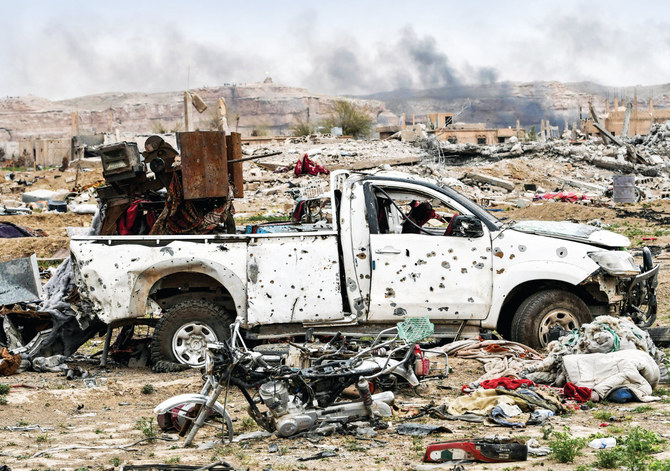
QAMISHLI, Syria: During the second week of August, the terror group Daesh carried out multiple attacks on Syrian regime soldiers in the governorates of Raqqa and Deir Ezzor, leaving dozens dead and more injured.
With attacks in Syria’s central and eastern regions only continuing to grow in frequency and severity, some may wonder whether the group was truly eliminated when its defeat was announced in 2019.
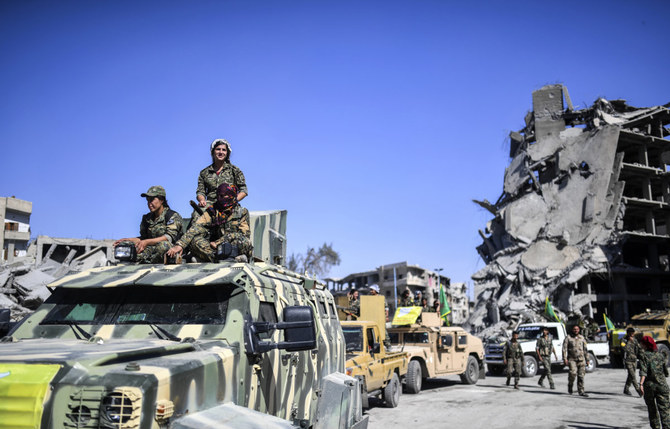
Saturday, March 23, 2019, was a joyous occasion for the men and women of the Syrian Democratic Forces, the multi-ethnic, US-backed force which led the ground war against Daesh in Syria, as well as the people living in the autonomous regions of northern and eastern Syria.
From Manbij to Kobani, from Raqqa to Hasakah and Qamishli, the streets of cities in Syria’s northeast were packed with people from all walks of life celebrating Daesh’s final defeat at the Battle of Baghouz.
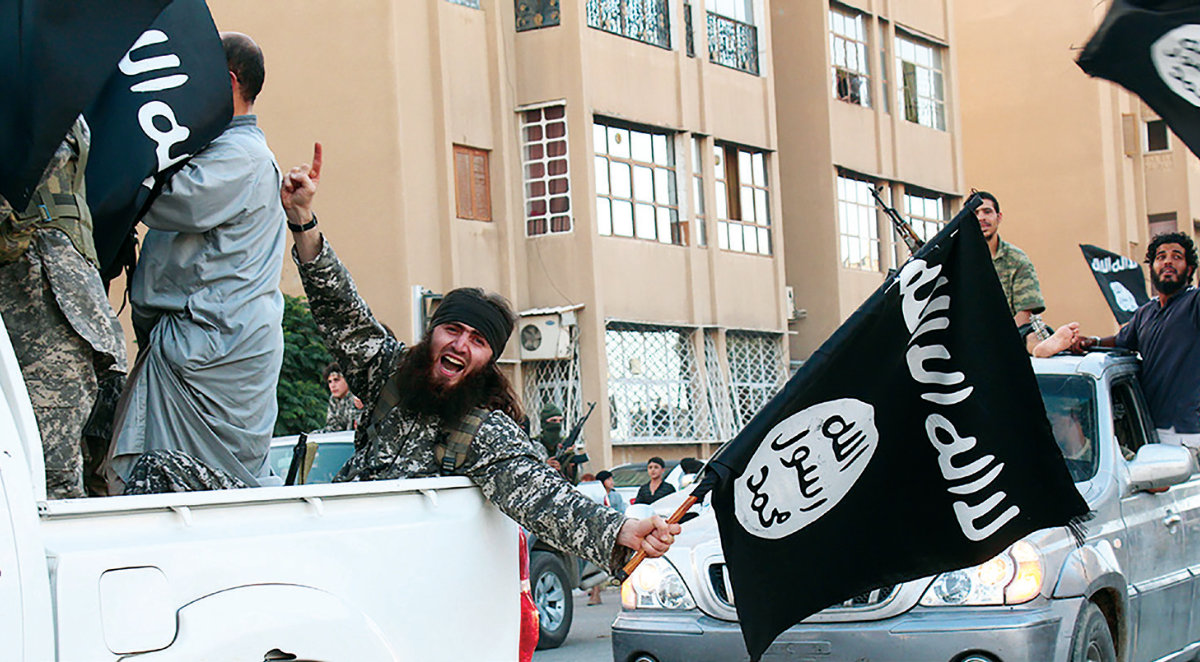

File photo shows Daesh militants parading in the Syrian city of Raqa on June 30, 2014, at the height of their reign of terror in parts of Syria and Iraq. (Welayat Raqa handout photo via AFP)
Little did they know that despite the group’s loss of territory, it would go on to maintain bases both inside and outside of the country, which it still uses to carry out operations in Syria.
“(Daesh) uses different frameworks for the continuation of its extremist ideology,” Sardar Mullah Darwish, a Syrian Kurdish journalist and director of Aso News Network, told Arab News.
The group “relies on cells spread in different areas in the governorates of Raqqa, Deir Ezzor, and southern Hasakah, and particularly in the Badia, where they are in areas that are not fully controlled by the coalition, the SDF, or even the armed forces of the regime and other military forces,” he said.
Darwish added that Daesh sustains itself via financial extortion, threatening wealthy residents and those working with international or local NGOs. He added that the use of motorcycles and the black veil known as the niqab are both ways in which the group attempts to camouflage itself among civilians.
A child stands by a bullet riddled wall in the northern Syrian city of Raqa, the former Syrian capital of the Daesh group, on August 21, 2019. (AFP file)
Daesh carries out attacks on both regime-held areas and regions held by the SDF. According to Darwish, these attacks are attempts “to show continued presence and strength.”
The divided nature of Syria complicates the response.
“What remains of the terrorist group’s remnants in our regions is limited to sleeper cells, and they are dealt with firsthand by our security and military forces in coordination and cooperation with the Global Coalition,” Abu Omar Al-Idlibi, commander of the SDF-aligned Northern Democratic Brigade, told Arab News.
“As for the rest of Syria’s geography, Daesh is still strong because it represents one of the reasons for the survival of the Syrian regime as well as a justification for the presence of its supporters, Russia and Iran.”
Al-Idlibi believes the presence of Daesh is used as a justification for Iran’s increasing military presence in Syria. Iranian-backed pro-regime militias, including the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, Basij Forces, Harakat Hezbollah Al-Nujaba, Kataib Hezbollah (also known as Iraqi Hezbollah), the Badr Organization, the Abu Al-Fadl Al-Abbas militia, the National Defense Forces, Liwa Al-Quds, Liwa Fatemiyoun and Liwa Zeynebiyoun, are all deployed across areas where Daesh remains strongest.
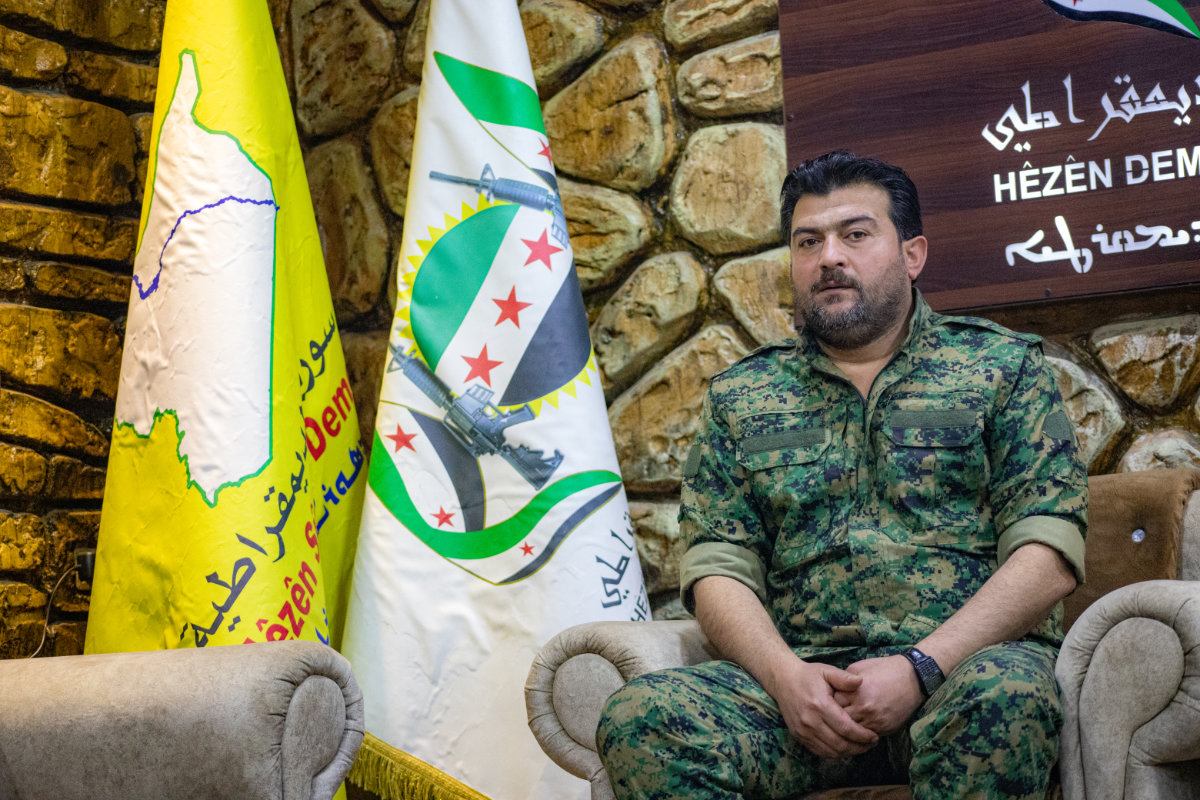

Abu Omar Al-Idlibi, commander of the SDF-aligned Northern Democratic Brigade. (AN Photo by Ali Ali)
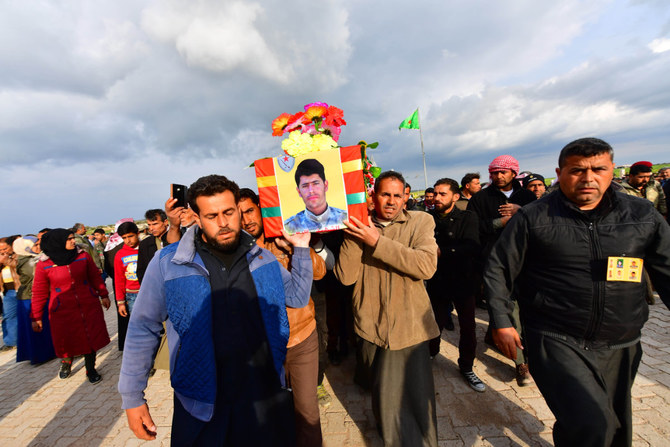
Since its territorial defeat in Syria, Daesh has carried out more than 1,400 attacks on military and civilian targets across the country, resulting in the deaths of more than 3,000 people.
These statistics, sourced from publicly available datasets compiled by the Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project, also show that more than 320 of these attacks were carried out even after the 2022 death of Daesh leader Abu Ibrahim Al-Hashimi Al-Qurayshi, the successor to Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi.
According to the Monitoring and Documentation Department of the local North Press Agency, direct Daesh attacks claimed more than 262 lives across the country in the first half of 2023 alone, the majority of which were civilians.
In addition to this, the terror group kidnapped more than 160 people. A large number of the victims of Daesh attacks and kidnappings were truffle pickers, who resort to scouring vast, unsafe areas of the Syrian Badia in order to gather the lucrative fungi amid difficult economic conditions.
The Syrian Badia is a massive desert, covering more than half of the country’s territory and spanning eight of Syria’s 14 governorates. The region has a history of use by insurgent groups, having been used by the Iraqi resistance during the Iraq War from 2003 to 2011.
The Badia’s geography, a mostly vast and empty expanse of rocky desert with inhabited settlements few and far between, made it ideal for Daesh as a base of operations after its flight from Baghouz.

An image grab taken from a video made available by Jihadist media outlet Welayat Homs on July 4, 2015 shows 25 Syrian government soldiers kneeling in front of what appears to be children or teenagers wearing desert camouflage, in the ancient amphitheater in the city of Palmyra, ahead of being executed. (AFP/Welayat Homs handout photo/File)
The region’s proximity to the Iraqi border further added to its allure.
“This region was well known as an area controlled by smugglers, even before the Syrian war,” said Darwish. “The border crossing between the two countries has large gaps … and there is no control of military forces such as the regime, the SDF, or the Iraqi army, and so Daesh relies on this region for its activities.”
Darwish said Daesh had in recent years dug an extensive network of tunnels in the Iraqi-Syrian border region to aid in its smuggling operations between the two countries.
For the armed forces tasked with responding to the Daesh threat, these tunnels have proved a strategic headache.
“The geographical features of the region between Syria and Iraq have a great impact on the ease of movement by Daesh, especially in the areas under the control of Iran and its militias in Al-Bukamal and Al-Mayadeen, as these border areas are transit points for terrorist organizations and militias between Iraq and Syria,” said Al-Idlibi, the Northern Democratic Brigade commander.
Despite the large network of Iranian-backed, pro-regime militias deployed across central Syria, Al-Idlibi is doubtful that Damascus is serious about confronting Daesh remnants in the Badia.
“Daesh moves freely in the areas of the Syrian Badia … it has not been truly confronted in these areas due to the fact that they are under the control of the Syrian regime and its allies.”
At the end of 2019, Syrian regime forces were withdrawn from the Badia region to focus on Damascus’ new offensive aimed at retaking Idlib from the coalition of Syrian opposition and Islamist groups that held it. Although a ceasefire was declared in Idlib in 2020, the Badia had meanwhile become one of Daesh’s new havens in Syria.
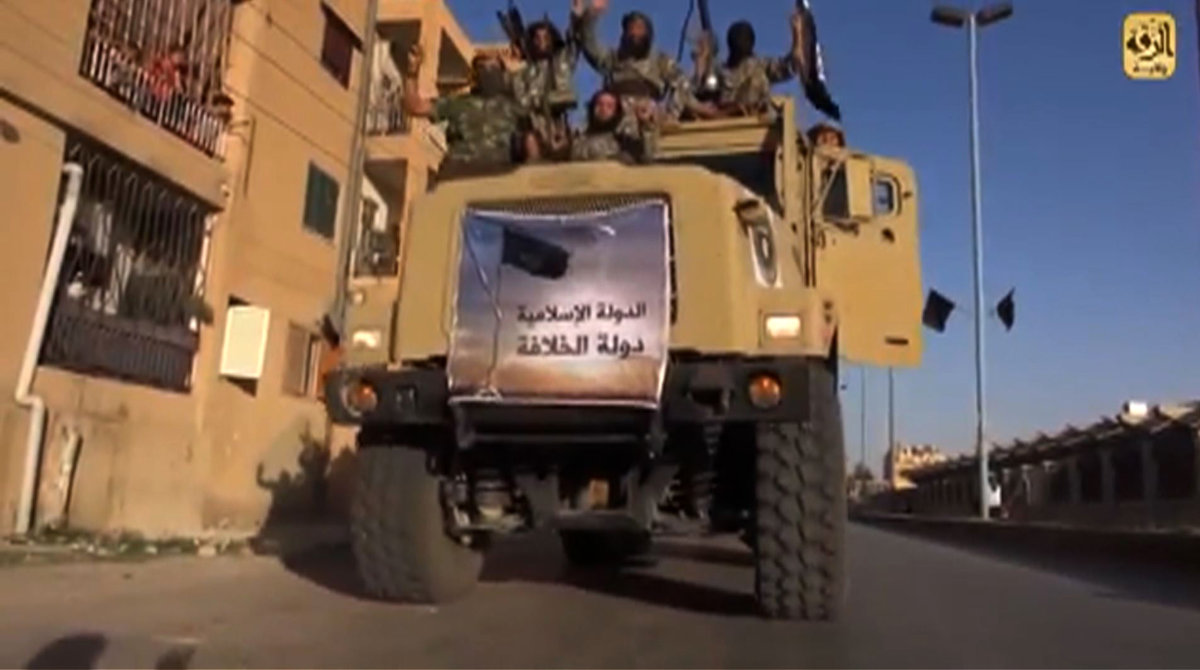

A screen grab taken from a video released on July 1, 2014, shows Daesh militants parading on top of a truck on a street in the northern rebel-held Syrian city of Raqa. (AFP / Welayat Raqa handout/File)
“There are many vast and intertwined regions between the Syrian regime areas and Autonomous Administration (of North and East Syria) areas, with many natural crossings and land, and river routes,” said Al-Idlibi.
“This allows Daesh to move easily in order to infiltrate our areas in northern and eastern Syria … (Daesh) also finds support through sleeper cells present in our regions, and thus we see the terrorist group carrying out operations (here) from time to time.”
Both military personnel on the ground and civilian observers warn that the loosely held regime areas of the Syrian Badia are not the only stronghold for Daesh. Areas in the country’s north and northwest held by a coalition of militias known as the Syrian National Army, or SNA, have also served as a relatively safe area for Daesh militants for years.
“It has become an obvious fact that instability on the social, economic and subsistence level, as well as the spread of armed organizations, extremist ideology, inhumane and criminal practices, and the suppression of freedoms in the occupied areas controlled by the factions of the so-called (Syrian) National Army and terror group Al-Nusra Front, are what provide an incubator and required quagmire for the survival and existence of the leaders and emirs of terrorist organizations, foremost of which is the terror group Daesh,” Al-Idlibi added.
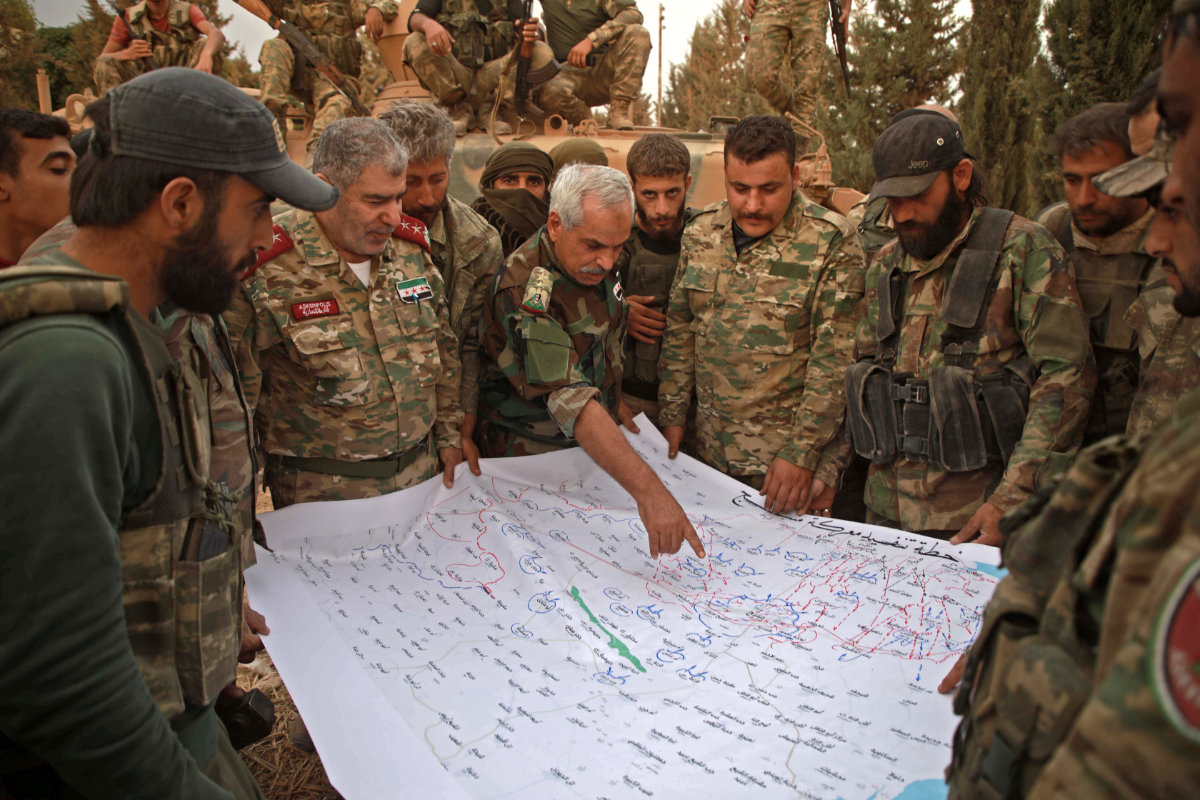

Officials of the Turkiye-backed opposition "Syrian National Army" opposition group led by Brigadier Adnan Ahmad, deputy chief of staff, hold a briefing meeting attended outside the village of al-Ghandurah northwest of Manbij in the north of Syria's Aleppo province on October 16, 2019, near the frontlines with Syrian Kurdish forces. (Aaref Watad/AFP)
Since 2019, coalition forces have carried out more than 13 air and drone strikes targeting Daesh in SNA-controlled areas, the latest of which killed a Daesh commander in a village near Jinderis, in the Afrin region, in April this year.
Furthermore, a 2021 report by Aso News Network compiled a list of 95 Daesh leaders among the ranks of SNA groups.
Darwish said that further research by Aso News Network uncovered information suggesting that the 2022 Daesh prison uprising in Hasakah, which claimed the lives of 121 SDF fighters and civilians, was supported by Daesh elements hiding out in SNA-held Ras Al-Ain.
The research also showed that several Daesh families had managed to escape the infamous Al-Hol camp and settle in Ras Al-Ain and neighboring Tal Abyad.
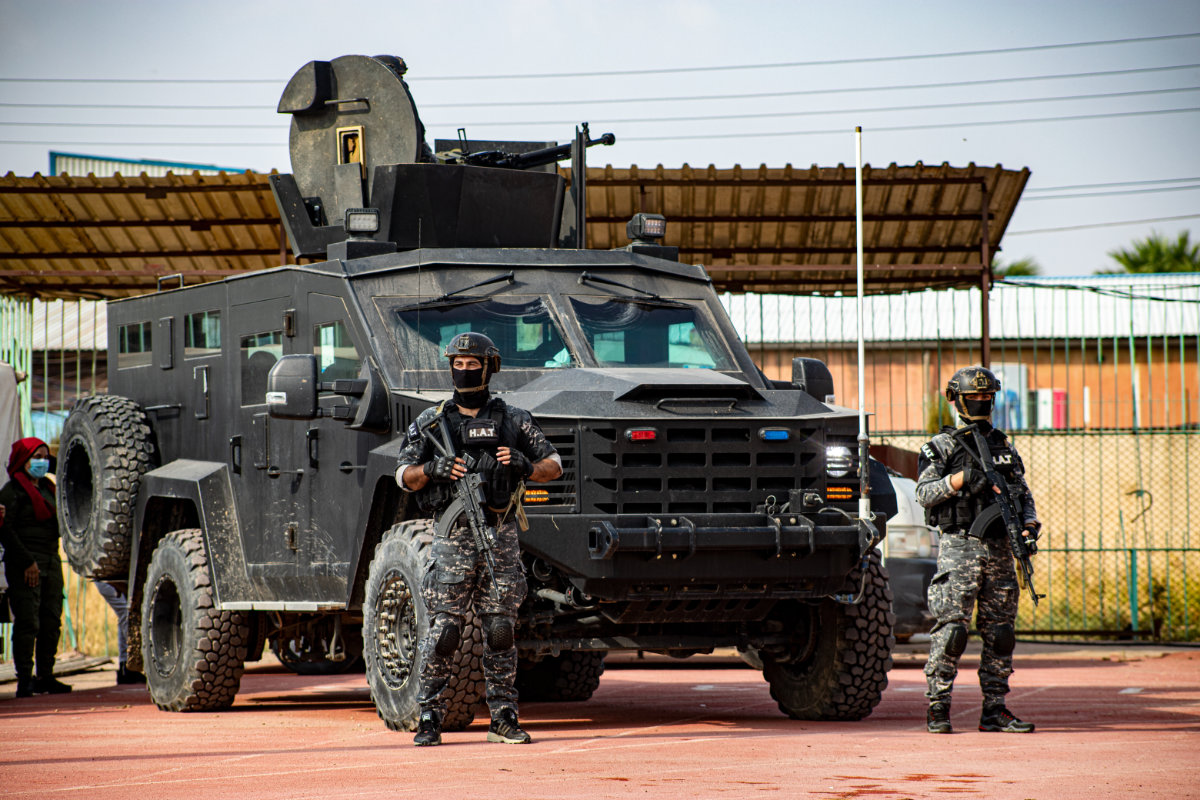

Members of an anti-terror unit of northeast Syria's Internal Security Forces, part of the SDF, are seen at a base in Qamishli. (AN Photo by Ali Ali)
General Michael Kurilla, commander of US Central Command, was in northeast Syria on Wednesday, where he visited the Al-Hol and Al-Roj Displaced Persons Camps and met with SDF officials to review the campaign to eliminate Daesh.
“The US, SDF, and the Global Coalition remain focused and committed on the enduring defeat of Daesh while addressing the humanitarian and security challenges at camps in northeast Syria,” Kurilla said in a statement.
While the SDF and coalition continue to combat terrorism, the solution to the terrorism problem in Syria, says Al-Idlibi, is a political one.
“The real solution to rid Syria of terrorism once and for all lies in the need to implement a political solution in Syria, which was unanimously approved by the (UN) Security Council in 2015 via Resolution 2254,” said Al-Idlibi.
“The application of democracy is the ideal solution to eradicate the sources of extremism and terrorism … because tyranny and terrorism are inseparable and interdependent; they are the reasons for one another’s survival.”





















