RIYADH: In a bid to attract global talent and diversify its economy away from oil, Saudi Arabia has added five new products to its premium residency program.
The program, launched in 2019, aims to allow eligible foreigners to live in the Kingdom and receive benefits such as exemption from paying expat and dependents fees, visa-free international travel, and the right to own real estate and run a business without requiring a sponsor.
The initiative aims to further boost the country’s ongoing economic transformation by creating employment opportunities and fostering transfer of knowledge, the Saudi Press Agency reported.
Specific requirements
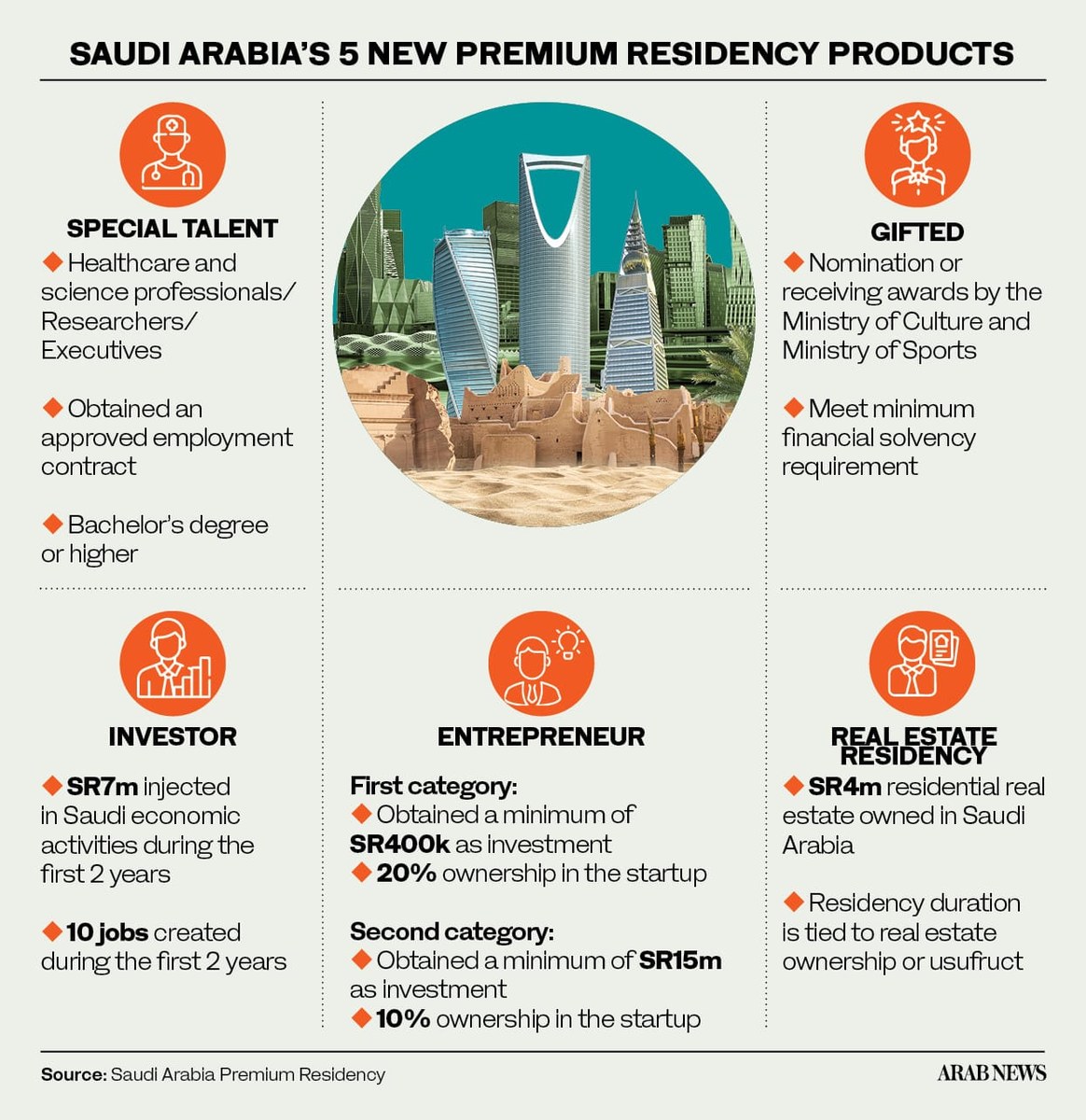
Residency products, each with its own specific qualification requirements, will run under categories such as special talent, gifted, investor, entrepreneur, and real estate owner. A one-off application fee for each category has been set at SR4,000 ($1,066).
“With the introduction of these five new premium residency products, we are opening doors to a world of opportunities for professionals and investors. Our aim is to contribute to Saudi Arabia’s effort as a prime destination for talents and investments, contributing significantly to our vision of a diversified, knowledge-based economy,” Mohammad Al-Sultan, CEO of the Premium Residency Center, told Arab News.
“Collaboration with our strategic partners across various government entities has been key in developing these residency products. We offer well-designed products beyond basic benefits, providing a holistic environment for our premium residents to live, work, and contribute to Saudi’s vibrant future,” the top official said.
He was also quoted as saying in a section of the local press that: “We’ve restructured family members’ eligibility for premium residency holders, now including parents as dependents. This change is part of our ongoing efforts to enhance the residency program.”
Benefits
The permit holders will now be able to obtain premium residency status for their family members, run businesses, make money transfers free of charge, and host and invite relatives.
“While each premium residency category has its specific validity period, all holders are required to adhere to the stipulated terms and conditions,” the official said.
In most cases, general application requirements will apply, including the need to hold a valid passport, have a recent medical certificate, and possess legal residency in Saudi Arabia (for those applying within the country).
“We’ve also extended the age limit for dependents to 25 years,” Al-Sultan told Al-Ekhbariya in an interview.
Investor
The investor option will offer direct permanent residency to those investing SR7 million and creating at least 10 jobs during the first two years. Those applying will be issued an investment license, and they must also provide a commercial register and articles of incorporation.
Edgard Tawk, CEO and co-founder of Eurisko, a multinational digital innovation firm, said these “offerings bring exciting opportunities for investors like us. Not only can we establish a corporate presence in Saudi Arabia, but we can also designate it as our strategic headquarters.”
He said with these added perks, the investor residency option “is poised to become a highly sought-after attraction for both regional and international investors.”
Commenting on the report, George Haddad, founder and creative producer at Saudi-based Yellowcore Productions, said: “As a film and TVC producer, the new premium residency options in Saudi Arabia offer the potential for easier access to a growing market, opportunities for business expansion, and the ability to capitalize on the country’s economic growth.”
Haddad was optimistic about the impact of these new policies on the overall growth of his sector. “You may find it easier to establish and expand your production activities, access talent and resources, and explore regional and international business opportunities in the film and TVC industry.”
Entrepreneur residency
This class will allow applicants to nominate two members of staff for special talent status.
Category-1 entrepreneur residency will provide a fixed-term five years renewable for one additional term (subject to meeting ongoing eligibility standards and living in the Kingdom for a minimum of 30 months within the five years). Applicants must have obtained a minimum SR400,000 investment from an accredited organization and hold at least a 20 percent share of the startup.
“Reflecting our commitment, a key criterion for the business investor residency is the provision of employment opportunities for Saudi citizens,” Al-Sultan noted.
The second category will grant permanent residency directly on the condition that the entrepreneur creates at least 10 jobs in the first year and 10 or more jobs in the second year. To qualify, a minimum SR15 million investment will need to be shown alongside proof of a 10 percent share in the business venture.
Real estate ownership
This residency plan will be tied to property ownership or usufruct. Criteria will include owning a real estate asset worth a minimum of SR4 million that is free of existing and future mortgages. Property ownership or usage must not be linked with real estate financing, real estate owned must be residential, developed, and not from undeveloped or unimproved land, and lastly, the property asset must be appraised by accredited valuers from the Kingdom’s Taqeem authority.
“We welcome applications from all nationalities. Our aim is to address the skills gaps in different sectors, so candidates meeting our requirements and objectives are encouraged to apply,” the CEO of the Premium Residency Center said.
Initially, Saudi Arabia launched a one-year limited-duration residency program with an annual fee of SR100,000 and the requirement to prove financial solvency. Meanwhile, unlimited-duration residency costs SR800,000 for permanent residency, again with proof of an applicant’s financial health.
“Saudi Arabia is not just a place to work and invest, but a land of opportunities where innovation, culture, and business thrive together. These new premium residency products serves as our invitation to the world to join us in our journey of transformation and growth,” Al-Sultan told Arab News.
Special talent
To gain the five-year special talent residency option, applicants must be professionals specializing in healthcare and science and earning at least a monthly SR35,000, or researchers with a minimum monthly salary of SR14,000.
Executives seeking special talent status will be required to have an executive-level employment contract, with monthly pay in excess of SR80,000.
“These new residencies are more than just permits; they are a commitment to shaping our nation’s future. By attracting special talents, entrepreneurs, and investors, we are not only boosting our economy but also enriching our cultural and scientific landscape, ” the top official of the Premium Residency Center said.
Gifted residency
This category will cover a fixed-term period of five years and be split into two categories. In the first case, applicants will need to be nominated or be a recipient of an award approved by the Saudi ministries of culture and sports. Alternatively, they must fulfill the minimum eligibility criteria approved by the two ministries.
Todd Albert Nims, a US national born in Saudi Arabia, was excited over the news. Talking to Arab News, he said: “Saudi Arabia is in my heart. It gave me so much (while I was) growing up. As a creative professional in film, theater and the arts, I am humbled to have had the good fortune to give back by helping to grow these sectors in the Kingdom after coming back from the US.”
Mohsin Ali Khan, a financial controller at a cloud gaming company in Riyadh, also expressed similar views. He said the introduction of the five new premium residency options marks a significant development in the Kingdom. He highlighted that the potential influx of specialized talent could have a positive impact on research and development initiatives in the country.














