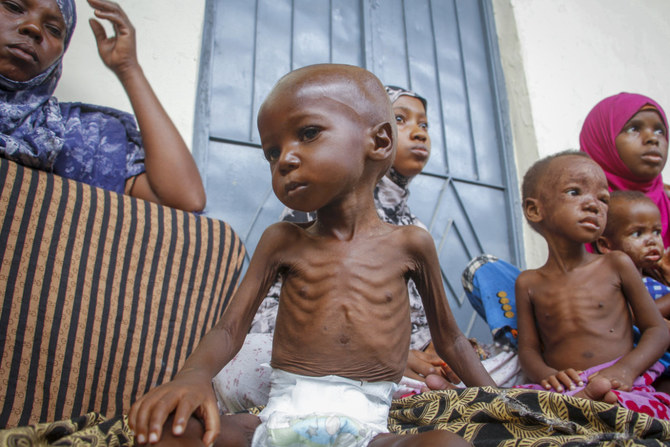
UNITED NATIONS: Somalia’s “dire hunger emergency” is spiraling upward with one-third of the population expected to face crisis or worse levels of food needs, but the UN has been forced to drastically cut food assistance because of a lack of funding, the head of the World Food Program said Thursday.
Cindy McCain told the UN Security Council the latest food security data show that over 6.6 million Somalis desperately need assistance including 40,000 “fighting for survival in famine-like conditions.”
But she said WFP was forced to cut monthly food assistance, which had reached a record 4.7 million people in December, to just 3 million people at the end of April – “and without an immediate cash injection, we’ll have to cut our distribution lists again in July to just 1.8 million per month.”
McCain, who visited Somalia last month, said she saw “how conflict and climate change are conspiring to destroy the lives and livelihoods of millions of Somalis.” She said the country’s longest drought on record, which killed millions of livestock and decimated crops, recently gave way to disastrous flash floods in the south.
Urging donors to be as generous as they were and hauling Somalia “back from the abyss of famine in 2022,” McCain warned that the survival of millions of Somalis is at stake.
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres visited Somalia in April “to ring the alarm” and appealed for “massive international support” for Somalia.
But the results of a high-level donors’ conference for three Horn of Africa countries – Somalia, Ethiopia and Kenya – on May 24 were very disappointing. It raised less than $1 billion of the more than $5 billion organizers were hoping for to help over 30 million people.
Only in the past few years has Somalia begun to find its footing after three decades of chaos from warlords to the Al-Qaeda-linked Al-Shabab extremist group and the emergence of Daesh-linked extremist groups. Last May, Hassan Sheikh Mohamud, who served as Somalia’s president between 2012 and 2017, was returned to the top office by legislators after a protracted contest.
Somalia has faced numerous attacks from Al-Shabab and recently the government embarked on what has been described as the most significant offensive against the extremist group in more than a decade.
Catriona Laing, the new UN special representative for Somalia, told the council that the government’s operations have degraded Al-Shabab militarily and dislodged its fighters from a number of areas which is “a notable achievement.”
But Laing said Al-Shabab remains a significant threat,” pointing to “a recent resurgence in the scale, tempo and geographic distribution” of its attacks including a June 9 attack on the Pearl Beach Hotel in the capital Mogadishu that killed nine people.
The African Union has a force in Somalia providing support to government forces battling Al-Shabab. Last year, the Security Council unanimously approved a new AU transition mission known as ATMIS, to support the Somalis until their forces take full responsibility for the country’s security at the end of 2024.
Laing said the drawdown of ATMIS and handover are proceeding, but her initial assessment “is that the complexity, the constraints, and pace of the transition process presents risks, (and) this will be challenging.”