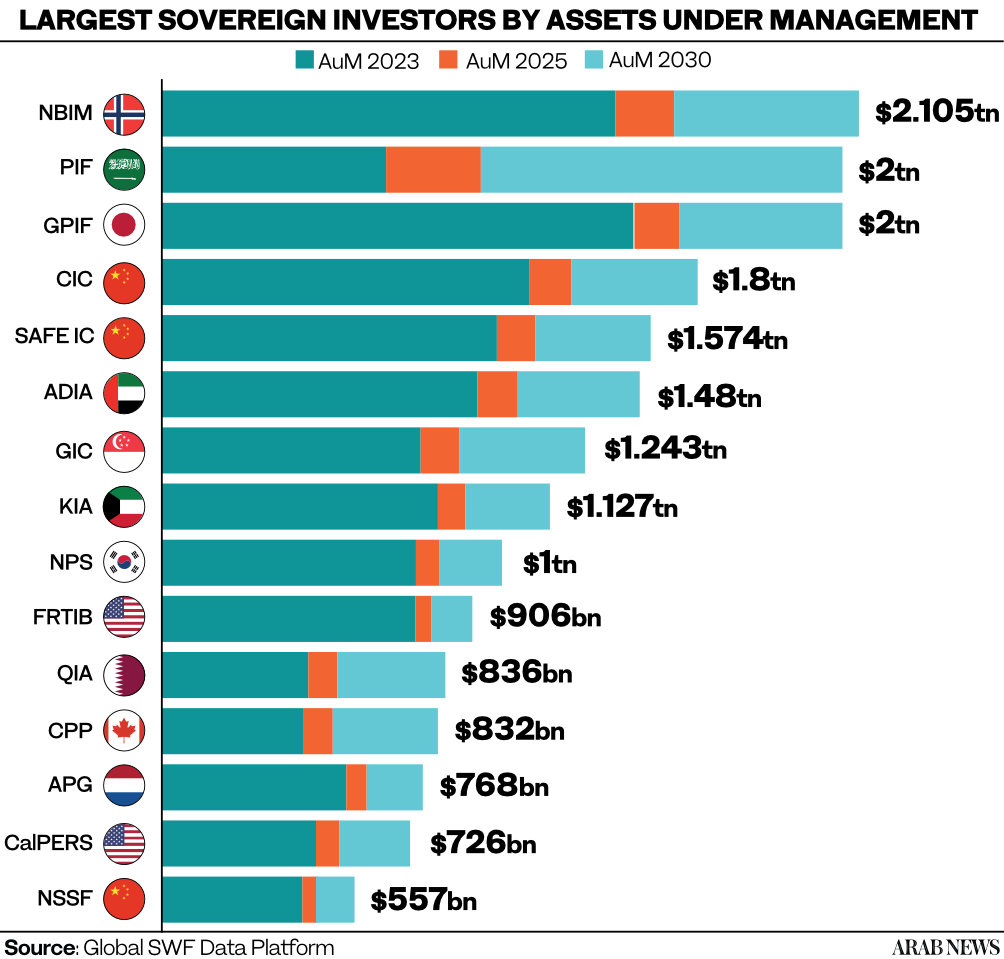
RIYADH: Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund is poised to reach $2 trillion in assets under management by 2030, propelling it from 5th to 2nd place globally among sovereign wealth bodies, according to Global SWF.
The organization that monitors activity in this area stated that PIF’s rapid ascent can be attributed to the fund’s focus on direct investments, emphasis on key sectors of the Saudi economy, dedication to sustainability through leading investments in renewables and green assets, and active participation in the digital economy.
The institute’s 2024 annual report disclosed that in 2023, PIF took the lead as the top investor among all sovereign wealth funds, allocating $31.6 billion across 49 deals – a 33 percent increase from the prior year.
This progress elevated the fund by 10 positions between global sovereign investors in new capital deployed within a mere three years.
In just eight years since its restructuring, the Saudi fund has become a dominant force both domestically and internationally, with the aim of advancing Vision 2030 and achieving the status of the world’s largest sovereign wealth fund by the end of the decade.
In March 2024, PIF’s assets under management surpassed $925 billion, up from $700 billion at the end of 2022, securing its position as the fifth largest global sovereign wealth fund, after the government transferred an additional 8 percent stake in Aramco to its portfolio.
The fund strategically delved into co-investments and forged joint ventures to bolster Saudi Arabia’s drive for economic diversification.
Noteworthy examples include partnerships with mining giant Ma’aden, tire makers Pirelli, and car manufacturer Hyundai.
This was alongside an agreement with Baosteel and Aramco for the construction of a steel mill.
The report highlighted that unlike numerous sovereign wealth funds that frequently choose co-investing as their primary strategy, both globally and in the Gulf region, PIF stands out with a strong preference for direct investments in private equity.
Specifically, it targets critical sectors of the Saudi economy, including sports and leisure, tourism, and gaming, as well as construction, and heavy industry.
Despite the clear advantages that co-investing offers – such as enhanced due diligence, favorable fee terms, and portfolio diversification – some sovereign investors may shy away due to concerns about deal visibility and relinquishing transaction control to other government funds.
According to the report, PIF stood out from other funds due to its substantial domestic investments, which significantly impacted its international investment capacity relative to other funds.
In 2023, Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund saw an 18 percent growth in its US equities portfolio, driven by rising stock values.
PIF maintained a passive approach, keeping major positions unchanged.
According to the report, its largest holding remained a 63 percent stake in Lucid Motors.
PIF initiated its investment of $1 billion in the electric vehicle rival to Tesla back in 2018, and following Lucid’s initial public offering three years later has continued to infuse capital into the company.
This included an injection of $2 billion in June 2023, and Lucid is on course to commence EV production in Saudi Arabia by 2025.
PIF’s US-listed portfolio includes $8.1 billion in gaming companies such as Activision Blizzard, Electronic Arts, and Take-Two, reflecting the Kingdom’s plan to invest $38 billion to become a hub for this sector as part of Vision 2030.
In its report, Global SWF discussed the challenges encountered by sovereign investors in recent years and the corresponding solutions they implemented in 2023 to enhance the resilience of their portfolios.
One significant challenge involved addressing the decarbonization of the global economy. This was tackled through the introduction of a new sustainable investment strategy, shedding light on “climate alpha.” This typically refers to investments or strategies that aim to address global warming and its associated risks and opportunities.
This could include investments in companies or projects that are focused on renewable energy and efficiency, sustainable agriculture, clean transportation, and other environmentally friendly initiatives.
Sovereign investors showcased their dedication to sustainability during COP28, highlighted by the UAE’s launch of a $30 billion climate-focused fund, supported by BlackRock and fellow state-backed wealth funds. The goal is to access these areas while also greening existing black assets through de-carbonization.
Meanwhile, Saudi Arabia has taken a leading role in direct investments within the EV and automotive sectors. As well as its stake in Lucid, the Kingdom launched its own EV carmaker, Ceer, in a joint venture with Taiwan’s Foxconn.
Further partnerships include collaborations with Tasaru for component localization, Hyundai for a car plant, and Pirelli for tire manufacturing.
According to Global SWF, sovereign investors directed a record $26.1 billion towards green assets in 2023, prioritizing investments in the energy transition, including renewables, battery storage, and EVs.
Gulf sovereign wealth funds contributed nearly half of this sum, leading the charge in driving the energy transition agenda.
The report also underscored another challenge encountered by sovereign funds, which is market volatility and the risks stemming from geo-economic fragmentation.
To tackle this issue, fund investors have embraced a more comprehensive total portfolio strategy. This strategy integrates alpha and beta return drivers, merging top-down and bottom-up analyses, with a significant emphasis on diversification.
By adopting this holistic approach, investors gain a thorough understanding of their investments, facilitating more informed decision-making, enhanced risk management, and the opportunity to optimize portfolio performance by focusing on the unique attributes and dynamics of each component within the portfolio.
The rise of disruptive artificial intelligence was also addressed in the report, which noted it represents a significant risk for sovereign investors as it can lead to rapid changes in industries, markets, and investment landscapes.
AI-powered technologies can impact traditional business models, alter consumer behavior, and introduce new competitive dynamics. To address this challenge, one proposed solution by sovereign investors is to integrate AI-powered portfolios into their investment strategies.
By incorporating AI technologies into portfolio management, sovereign funds can leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to gain valuable insights.
AI-powered portfolios can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying trends, patterns, and market signals that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts. This can lead to more accurate risk assessments, better market timing, and enhanced investment decision-making.
Additionally, AI can enable sovereign investors to automate certain aspects of portfolio management, such as rebalancing, trade execution, and risk monitoring. This not only increases operational efficiency but also allows for more agile responses to changing market conditions.
According to the report, 2023 saw sovereign wealth funds adjusting their real estate investments amidst concerns of global interest rate hikes and a potential property bubble.
Despite an overall softening in the market, some segments, such as data centers and affordable housing, saw growth as fund investors aligned with emerging megatrends. Data center investments surged by 150 percent to $7.6 billion in 2023, indicating a strong focus on future-oriented assets.
This shift reflects a move from traditional investments to a more sophisticated strategy, exemplified by PIF’s forming partnerships to develop data centers.
The report flagged up that in 2023, the GCC region – led by the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority, Abu Dhabi’s Mubadala, ADQ, PIF, and the Qatar Investment Authority – saw a record surge in sovereign capital to $4.1 trillion in assets under management, with transactions totaling $82.3 billion.
Projections indicate these sovereign wealth funds could reach $7.6 trillion in assets by 2030. This growth, according to the report, is fueled by high oil prices and a maturing investment landscape, driving economic diversification with growth forecasts of 3.6 percent and 3.7 percent for GCC nations in 2024 and 2025.
In this region, two distinctive sovereign wealth fund management approaches were highlighted by Global SWF.
Abu Dhabi’s strategy involves the establishment of multiple SWFs, each with specific missions overseen by different royals. Saudi Arabia, on the other hand, centralizes its investment and strategic efforts under PIF, aligned with the government’s overarching vision.
Further, its leaders have no problems in announcing grand plans for the fund, using it in its name to buy football clubs or golf leagues, and in sharing its finances publicly given its fundraising efforts, in a rather refreshing fashion, the report said.
The institute presented updated projections in the State-Owned Investors 2030 section, factoring in the industry’s recovery in assets under management in 2023.
It anticipates that public pension funds and central banks will reach $54.9 trillion by 2025 and $71 trillion by 2030. By then, Norway’s Norges Bank Investment Management, Saudi’s PIF, and Japan’s Government Pension Investment Fund could lead the table with over $2 trillion in assets under management each.














