DUBAI: For decades, the Middle East and North Africa region has struggled to meet its growing water needs. With populations booming and natural sources of freshwater rapidly depleting, finding sustainable solutions to address the precarious state of the region’s water security is more urgent than ever.
Water insecurity has exacerbated conflicts and political tensions in many Arab countries, significantly impacting the health and well-being of its people. In nations such as Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, and even several of the Gulf states, many communities lack access to plentiful clean water.
While about 40 percent of the global population experiences water scarcity, the MENA region is considered among the world’s most water-insecure, with about 90 percent of children living in areas of high or extremely high water stress. According to UNICEF, the region is home to 11 of the world’s 17 most water-stressed countries.

The reputed home of the biblical Garden of Eden, Iraq's southern marshes of Chibayish, have been battered by drought as well as reduced river flows from neighboring Turkey and Iran. (AFP)
“Countries with rapid population growth, an arid climate, and heavily water-consuming agricultural activities are at a much higher risk of facing significant water scarcity before 2050. These nations will therefore require larger counter operations in order to negate the pending impact,” Walid Saad, CEO and co-founder of World of Farming, told Arab News.
“This is a challenge that requires a collaborative approach between public and private sector organizations, and the implementation of technology and innovative solutions across industries, to help ensure greater water efficiency and security for future generations.”
A 2020 report by Orient Planet Research found that the Gulf Cooperation Council area’s water needs will reach 33,733 cubic meters per year by 2050. However, the region’s projected future storage is just 25,855 cubic meters.
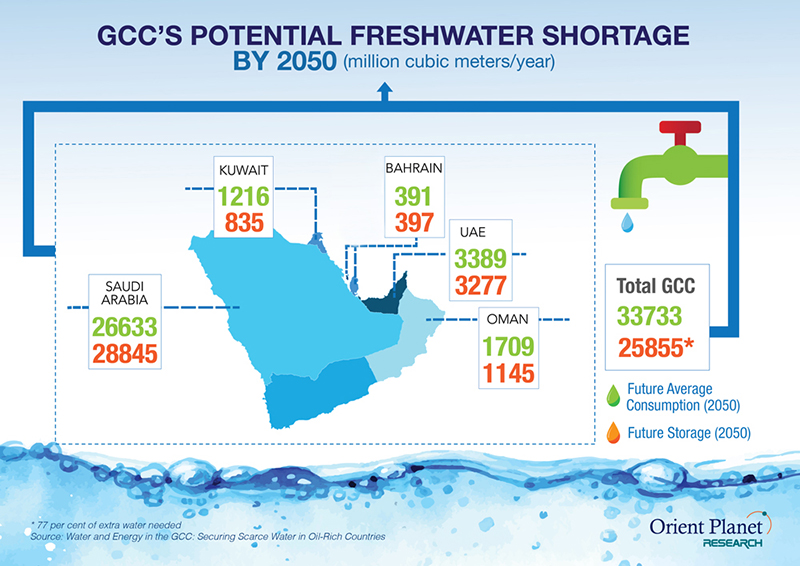
Orient Planet Reseach illustration
This means the region needs to boost its water stocks by 77 percent to meet the requirements of its population within the next 30 years.
Identifying ways to mitigate and adapt to climate pressures has become a top priority for regional governments. The coming year is expected to be one of the hottest on record, with extreme weather events likely to grow in scale and frequency and, in the process, exacerbate existing problems of the water-stressed region.
INNUMBERS
11 World’s most water-stressed countries (out of a total of 17) that are in MENA region.
90% Children in areas of high or extremely high water stress in MENA.
77% Increase in water stocks needed by 2050 to meet GCC population’s requirements.
By the end of the century, scientists expect average temperatures in the Middle East to rise by 5 degrees Celsius, making parts of the region potentially uninhabitable if action is not taken urgently to tackle the causes of man-made climate change.
In addition to extreme weather, climate-related water scarcity is expected to wipe up to 14 percent off the region’s gross domestic product over the coming 30 years, according to the World Bank.
As about 60 percent of the region’s freshwater originates from external territories, international relations also play a crucial role in water security.
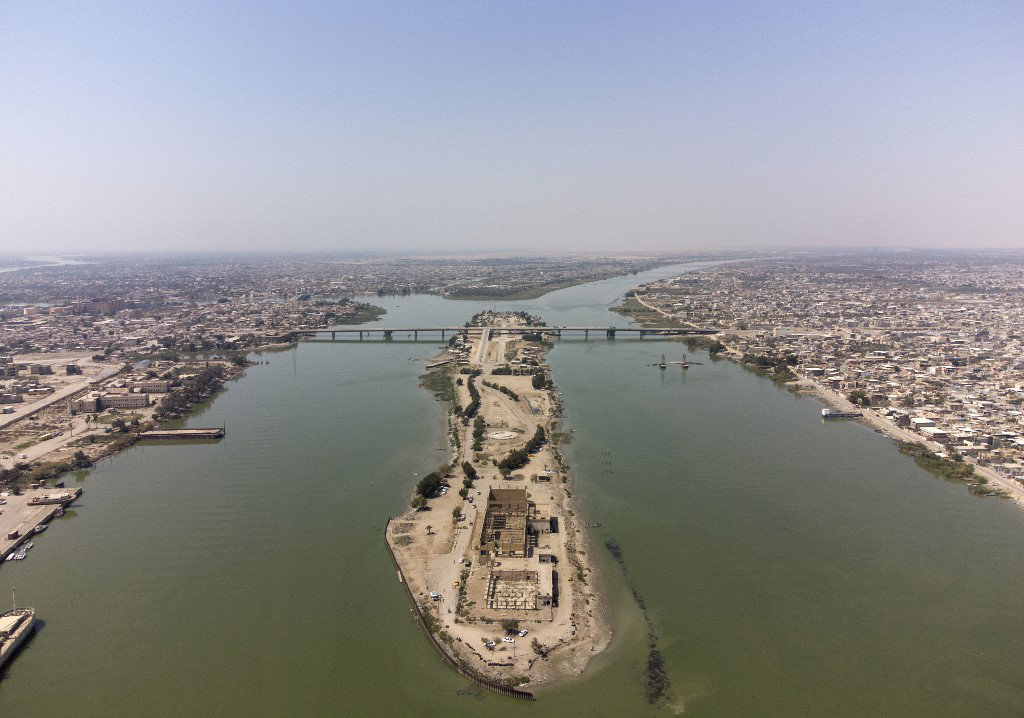

A view of the Shatt al-Arab waterway in Iraq's southern city of Basra, where the Euphrates and Tigris meet. Both rivers originate from Turkiye. (AFP)
The Nile River, for instance, runs through or along the border of 10 other African countries before it reaches Egypt, making Ethiopia’s GERD dam project a point of contention, while Iraq and Syria are fed by the Tigris and Euphrates, which both originate in neighboring Turkiye where large dam projects are also underway.
Jordan and the West Bank, meanwhile, rely on the Jordan River, whose source lies in Israeli territory. Conflicts, rivalries and failures to cooperate on shared water access can lead to pollutants, fish-stock depletion and water shortages further downstream.
In the face of these challenges, several Arab governments are now prioritizing investment in new innovations and technologies to help conserve freshwater sources, recycle and reuse wastewater, and reduce the environmental harm of desalinating seawater.
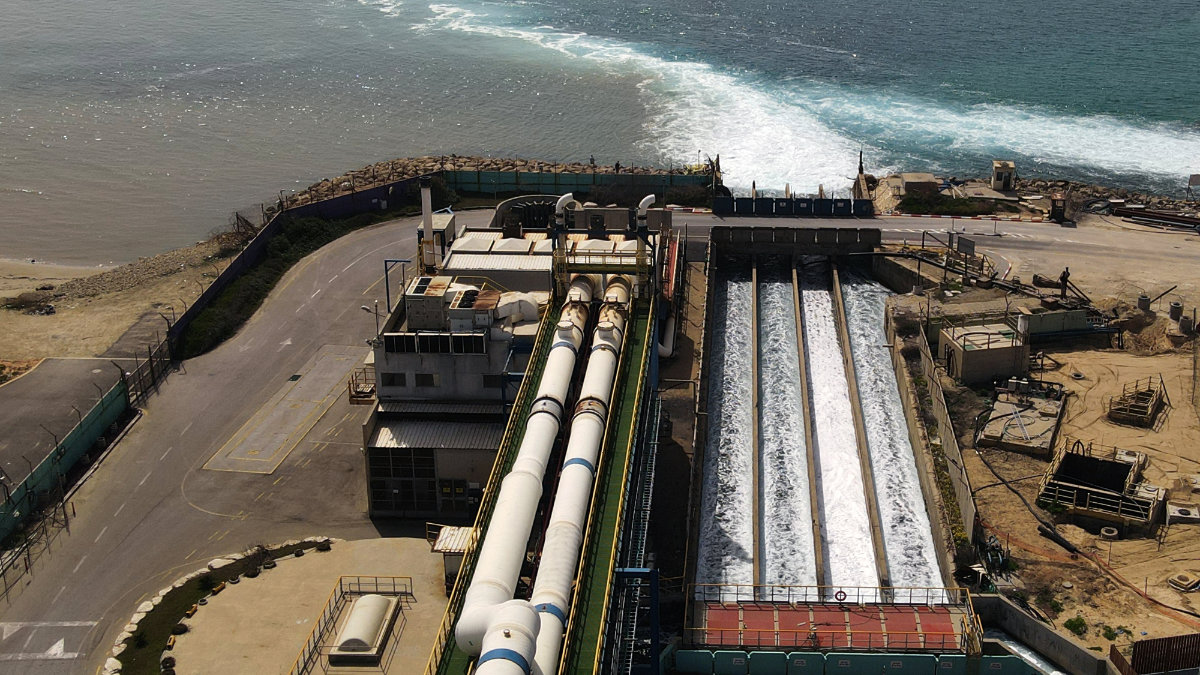

Israel's Hadera desalination plant plans to pump excess output into the Sea of Galilee, depleted by overuse and threatened by climate change. (AFP)
“Technologies such as membrane bioreactors, reverse osmosis and ultraviolet disinfection are being used to treat wastewater to a high standard, making it suitable for reuse in irrigation, industrial and even potable uses,” Fawzi Al-Dibis, manager of sustainability and climate change at WSP Middle East, told Arab News.
Another solution is localized greywater treatment, which allows for the use and reuse of water at source, thereby avoiding additional pumping costs. At present, about 80 percent of the world’s wastewater is being discharged untreated into the environment, according to the UN.
Atmospheric water harvesting is another promising means of overcoming water scarcity by collecting water from the air through various methods, including condensation, dew collection and fog harvesting.
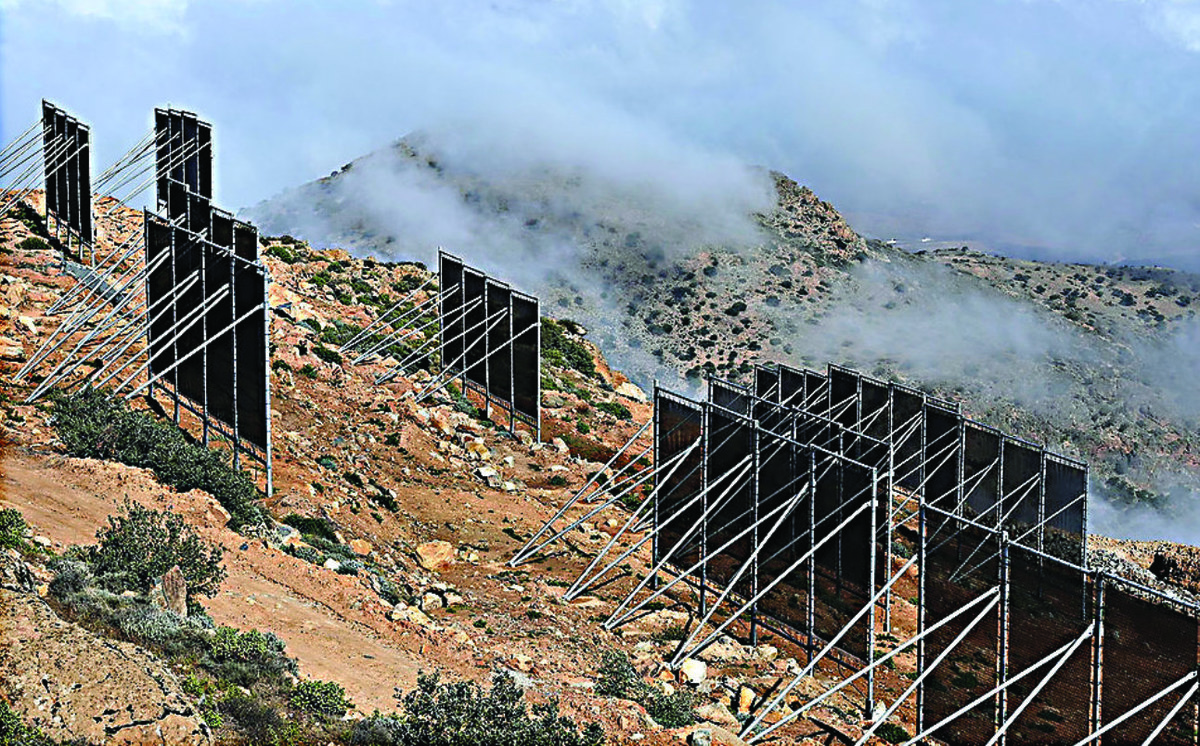

Water is harvested from fog clouds in Morocco using technology developed by the German Water Foundation. (Supplied)
Agriculture accounts for almost 80 percent of the MENA region’s water usage, compared to the 70 percent global average. According to the World Bank, freshwater is being drawn from natural underground aquifers faster than it can be replenished.
To monitor and control this dwindling resource, new smart water management systems, employing artificial intelligence technology, are being developed, Al-Dibis told Arab News.
“These technologies help to analyze data from various sources, such as weather forecasts and sensor networks, to make more accurate predictions of water availability, and to optimize the distribution and use of water resources,” he said.
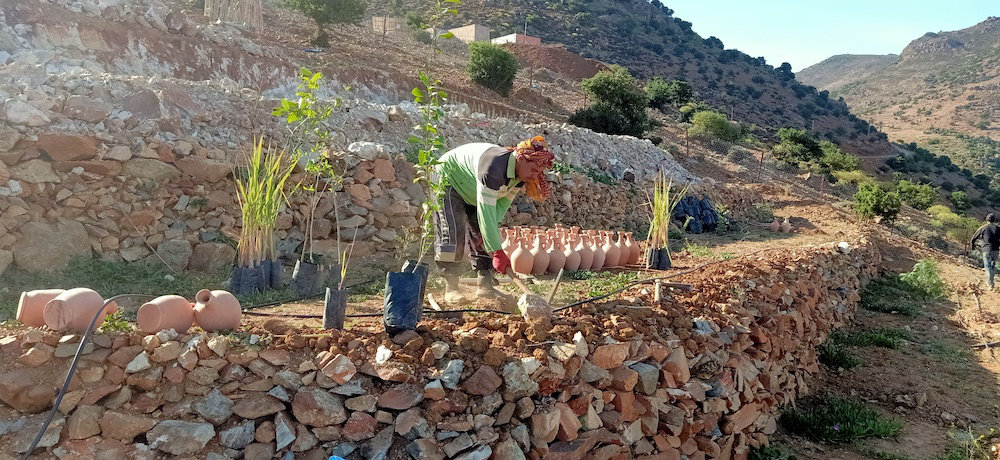

Agriculture alone accounts for around 80 percent of water usage in MENA region, according to the World Bank. (Supplied)
If farming and irrigation can be made more sustainable, Saad says that the region could also reduce its carbon footprint by growing more of its own crops, thereby cutting its reliance on imported goods.
“The use of smart irrigation and automation in agriculture provides savings in water consumption by optimizing the amount of water needed, in controlled time periods,” he said. The process can be automated using remote wireless sensors that gather live data to make accurate predictions regarding irrigation schedule, location and requirements.
A more holistic approach, implementing “a closed-loop system” in agricultural operations, could reduce the strain on all elements of water supply in the region and ease the existing reliance on transportation, outsourcing, and infrastructure beyond the local ecosystem.
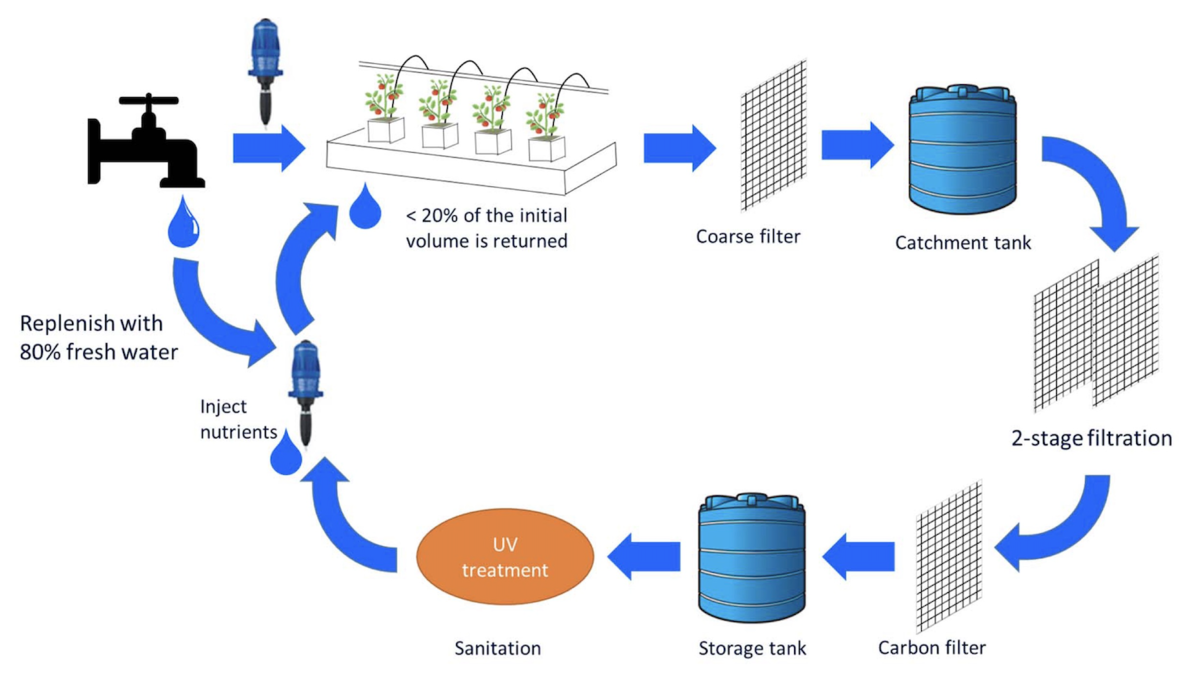
A sample closed-loop water treatment system for crops, designed by e-Gro, a collaborative effort of American floriculture specialists. (Diagram courtesy of e-gro.org)
Clean technologies and other innovations are also being deployed to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other harmful byproducts during the desalination process. “Fortunately, the science of new materials is offering new solutions to current desalination plants,” Al-Dibis said.
Saad concurs that leveraging new technologies is crucial to reducing the region’s dependence on desalination to meet its water needs. “The Middle East is leading the charge for many of these developments, spurred on by the drier climate and heavy reliance on importation,” he said.
The UAE launched its Net Zero 2050 strategy in 2021, aiming to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions in line with its global climate commitments and to address its own environmental challenges.
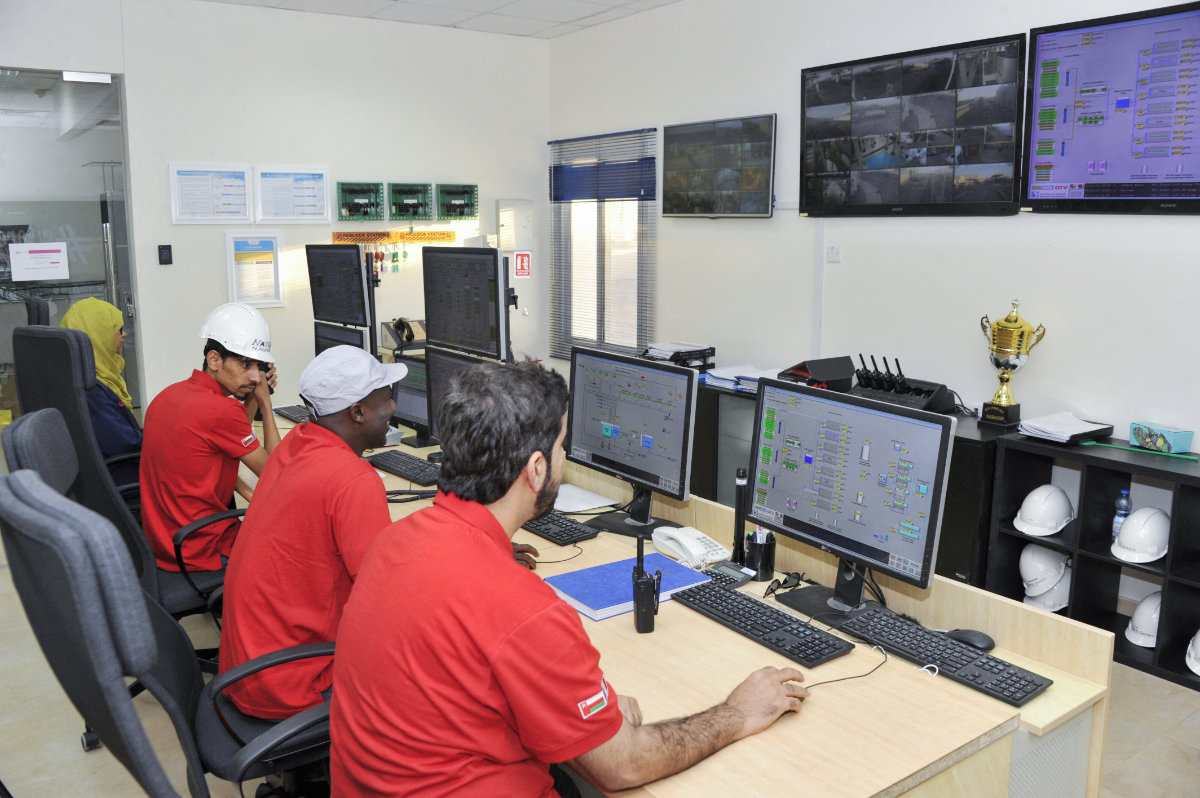

Engineers monitor control panels at a desalination plant in the Omani port city of Sur, south of the capital Muscat. (AFP)
The UAE’s water table has dropped by about 1 meter a year over the past 30 years, giving the country less than 50 years until all its natural freshwater resources are depleted.
Similarly, Saudi Arabia has rolled out its Vision 2030 initiative, part of which focuses on the optimal use of water resources, reducing consumption and using renewable water, together with its Saudi Green and Middle East Green initiatives.
The Kingdom’s NEOM smart city giga-project taking shape on the Red Sea coast also aims to reduce average water loss from 30 percent to 3 percent by building infrastructure and optioning innovative technology through ENOWA, its energy and water subsidiary.

NEOM says it will have strategically located water reservoirs placed throughout its network and up to 10 pipeline and pumping stations to ensure abundant drinking water supplies. (Supplied)
“This endeavor will provide a blueprint for achieving sustainable water and resource management at scale, and once achieved, a success model the rest of the world may adopt or adapt,” Saad said.
While acknowledging that technology and real-time innovation are essential to reducing water waste, Saad believes the preservation of natural resources can only be achieved through cooperation between governments, businesses and consumers.
“The decisions we make when we source and consume our food and the way we live our day-to-day lives can all have an impact,” he said.
“Everyone can contribute to the overall goal of sustainability by addressing our own day-to-day habits and decisions.”


















