CHIANG MAI, Thailand: Thai tourist hotspot Chiang Mai was blanketed by hazy smog Friday, as residents and visitors to the usually picturesque northern city were left wheezing in the toxic air.
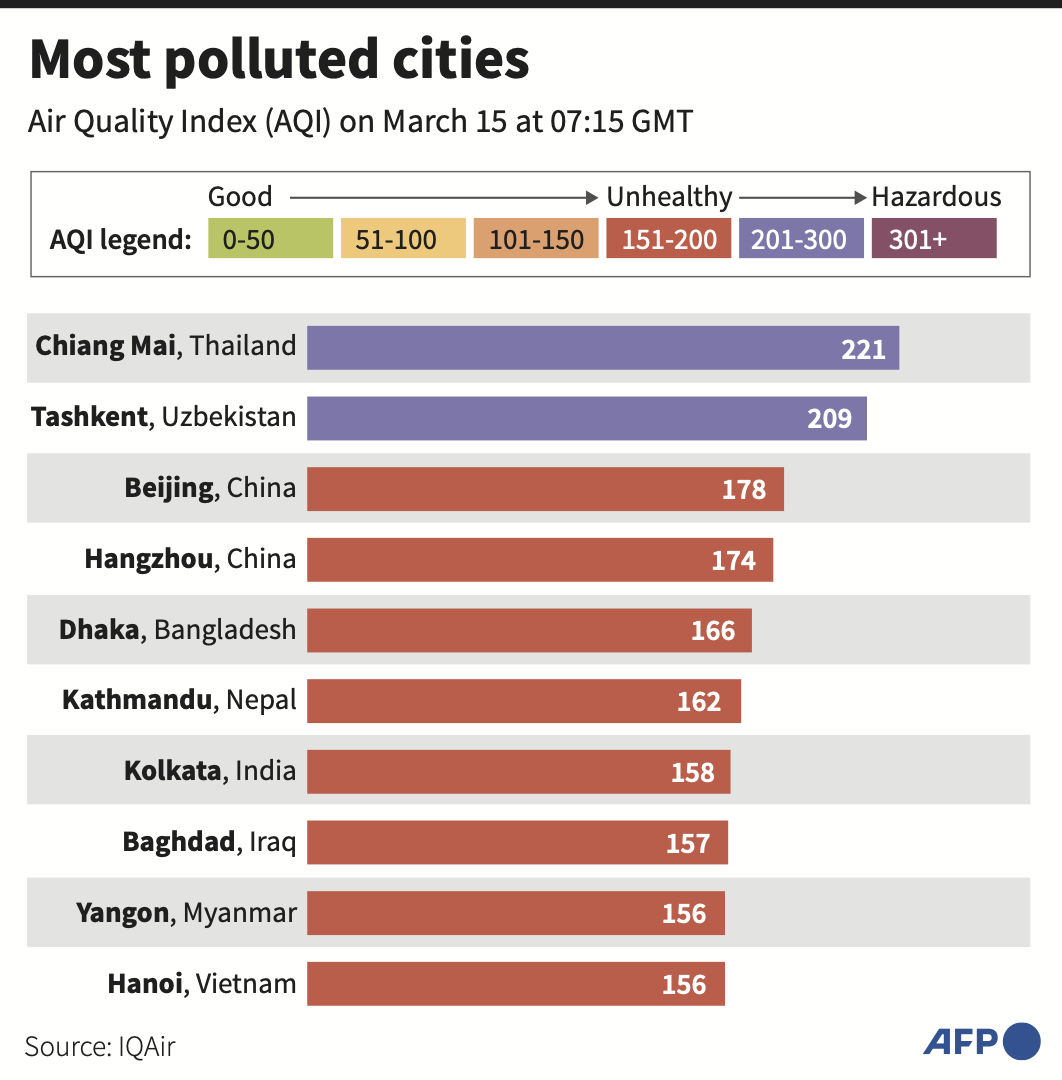
The country's second largest city topped air monitoring website IQAir’s table of the world’s most polluted cities early Friday.
Levels of PM2.5 pollutants — cancer-causing microparticles small enough to enter the bloodstream through the lungs — were classified as “very unhealthy” and hit more than 35 times the World Health Organization’s annual guideline.
“It’s very high. All I have is this mask which is the same one I used for Covid,” orange seller Kamol, 62, told AFP at the city’s Warorot Market.
Thailand’s former prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra, who was recently freed early from a jail sentence for graft and abuse of power following 15 years in self-exile, visited the market on Friday, donning a face mask while he posed for photos with well-wishers.
High levels of pollution frequently hit Thaksin’s hometown of Chiang Mai during the early months of the year when farmers often burn crops to clear land, and forest fires and exhaust fumes also add to the problem.
Rising awareness of the health implications has prompted some action from the government, with Prime Minister Srettha Thavisin’s cabinet approving a Clean Air Act to tackle the issue in January.
The premier is also due to visit later Friday and is expected to meet with organizations tackling forest fires on Saturday.
But Chiang Mai residents — like orange seller Kamol, who sighed and shook his head when asked — said they had received no help.
“I need to get my health checked every year, especially for respiratory diseases,” he said.
A government agency warned this month that more official action was needed, saying at least 10 million people required treatment for pollution-related health problems last year.
“The pollution is always high, especially this time of year,” said 50-year-old Sariya while shopping for groceries in Chiang Mai.
“There is nothing we can do about it since it’s always high.”
Sariya, who gave only one name, also said the city’s location — nestled between hills, trapping the toxic smog — made the situation worse.
But he was “more worried” about people living there with underlying health issues, adding: “We need to help ourselves.”
Last year, sky-rocketing levels of pollution saw international tourists discouraged from visiting, with vendors despairing for business, as the Thai Hotel Association Northern Chapter also warned domestic visitors were canceling bookings.
But in Chiang Mai on Friday, the streets were filled with ambling tourists who seemed unperturbed by the smog.
“I’m not afraid of the pollution,” said 32-year-old Chinese tourist Andy, visiting from Chengdu, who said his country also suffered from poor air pollution.
“I just enjoy the city because it’s very nice.”
French programmer Guillaume Tieufri, 44, said the pollution had not spoilt his four-day trip.
“You just have to go on and live your day.”


















