RIYADH/NEW DELHI: In an era of increasing global interdependence in a wide range of sectors, from energy supplies to food security, the effects of decisions and events in one country rarely remain limited to that country.
Take the India government’s recent move to impose a 40 percent duty on onion exports in a bid to calm rising domestic prices. The announcement has prompted concern in import-dependent countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council area about securing adequate supplies of the vegetable.
India, the world’s leading onion exporter, said the duty is in the “public interest” and will remain in place until December 31. What this means for GCC countries is that local markets must brace for possible price fluctuations of a staple of the kitchen.
“Since onions are a basic ingredient in cooking, the 40 percent export duty levied by India will add to food inflation in the (Gulf) countries, given the already strained supply chains for wheat and rice,” Anupam Manur, an economist at public policy research and education organization the Takshashila Institution in Bangalore, told Arab News.
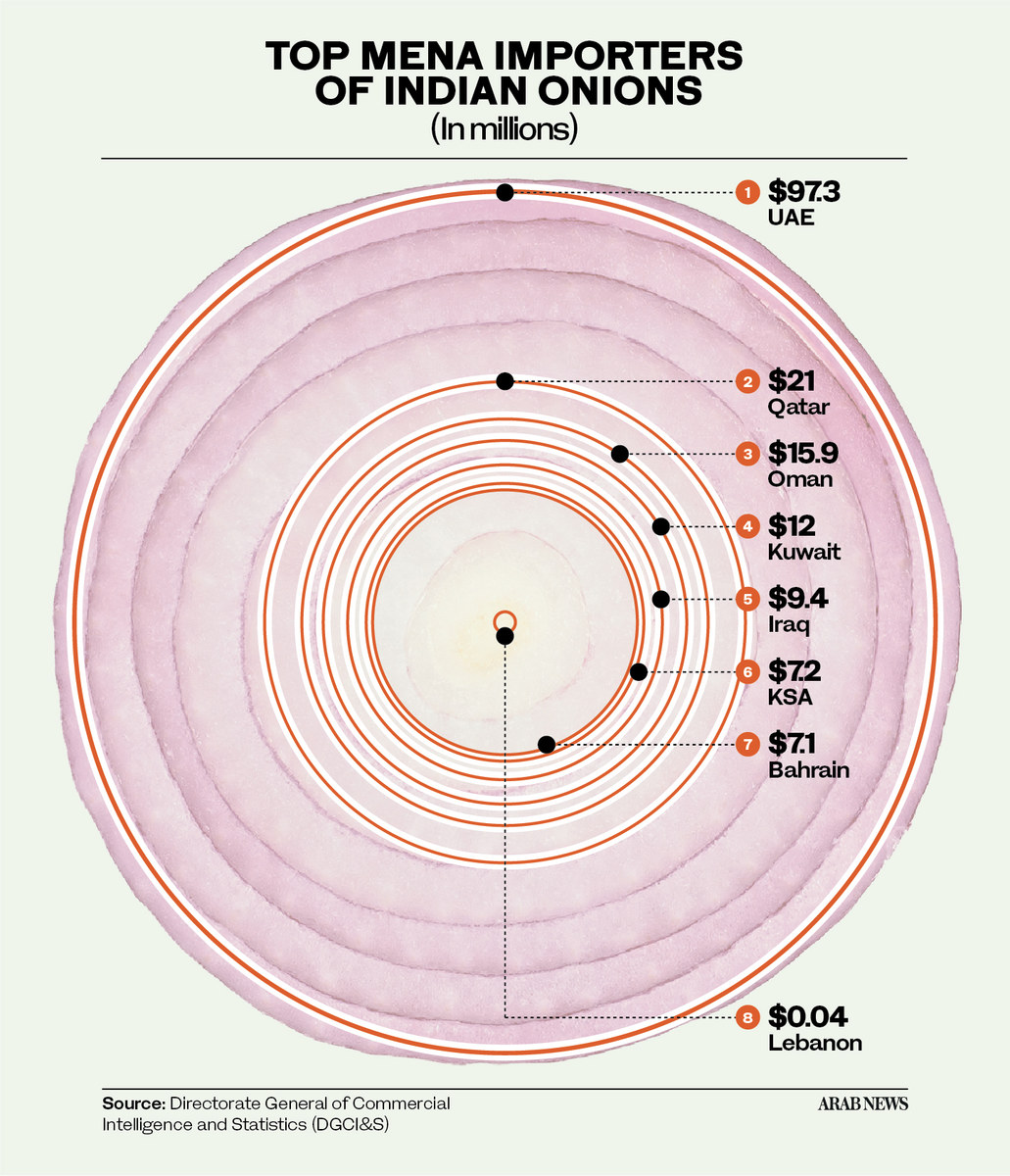
According to the Observatory of Economic Complexity, the UAE imported $41.7 million of onions from India in 2021, which made the country the fourth-largest importer of Indian onions that year.
The volume of Emirati imports of onions from India has been rising in recent years. In 2020, the value of the trade was $34.8 million, up from $27.7 million in 2019. The increase is likely due to the UAE’s growing population and the normally relatively low price of Indian onions.
The imposition of the new export duty could well raise the price of onions across the GCC region and eventually lead to shortages, affecting consumers and businesses. As a result, families accustomed to having onions as a key part of their daily diet might be compelled to adapt their cooking habits.
India said it imposed the duty to boost domestic supplies and thereby bring down rising local prices. “Onion prices had been inching up over the last three weeks,” Pushan Sharma, research director of Mumbai-based CRISIL Market Intelligence and Analytics, told Arab News.
“As per data from India’s Ministry of Consumer Affairs, onion prices on Aug. 19 reached over 30 rupees ($0.36), which is 20 percent higher than last year.”

A vendor cleans and sorts onions at a stall in the market in Bengaluru on April 7, 2023. (AFP)
The effects of a fickle climate on crops have also played a role in the apparent shortages of local supplies.
“High rainfall in July 2023 in key producing regions of Maharashtra and Karnataka damaged the stored onion crop,” said Sharma. “Traders had around 2.5 million tons of onions stored and it is estimated that around 10 to 20 percent of the stock got damaged.
“The rabi season, or winter crop, which produces 70 percent of India’s onion requirement, typically matures in March. However, this year we saw high temperatures in February and unseasonal rainfall in March, which caused early maturity of the rabi crop and reduced the shelf life of this year’s rabi onion crop from six to five months.”
With the rabi crop expected to be depleted by early September, prices have increased further.
“The effect of the price rise will be immediate and will gradually accentuate,” said Manur.
“The news of the export duty will have already reached households and traders, who will put in higher buy orders which, by itself, will lead to a price hike. The price of onions in the market tomorrow would have already factored in a future price rise.”

Pushan Sharma said that high rainfall in July 2023 in key producing regions of Maharashtra and Karnataka damaged the stored onion crop. (AFP/File)
The imposition of a high export duty is not unprecedented. India took similar actions to stabilize the domestic price of wheat by banning exports in 2022, restricting rice shipments in July this year, and lowering import duties on edible cooking oils.
“Sudden supply shortages are not new, especially in the agricultural and food sector,” said Manur. “A recent example is the global wheat shortage when Russia invaded Ukraine.
“Despite the fear, countries around the world coped. Some had to dig into their reserves, while other countries expanded their production to meet the demand. Something similar will happen here as well. Other producing nations will respond to the higher prices and increase their supplies.”
Given that New Delhi has said the export duty will be applied only until the end of this year, the hope is that any price hikes will be temporary.
“The increase in onion prices is expected to be short lived,” said Sharma of CRISIL Market Intelligence and Analytics. “Consumers are expected to bear the brunt of higher prices (in the absence of export curbs) only during the lean period (until the end of September or early October).
“From October onward, when kharif (monsoon or autumn season) and late kharif supplies will come into the market, prices are expected to trickle down to their regular levels.”
However, abrupt changes in export policies could result in importers looking elsewhere for more reliable sources.

The imposition of a high export duty is not unprecedented. India restricted rice shipments in July this year. (AFP)
As far as wider economic relations between India and GCC countries are concerned, “this move is not going to affect trade dynamics because it is only a short-term measure,” Ajeet Kumar Sahoo, assistant professor at the Center for International Trade and Development at Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Delhi, told Arab News.
“I don’t see that onions can impact the balance of payment with other countries. But there is no doubt that the consumers of other countries will be having a limited supply of onions, so that prices of onions will be higher, but that would be for the short term.”
Muddassir Quamar, also an associate professor at Jawaharlal Nehru University, similarly believes trade relations between India and the GCC bloc will continue to grow in strength regardless of the onion crisis.
“In the short term it might increase the food import bill for the GCC countries but might not affect long-term trade relations as food imports fluctuate and are dependent on agricultural production and market-control policies of individual countries,” he told Arab News.
Food security is a concern for Arab countries and so the current situation with onion imports raises important questions about the reliability of supply chains. But any temporary shortage of onions is not expected to cause any major problems.
“This will not have an impact on food security, per se, as onion is a flavoring agent rather than a purely nutritional one,” said Manur. “So, citizens of the GCC may experience blander food but will not see a threat to food security.”

An Indian worker uproots onions at a farm at Vasna Keliya village near Dholka, some 35 kms from Ahmedabad on December 4, 2018. (AFP)
Nevertheless, major importing nations in the Arab world might need to start considering strategies to diversify the sourcing of onions, or even bolster domestic cultivation, to mitigate the possible effects of this vulnerability in future.
“Every country has to take this issue very seriously, especially with the likes of food items, lifesaving drugs, and petroleum products,” said Sahoo.
“They have to find alternatives, otherwise the future will be very difficult. Every country has to have self-sufficiency, especially in food, water and energy.”
Fortunately, the Kingdom and the other GCC countries appear to be doing just that by developing strategies to protect their supply chains from disruption.
“Saudi Arabia has recently initiated a food security authority to deal with such incidents and I expect something similar happening in the rest of the GCC countries,” Talat Hafiz, a Saudi economist and financial analyst, told Arab News.

Talat Hafiz, a Saudi economist and financial analyst.
A number of additional measures could be available for GCC governments to mitigate the effects of the export duty, including subsidies for consumers and widening the global pool of onion suppliers. Simply shifting to other suppliers might not be a viable long-term solution, however.
“It can be expected that the other exporting countries — Pakistan, China and Egypt — will hike their onion export prices in response, given their limited surpluses for exports and the sudden supply gap,” said Manur.
“In the short run, a supply crunch can be expected but increased prices could lead to higher production in the next agricultural cycle.”

















