DUBAI/NEW DELHI: India’s decision to ban the export of several varieties of rice in order to ensure sufficient supplies at home is pushing up prices on the global market, a development whose impact on food-insecure countries is being viewed with concern by experts.
Although the ban does not include the popular basmati variety, which is a staple at Gulf dinner tables, it is triggering an increase in the prices of all rice varieties, adding to the vulnerabilities of import-reliant economies of the Middle East and Africa.
While the Indian restrictions might contribute to food price inflation in the Arab region, economists who specialize in the field of agriculture do not anticipate a rice shortage.
“The impact is not going to be restricted to exporters to the Arab countries, nor rice production levels in the Arab region,” Fadel El-Zubi, lead consultant for the UN Food and Agriculture Organization in Jordan and the agency’s former chief in Iraq, told Arab News.

Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, chief economist at the International Monetary Fund, said last week that the move would increase price volatility and should be reconsidered. (AFP)
“The impact will be seen on global prices in stock exchange markets.”
He said the price increases would not be limited to the cereal coming out of India but would apply to rice produced in other markets too, from the US to Australia.
“This is going to be the main impact. Yet, the increase in prices won’t be similar to the increase in wheat prices. (Also) the increase in rice prices will be for a short term. This is my expectation.”
El-Zubi was referring to the soaring price of wheat on the world market as a result of the war between Russia and Ukraine, which before February 2022 were jointly responsible for almost a third of the world’s wheat and barley production.
Russia’s blockade of Ukraine’s Black Sea ports following its invasion led to fears of grain shortages and spiraling food prices, whose impact would have been felt most by the world’s most food-insecure nations, particularly in Africa.
Last summer, a UN- and Turkiye-brokered deal between Russia and Ukraine allowed both nations to continue exporting grain. But earlier this month, Moscow withdrew from the Black Sea Grain Initiative, renewing fears of food-price inflation.
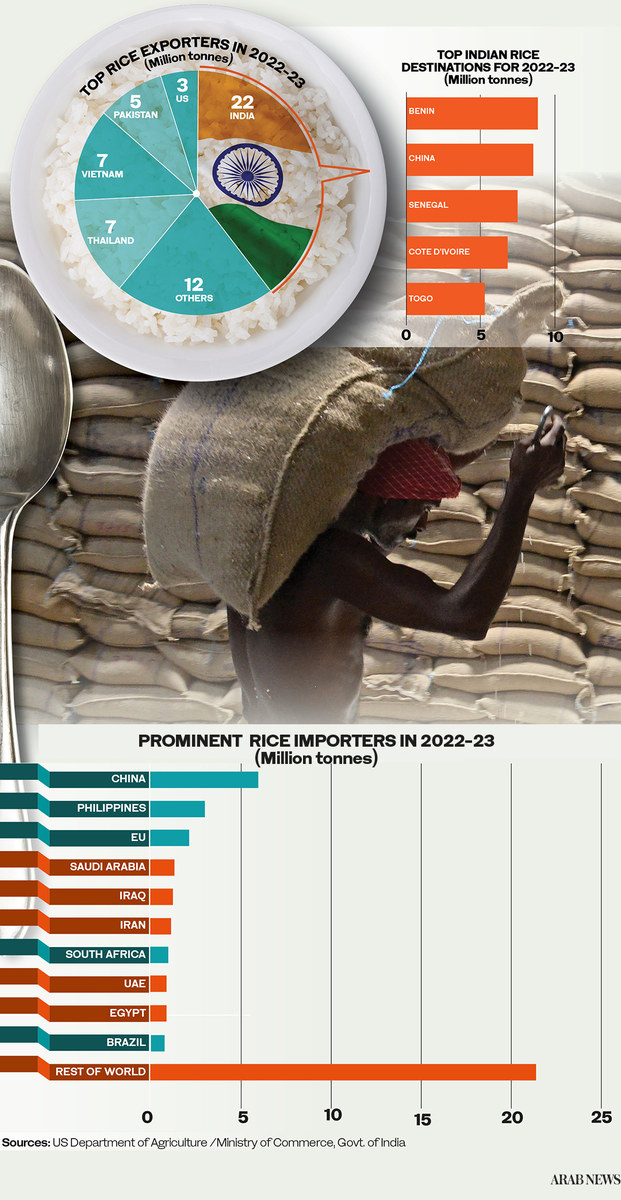
The ban on exports of non-basmati white rice imposed on July 20 by India — the world’s largest supplier of rice, accounting for almost 40 percent of global trade — has added to those fears.
Responding to the Indian decision, Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, chief economist at the International Monetary Fund, said last week that the move would increase price volatility and should be reconsidered.
“In the current environment, these types of restrictions are likely to exacerbate volatility in food prices in the rest of the world and they can also lead to retaliatory measures,” he said.
“We would encourage the removal of these type of export restrictions because they can be harmful globally.”
But Indian food policy analyst Devinder Sharma believes the ban was the correct response to guarantee India’s own food security. He said the IMF was not justified in criticizing India’s market controls when Western nations continued to use vast quantities of grain for making biofuels.
“Despite the threat from the IMF, I think the Indian government has taken the right decision. India’s own domestic food security is of paramount importance,” Sharma told Arab News.
“Regarding the shortfall in the global supply, why don’t you ask America and Europe to cut down on ethanol production? The former consumes 90 million tons of food grain for its ethanol production, while the EU uses 12 million tons. They should stop it.
“India has to take care of its own food security. Imagine, 3 million people died in the 1943 Bengal famine because food was diverted. I think India has taken the right decision.”
For now, anecdotal evidence suggests few consumers in Arab countries are concerned about the impact of India’s export ban.
“We in Jordan consume basmati rice and not the white non-basmati rice that was included in the ban,” Jamal Amr, foodstuff representative at Jordan’s Chamber of Commerce, told Arab News.
He said Jordan bought most of its rice from the US, the EU, East Asian countries, Uruguay and Argentina.
“I am not stockpiling rice and I am not planning to. Things look normal to me,” Emirati housewife Umm Mohamed, a resident of Dubai, told Arab News. “My family and the domestic helpers all eat rice as a main staple.”

A farmer harvests at a rice paddy on the outskirts of Srinagar, India. (AFP)
The picture is the same in Saudi Arabia. “Rice is the main source of food in Saudi Arabia,” retired engineer Abu Akram said.
“In every main meal, we have to put basmati rice on the table. Saudi families usually store rice in quantities that can last for a month or two.”
He said he was not concerned about a possible price rise, but was thinking of asking his sons to buy extra rice, “just in case.”
In the era of globalization, involving free movement of goods, people and capital, the shopping habits of rice eaters in the Arab world are not immune to fluctuations in the fortunes of Indian agriculture.
India’s farmers typically start planting rice and other water-intensive crops from June 1 to coincide with the annual monsoon season. However, the country received 10 percent less rain than the average for June, with that figure rising to 60 percent in some states.
Although the monsoon rains have now arrived, the delay held up the planting of summer crops, a setback that experts believe prompted the Indian government to curb exports of rice.
Just a few days after the restriction was imposed, the UAE announced its own four-month ban on the export and re-import of all rice varieties, starting from July 28.
The UAE imports almost 90 percent of its food, making it especially vulnerable to fluctuations in global prices. According to Reuters data, the UAE was among the top 10 importers of non-basmati rice from India in 2020, buying almost 346,000 tons.
Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, Yemen, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, the UK and the US also feature among the top 10 importers.

A farmer spreads unpolished rice to dry along a highway in Toopran Mandal in the Medak district, some 55 km from Hyderabad on November 11, 2021. (AFP)
Large quantities of rice imported by the UAE are later exported after packaging in the free zones. The ban on re-importing will therefore affect countries that buy packaged rice from the UAE.
Other countries that are likely to feel the squeeze of India’s export ban are African importers such as Benin. But even big economies like China will be affected, despite it being a major rice producer in its own right.
Arab countries that are likely to suffer the most from India’s export ban are Egypt, Algeria and Sudan, all of which already face economic turbulence and the effects of rising wheat prices. In Sudan’s case, a deadly feud between two generals since April 15 has compounded the woes of a population ravaged by hunger and malnutrition.
Unsurprisingly, some observers believe India made the wrong call, undermining its carefully cultivated image as a reliable trade partner and aspiring leader of the Global South.
“I feel the ban on the export of rice is a knee-jerk reaction to control prices in the domestic market with elections in view,” said Gokul Patnaik, former chairman of India’s government-affiliated Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority.
“But it gives a very bad name to India which is emerging as an agri-exporter. Earlier, India was a net importer and of late it had earned a good reputation as an exporter. Countries which are buying from India will definitely feel this kind of reaction. To switch on and off is not good if one is to be a consistent exporter.”
He added: “What the government could have done was to control the taxes. It could have increased export tax. If you are going to be in international trade, you should always be open to import and export. You should not ban.
“Importing countries expect you to be consistent and you should not only be a fair-weather friend. Export-import is a question of trust. If you lose trust, people don’t want to continue.”

The ban on exports of non-basmati white rice imposed on July 20 by India. (AFP)
It is not just rice that has become costlier in India in recent weeks. The prices of tomatoes and other staples have also risen following the late arrival of the monsoon rains in some parts of the country and unexpectedly heavy downpours in others.
With heavy rains damaging standing crops in some regions, predictions now are of poor harvests and even higher prices of farm produce. Public anger over food inflation could become a clear disadvantage for the government, which faces several regional elections this year in the run-up to the national vote.
Brajesh Jha, a professor at the Institute of Economic Growth in Delhi, takes the view that India is ill equipped to be a major exporter, but believes the ban is largely tied to the general election next year, which takes primacy over international relations.
“India is an exporter of food grains. (But) the kind of arable lands and the population that is dependent on foodgrains (means) India cannot be an exporter,” he told Arab News.
“Rice is exported from those areas which are semi-arid. The way the population is increasing, India needs lots of food grains.
“No doubt India’s standing among the community of nations will get a beating with this kind of decision, but the election is way more important (for the government) than the impression people form about it.”
Other experts say the Indian government should have implemented alternative policies that would have avoided compounding the global food crisis while at the same time stabilizing domestic prices.
“India could have used this opportunity to be a global leader that is helping against a potential food crisis,” Anupam Manur, an international trade economist at the Takshashila Institution in Bengaluru, told Arab News.
“Instead, imposing a ban on an essential commodity at such a time will weaken India’s arguments against other countries weaponizing supply chains by imposing export controls on semiconductors, rare earth elements or medical application programming interface.”

Workers transplant rice paddy in West Bengal, India. (Getty Images)
He added: “If it truly wants to mitigate a domestic price rise, the government can open up the warehouses which have more than adequate rice stocks.
“India might not bend to international pressure, but if domestic production increases, it might yet make a grand gesture of relaxing the ban.”
While such a gesture would ease global concerns, El-Zubi says that many Arab countries, including Egypt, Iraq, Syria and Jordan, are in no position to meet their own demand for wheat and rice as they lack the necessary water resources.
“Jordan produces only 3 percent of the wheat it needs,” he told Arab News.
According to him, Arab countries with fragile economies face serious challenges from food shortages, so they should expand the sources from which they buy strategic food staples, diversify payment methods and broaden their food supply chains and routes.















