RIYADH: In February the Jameel Arts & Health Lab was established to show how the arts have the power to help tackle climate change and the global health crisis.
From Dec. 1-3, the lab presented COP28 Healing Arts Week, a platform to promote the role of the arts at the intersection of health and climate. Included was a high-level panel in the COP28 Green Zone titled “Arts, Health and Climate” moderated by Princess Mashael Saud Al-Shalan, co-founder of Aeon Collective.
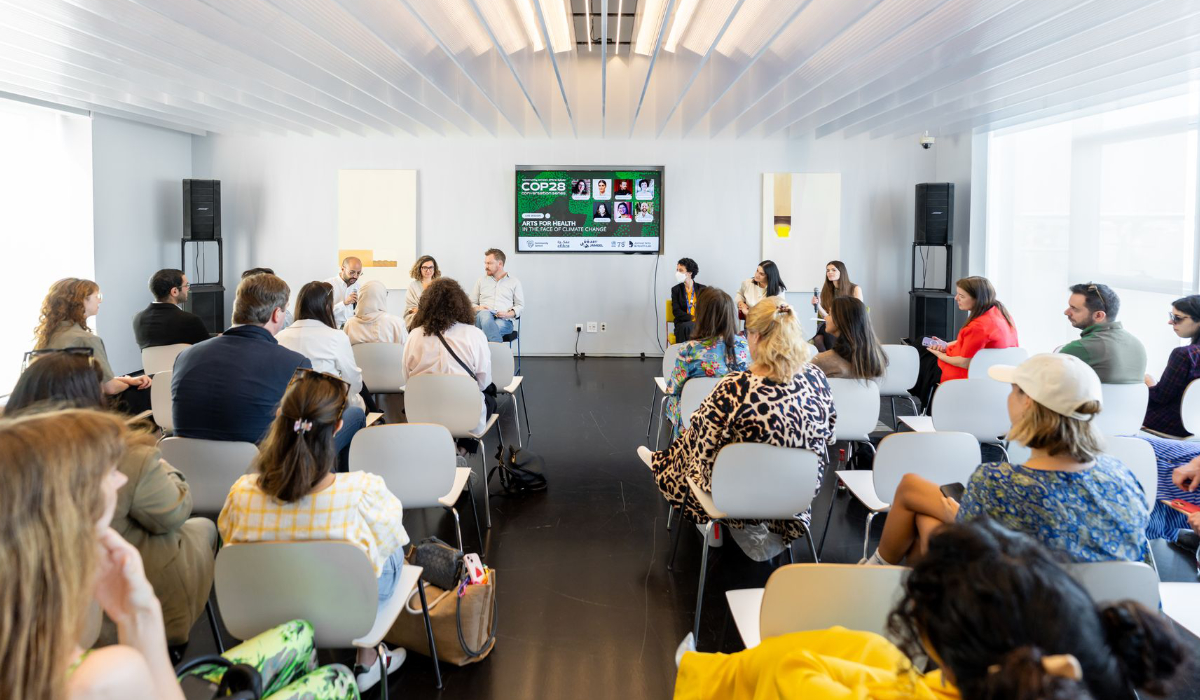

The lab aims to show more evidence regarding the relationship between arts, health and climate change, especially in displaced populations. (Supplied)
A panel on “Safeguarding Our Planet: Biodiversity, Climate and One Health” was held at the Saudi Pavilion in the Blue Zone featuring Princess Mashael; Prince Sultan bin Fahad, chairman of the Saudi Water Sports and Diving Federation; Princess Hala bint Khaled, president of the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation; Raquel Peixoto, associate professor of microbiology at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology; Richard Bush, chief environment officer at NEOM; Christopher Bailey, founding Co-Director of Jameel Arts & Health Lab; and Catherine Cone environment and sustainability director at the Royal Commission for AlUla.
“The climate crisis is a health crisis,” stated Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, director general of the World Health Organization. “The arts can be a powerful ally in our quest to improve health for all.
HIGHLIGHTS
• Jameel Arts & Health Lab is the first major arts and health initiative in World Health Organization’s history.
• It was established as a result of agreements between the WHO, the Steinhardt School at New York University, Community Jameel and Culturunners.
• For more information about the lab’s work, check jameelartshealthlab.org.
“I have seen the impact of the arts on community well-being, and I’m very pleased that this collaboration (with the Jameel Arts & Health Lab) will help us understand the science of that impact in order to improve the lives of people from all backgrounds.”
The Jameel Arts & Health Lab is the first major arts and health initiative in the WHO’s history.

Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, World Health Organization director general
“We are interested in connecting the arts and health with climate change because obviously the climate crisis is a health crisis. There’s no doubt that now the question is to understand whether or not the arts might be able to offer answers to these crises,” Clea Daridan, senior curator and culture lead at Community Jameel, told Arab News. “At COP28 we were trying to explore how the intersection between arts, health and climate change from a research and a policy perspective because it is through the implementation of policy that change can happen.”
I have seen the impact of the arts on community well-being ... this collaboration (with the Jameel Arts & Health Lab) will help us understand the science of that impact in order to improve the lives of people from all backgrounds.
Tedros Adhanom, Ghebreyesus World Health Organization director general
The lab focuses on overlooked and underserved communities. It was established as a result of agreements between the WHO, the Steinhardt School at New York University, Community Jameel and Culturunners.
According to its website, the lab “will coordinate and amplify scientific research into the effectiveness of the arts in improving health and wellbeing” by “leveraging data, artist-led advocacy and a global ‘Healing Arts’ campaign that aims to drive policy implementation across 193 UN member states.”

Clea Daridan, Community Jameel senior curator and culture lead
Stephen Stapleton, co-director of the lab and CEO of Culturunners, told Arab News: “The Jameel Arts & Health Lab has been at COP advocating for the important role of the arts in telling the story of the climate crisis as a health crisis.
There’s no doubt that now the question is to understand whether or not the arts might be able to offer answers to these crises.
Clea Daridan, Community Jameel senior curator and culture lead
“In so doing to inspire the behavioral change, on both a personal and societal level, which is so urgently needed … through arts therapies and self-expression, the arts can also help those most vulnerable to cope with the psychological impact of the perceived and real changes which are already affecting millions of people around the world.”
Through the lab’s COP28 Healing Arts Week, Bailey and Stapleton participated in various events at the Jameel Art Center, the Saudi Pavilion, and in the Green Zone.

Stephen Stapleton, Culturunners CEO
The week culminated in an evening with Ghebreyesus, hosted by Community Jameel and the WHO Foundation.
The arts represent a relatively new area in modern healthcare and one that has grown rapidly since the late 1990s. Recent research shows strong evidence for the positive impact of the arts on our health and well-being.
The arts can also help those most vulnerable to cope with the psychological impact of the perceived and real changes which are already affecting millions of people around the world.
Stephen Stapleton, Culturunners CEO
In 2019 the WHO Regional Office for Europe reported how engaging in the arts and creative arts therapies can have wide-ranging positive impacts and health outcomes, including mental and physical health promotion, ill health prevention, and the management and treatment of health conditions and symptoms.
Other research has demonstrated the benefits of general as well as targeted arts-based interventions for different populations, including community-based museum programs for people living with dementia, community dance classes for those living with Parkinson’s disease, music therapy to reduce stress and drama therapy to support the social and emotional skills of children and young people, among other examples.
The lab aims to show more evidence regarding the relationship between arts, health and climate change, especially in displaced populations. (Supplied)
Additionally, a 2022 report by the CultureForHealth project demonstrated how the arts can help to address specific public health challenges, including the need to support the health and well-being of young people, health disparities, and the mental health challenges faced by forcibly displaced people.
“Through the Jameel Arts & Health Lab we are generating data and rigorous studies to prove the effectiveness of the arts on health and well-being,” added Daridan. “It is by leveraging this data that we will be able to drive policy implementation across the 193 UN member countries. Now, when it comes specifically to the link between arts, health and climate change, this is also a specific area of research that the lab is currently conducting.”
This year, the lab partnered with the Lancet, a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, one of the oldest of its kind, to lead a global series on the health benefits of the arts with a focus on non-communicable diseases, the leading cause of death and disability worldwide. The outcomes will be published in early 2025.
Daridan added that the lab was working on a report, likely published in the first quarter of 2024, to show more evidence regarding the relationship between arts, health and climate change, especially when it comes to displaced populations.
For more information about the lab’s work, check jameelartshealthlab.org.

















