JEDDAH: Digital technologies are transforming the way in which people of all languages and backgrounds communicate, making work, study and socializing across national and cultural boundaries easier and more inclusive.
However, many of the latest innovations in communications technology have tended to be geared toward smartphones, tablets and e-readers — formats that are not always conducive to people with visual impairments.

French inventor Louis Braille. (Supplied)
Now, recent enhancements to a 200-year-old system of writing are helping people with visual disabilities feel included in a greater variety of jobs and fields of study and forms of entertainment.
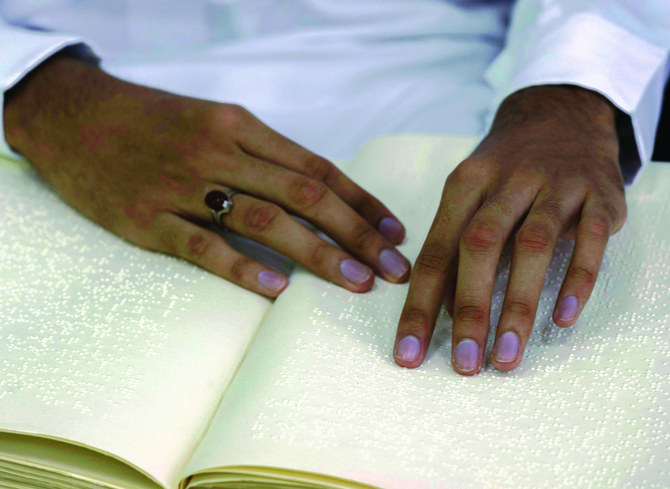
French inventor Louis Braille, who lost his sight at the age of three, in 1824 developed a system of communication consisting of a code of 63 characters, each made up of one to six raised dots arranged in a six-position matrix or cell, designed to fit under a fingertip.
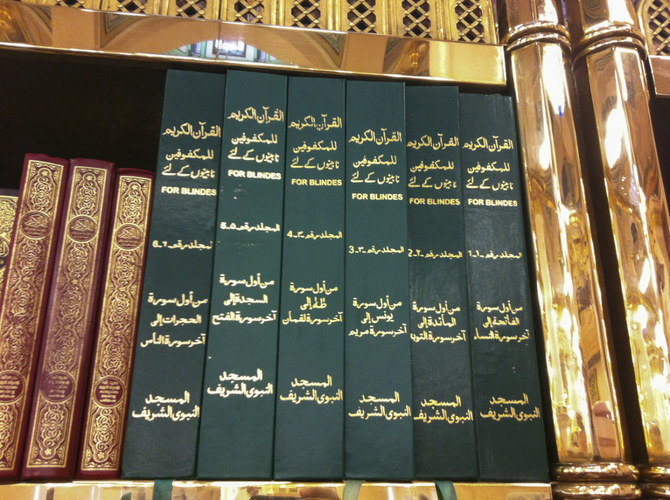
These characters, known as braille, are embossed in lines on paper and read by passing the fingers lightly over the manuscript. From alphabets to musical notation, braille opened a world of possibilities for the visually impaired.
According to the World Health Organization, around 40 million people worldwide are blind, while another 250 million have some form of visual impairment. A survey conducted in 2017 by Saudi Arabia’s General Authority for Statistics found that some 811,610 Saudis are visually impaired.
A unified Arabic braille code was adopted in the 1950s as part of the move toward a universal braille system. This has allowed many of them to live, work and study unsupported.
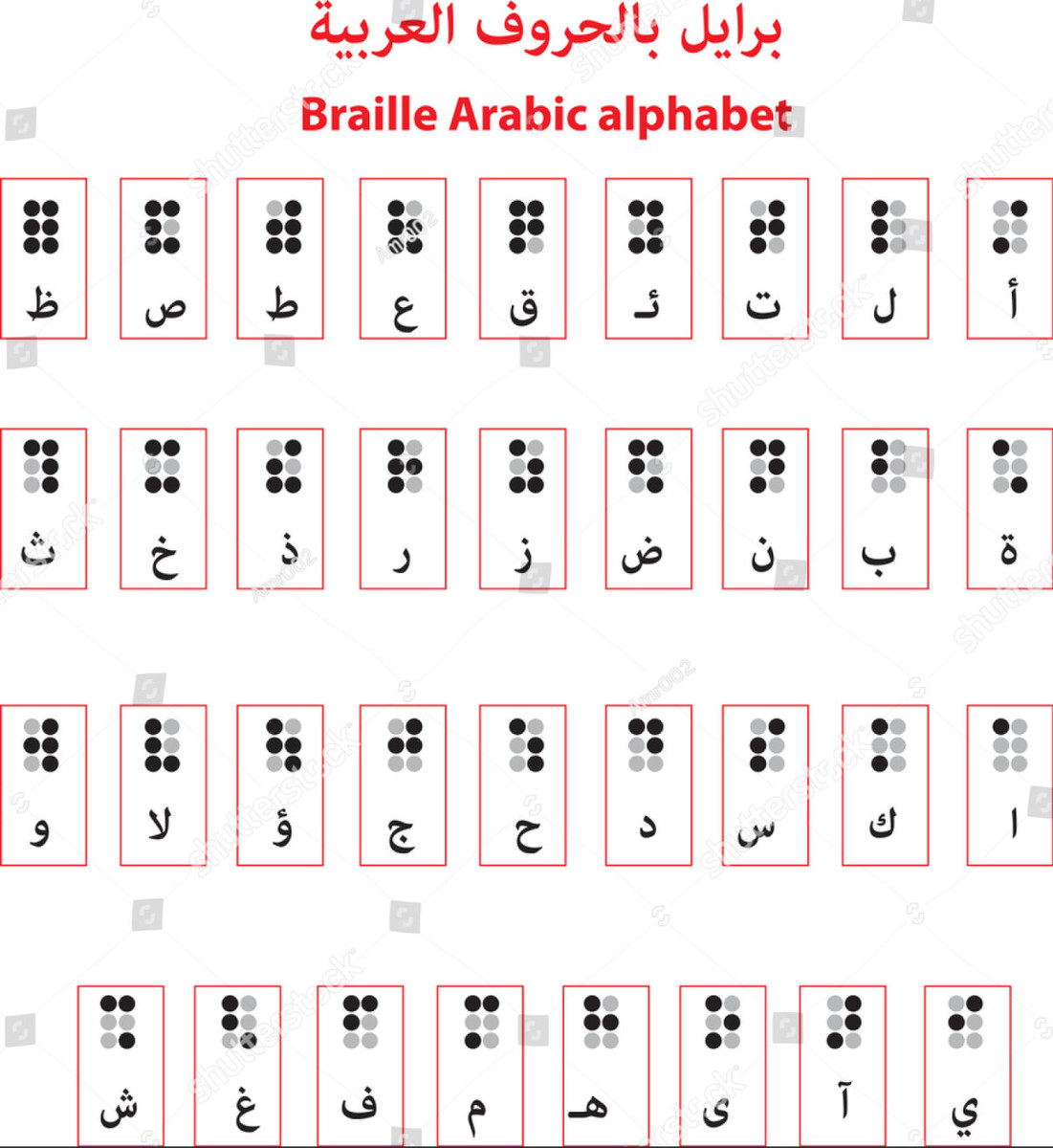
The Arabic braille alphabet. (Shutterstock image)
Authorities in the Kingdom have taken measures to create a more inclusive society, using braille on the packaging of medicines and by establishing work programs to integrate the visually impaired into the workforce.
The Kingdom has also established branches of Al-Noor Institute for the Blind, which provide courses for school children, in addition to integrated classes in universities through a national program that guarantees the right to an education.

A student at a school for the blind in Riyadh is pictured operating a machine in a photograph taken on April 25, 1967. (Getty Images)
Speaking to Arab News, Khaled Al-Harbi, spokesperson for the National Association of the Blind, known as Kafeef, said education paved the way for those with special needs to become an integral part of their communities.
Kafeef’s mission, he said, is to empower people with visual impairments through programs launched in coordination with government and private entities.
“I, like many members, received moral support and guidance from Kafeef from a young age, and enrolled in programs,” Al-Harbi told Arab News.
“We were provided tools, learned new skills using our hands, and, with time, we launched several awareness programs and braille training courses for the visually impaired and visually acute with the latest — Iqra — the first certified braille training program.
“We’ve seen lately several initiatives that target the community, such as sending gift cards in braille, and it’s very commendable, but it can also go the other way. There is a need for more inclusion from the visually impaired to utilize technology for their benefit and the benefit of the community.”

Tech advances in audio software and screen-reading programs on computers and smartphones have made life easier for the visually impaired. (Shutterstock)
As digital developers have tended to prioritize audio software, such as screen-reading programs on computers and smartphones, some argue that braille has become a less important tool for people with visual impairments.
However, researchers believe learning braille from an early age can greatly improve literacy, as it is a much better way to understand punctuation, grammar, and spelling than using audio resources alone.
For many years, electronic braille devices were prohibitively expensive, placing them out of reach of many people with visual impairments, particularly those in developing countries. Now prices are beginning to fall and the demand for new software is growing.
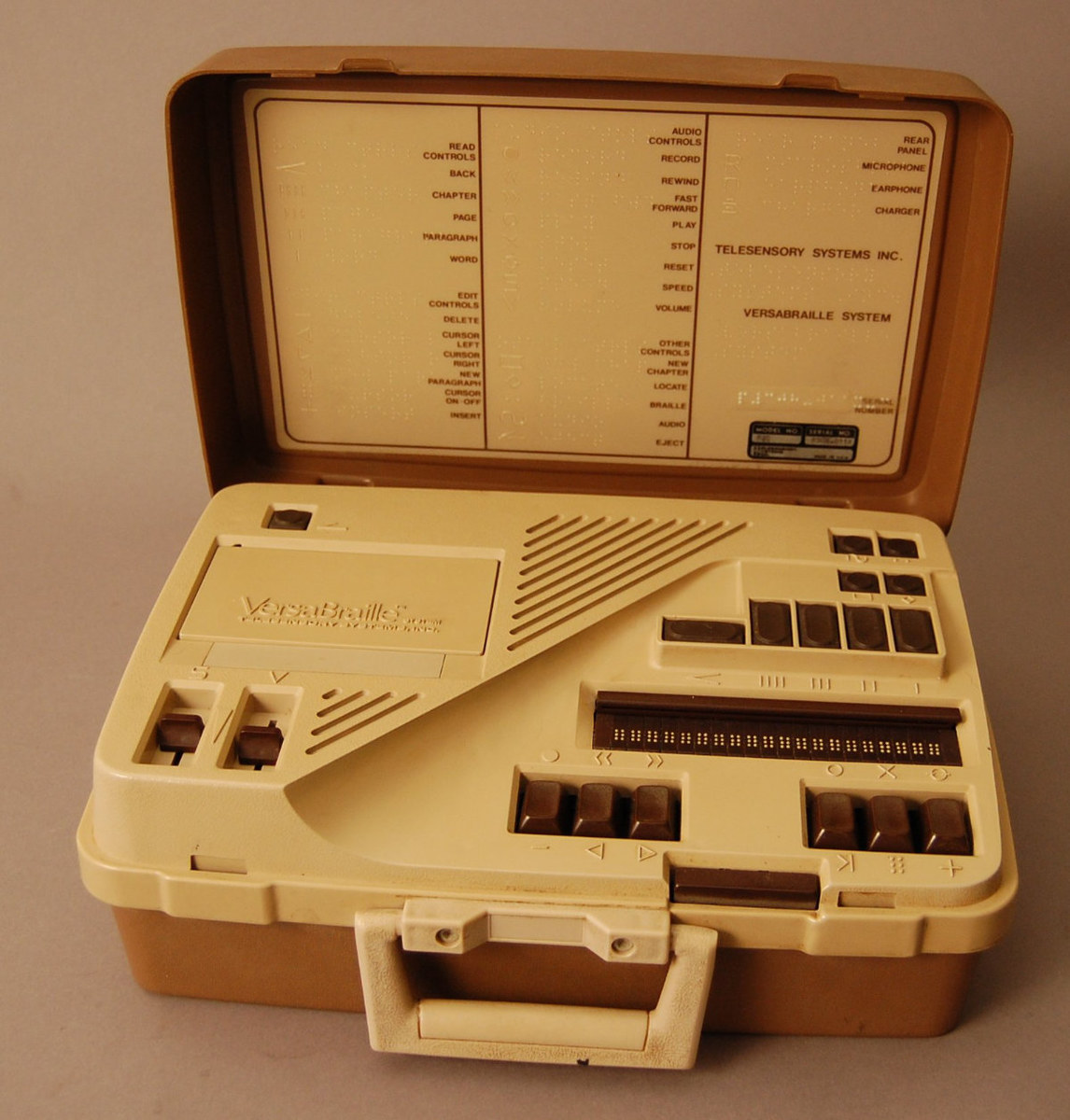

VersaBraille by American manufacturer TeleSensory Corporation was first made commercially available in 1982. (Wikipedia)
The first braille displays appeared in the mid-1970s, and the first commercially produced braille display, the VersaBraille, was released in 1982. Five years later, the Braille ‘n Speak was released as the first portable notetaker.
Newer refreshable braille devices make it possible for users to read text from a digital screen when connected to a PC, tablet or phone. Such devices mimic the familiar raised dot patterns using tiny movable pins.
FASTFACTS
811,000 people in Saudi Arabia have some form of vision disability, according to the GSTAT Disability Survey 2017.
A unified Arabic braille code was adopted in the 1950s as part of the move toward a universal braille system.
However, with such a heavy reliance on cables and bluetooth connectivity, these systems are not always the most practical or user friendly. Furthermore, physical braille keyboards that allow users to enter text are not particularly mobile.
It was these drawbacks that led Google to develop its own innovative built-in keyboard called TalkBack, which comes as a part of the Android Operating System and does not require any external hardware.

In 2018, Google also launched an AI-powered app called Lookout to help low-vision users interact with their surroundings. The app can read signs and labels, scan barcodes, and even identify currencies.
In 2014, Apple introduced its own on-screen braille keyboard for iPhone, iPad and iPod Touch devices called iBrailler Notes.
The app enables users to navigate across text and perform tasks without connecting additional hardware. One striking feature of the app is that the keys automatically form around the fingertips when they are placed on the screen.

iBraille Notes on-screen braille keyboard by Apple. (Social media)
Many new braille technologies are yet to reach the market and several are still in the conceptual or prototype phase. New scanning features, audio descriptions, language identifiers, machine-learning tools, text mining, and speech processors could all soon appear in forthcoming assistive technologies.
Abdulrahman Al-Atawi, a professor at the college of computing and informatics and supervisor of the Center for Innovation in E-learning at the Saudi Electronic University, the first university in the Kingdom to exclusively adopt e-learning strategies and technologies, told Arab News that such technologies will play a significant part in students’ journeys.
In January, the Global Trends in E-Learning forum was held in Riyadh, where global leaders in the education sector shared their insights, exchanged experiences and discussed strategies to serve the online learning process.

The two-day Global Trends in E-Learning event that took place in Riyadh on Feb. 21-23 brought together resource persons and participants from 20 countries and 50 companies. (AN file photo)
As part of the forum’s objectives, a contest for EdTech entrepreneurs, faculty and students from across the Kingdom showcased innovative projects using emerging technologies to serve the education sector.
Al-Atawi, who also headed the Committee for the Innovation Oasis and GTEL Demofest, said some of the winning projects were focused on people with special needs.
“For many, the braille code allows the blind and visually impaired to read any form of writing, but when it comes to images and pictures, that’s another story,” he said.
“One of the winning projects, a smart reader for the visually impaired, found a solution to that, verbally describing that image.
“In this era of modern science, we wish to get every bit of information in digital form. With the right tools, we can help members of the special needs community.”





















