flexible enough to survive these complex circumstances,” Melody Mock-Gruet, a public law expert teaching at Sciences Po Paris, said in a written note. “Institutions are more solid than they appear, even when faced with this experimental exercise.”
“Yet there remains another unknown in the equation: the population’s ability to accept the situation,” Mock-Gruet wrote.