DUBAI: Summer of 2022 has seen a rash of wildfires, flash flooding, dust storms, and record high temperatures across the planet, which scientists believe are only the latest expressions of man-made climate change.
Experts warn that such extreme weather events will grow in frequency and severity unless the world acts decisively to cut greenhouse gas emissions and ensures that temperatures do not exceed 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
With the transition to renewable energy sources appearing to stall in recent months, the hope is that the 27th UN Climate Change Conference, to be held in Egypt in November, will, somehow or other, get the climate agenda back on track.
There is an expectation ahead of each COP summit that the host country will emphasize the needs, priorities, and circumstances of its own geographic and cultural space. This year it is the turn of Africa and the Middle East.
“This is a great opportunity for Africa and the MENA region to raise awareness of their challenges and the solutions needed to tackle climate change,” Zitouni Ould-Dada, deputy director in the Climate and Environment Division at the Food and Agriculture Organization in Rome, told Arab News.
“The Egyptian presidency has a great opportunity to convene and facilitate to help countries and other actors raise their ambition and take collective action for mitigation, adaptation and building resilience.”
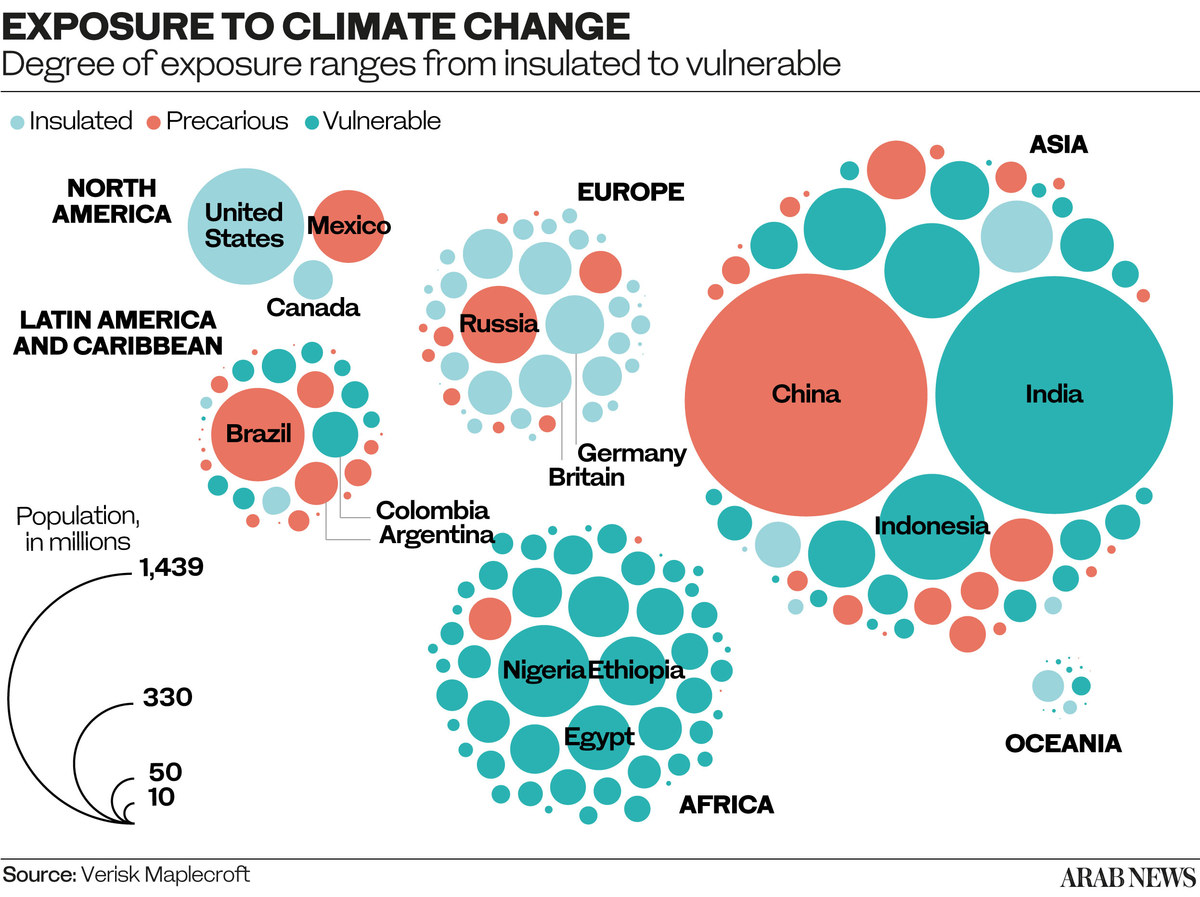
Preparations for COP27 have given Egypt the added impetus to address its own climate challenges. According to the World Bank, mean annual temperatures in the North African state could rise by 2 to 3 degrees Celsius by 2050.
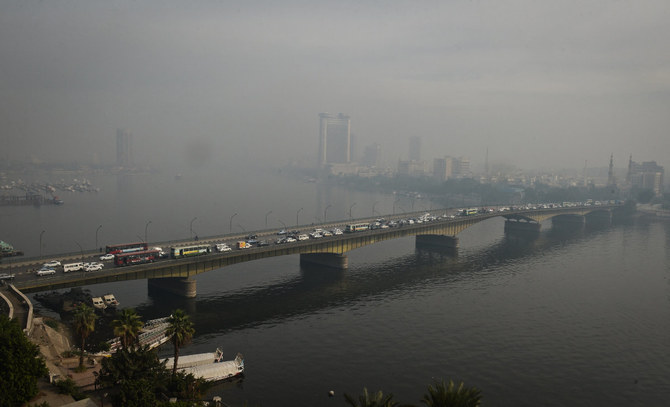
Cairo is considered one of the world’s most polluted cities, where industry, traffic congestion, and substandard waste management have led to poor air quality and associated health problems.
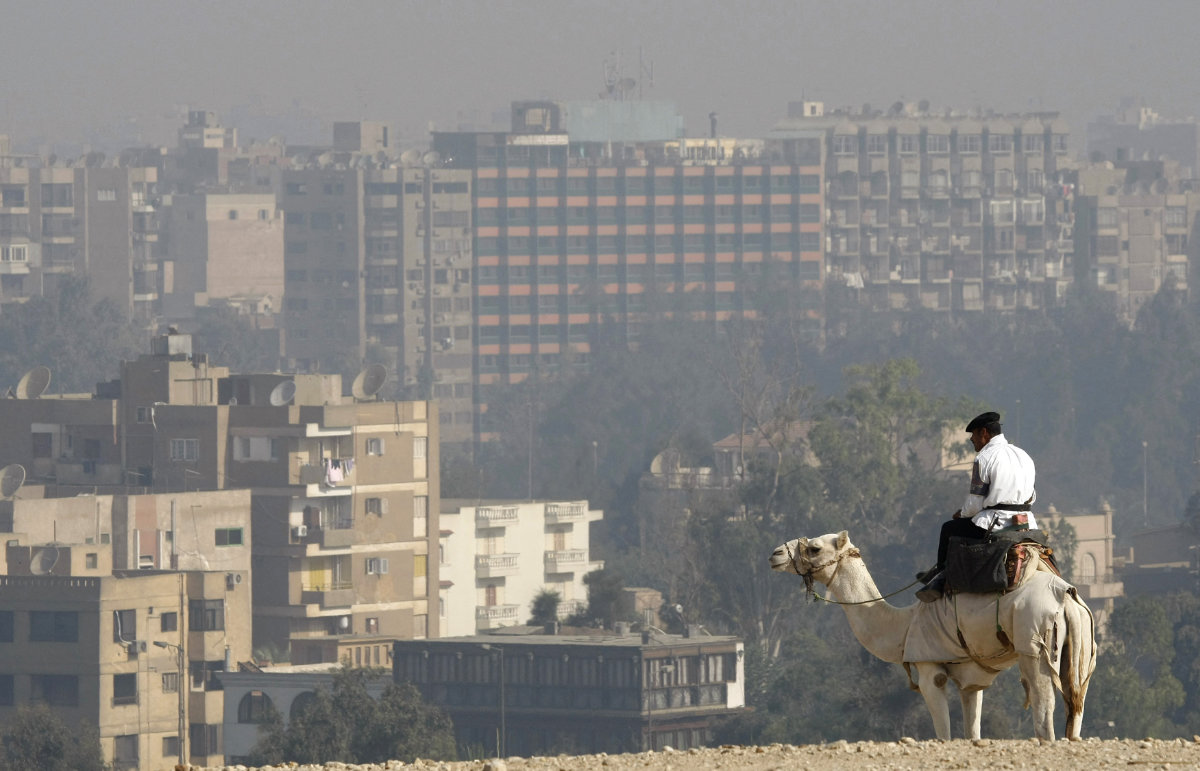

A camel-mounted tourism policeman in the Giza Plateau silhouettes against the pollution smog covering the city of Cairo. (AFP file)
Egypt’s Ministry of Health says around 2 million people per year on average seek medical treatment for respiratory problems related to poor air quality.
In honor of COP27, Egypt has transformed its Red Sea resort town of Sharm El-Sheikh, which will host the summit, into a sustainable green city, in part with the help of a $7 million grant from the Global Environment Facility.
Dubbed the Sharm Green City Project, the site has utilized low-carbon technologies, implemented environmental protection policies, and introduced improved waste management practices.
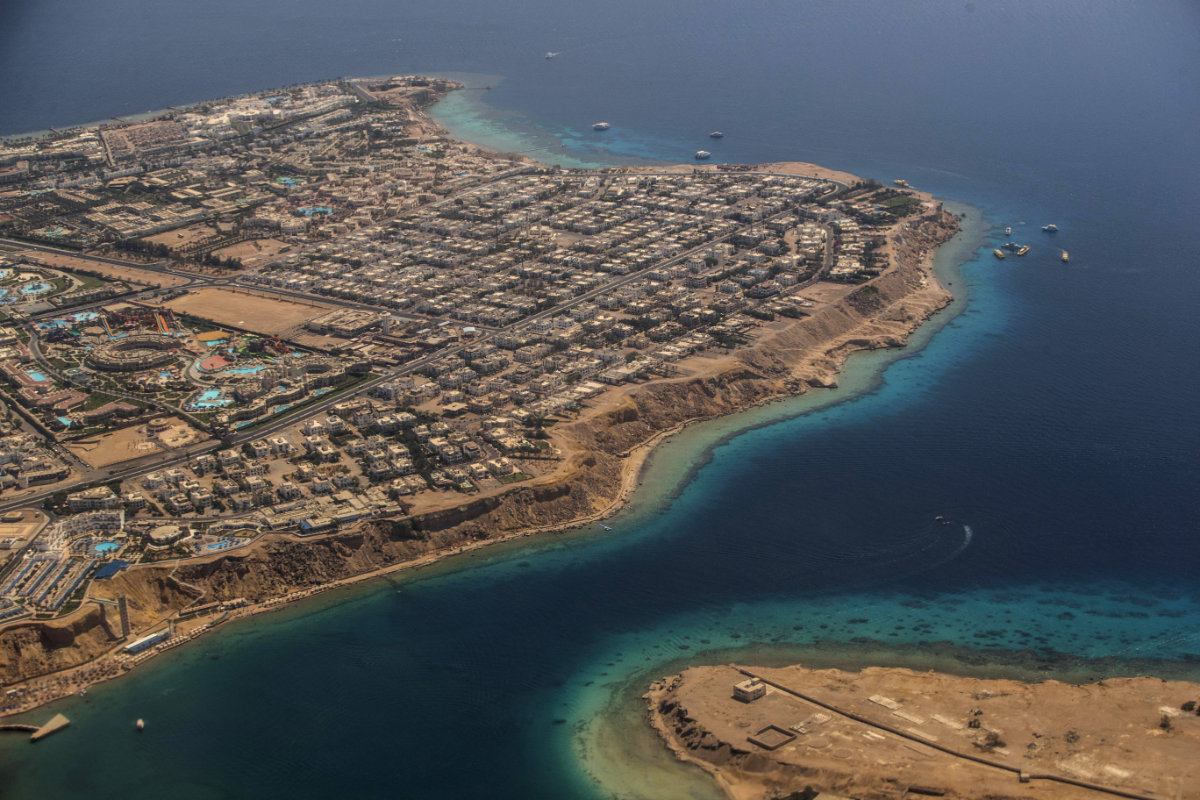

An aerial view of residential lots and luxury hotels in the Hadaba district of Sharm el-Sheikh at the southern tip of the Sinai peninsula. (AFP file)
As part of its wider greening agenda, Egypt also recently announced a new partnership with the UAE’s Abu Dhabi Future Energy Company for the production of green hydrogen.
“Entering the Green Hydrogen Alliance is a good opportunity for Egypt to invest in its clean energy,” Mahmoud Mohieldin, a World Bank Group senior vice president and the UN climate change high-level champion for Egypt, told an event at the American University of Cairo in June.
Egypt has lofty ambitions to build on the many carbon-cutting pledges made by participating nations at COP26 in Glasgow, Scotland, last year. Delegates will be presented with the latest findings on climate change and the measures needed to prevent it.
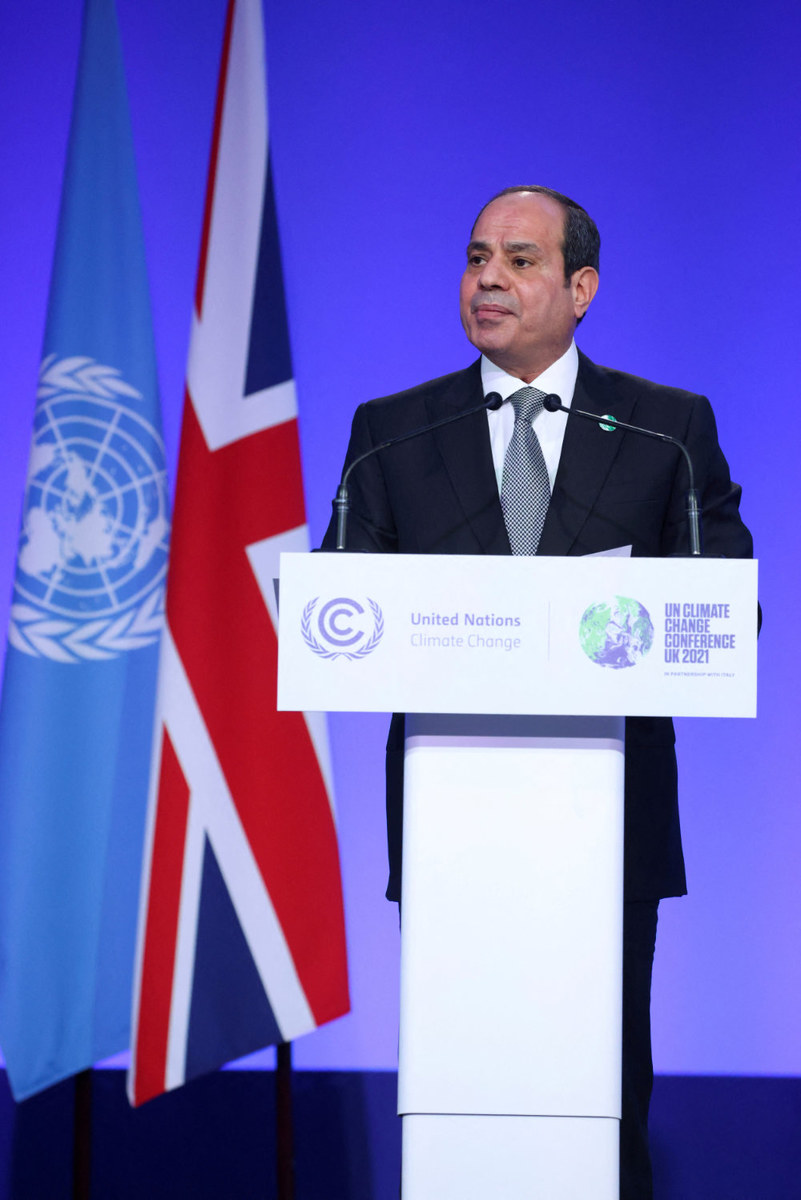

Egypt's President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi presents his national statement during the COP26 UN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, Scotland on Nov.1, 2021. (AFP)
“COP27 witnesses the release of at least two very important chapters in the work of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change that provides the international community with the most recent data-based available science on climate change in terms of impact as well as what needs to be done in terms of solutions,” a spokesperson from the COP27 presidency team told Arab News from Cairo.
“We had two reports that were issued, one in February and the second one in April, portraying a very bleak picture about where we are now, about the fact that we are so off track on what needs to be done, and also explaining in detail the adverse impact of climate change on almost every sector and every region in the world.
“It is a sobering moment where we are all converging around scientifically established facts that the window of opportunity is rapidly closing, and there is still so much that needs to be done at scale and on a very timely basis.”
FASTFACTS
COP27 will be held in Egypt’s Red Sea resort town of Sharm El-Sheikh, Nov. 7-18.
Organizers say this year’s summit will focus on mitigation, adaptation, and finance.
A lot has changed since COP26. The war in Ukraine led to a Western embargo on Russian oil and gas, causing a spike in global energy prices. In many countries, still recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic, this has prompted a cost-of-living crisis.
In response to price rises, energy-hungry governments have called on oil and gas producers to boost their output, while others have switched back to the cheaper but far dirtier alternative of coal, setting back the transition to green renewables.
“For this reason, it is crucial that at COP27 we keep reiterating the message that we need continued strength and commitment to the climate agenda,” the COP27 presidency spokesperson said. “The climate response cannot be deprioritized, rescheduled, or put on pause until we do the rest of the firefighting.”
Indeed, organizers say this is the year when governments must move their climate mitigation, adaptation, and financing plans from the negotiating table to real-world application.
“Following progress at COP26 in Glasgow, international efforts enter a critical new phase as we look to COP27 in Egypt: Implementation of the Paris Agreement at the national level,” the spokesperson said.
“It is the implementation COP, the first COP where nations must show how they will, through legislation, policies, and programs, and throughout all jurisdictions and sectors, begin putting the Paris Agreement to work in their home countries.
“COP27 is about supporting all segments of society, including non-party observers, under the banner of ‘inclusive multilateralism’ to drive significantly more climate action. We have spent almost six years negotiating the operational rule book of the Paris Agreement from 2015 and have concluded most of the details.

Eleven days of UN talks in Paris in 2015 have failed to achieve agreement on a climate pact aimed at sparing future generations from worsening drought, flood, storms and rising seas. (AFP file)
“Now is the time when we translate what is being agreed at negotiation tables and conference venues into concrete deliverables on the ground that have preferably a quick impact on the livelihoods of people and that can mitigate the impact and make the ambitions of these deliverables a reality.”
That said, the pressure is on for Egypt and COP27 organizers following a “disappointing” fortnight of talks at the 56th session of the Bonn Climate Change Conference in June.
Delegates representing the world’s developing countries said they were the ones paying the price for climate change brought about by hundreds of years of emissions released by industrialized nations.

Signing of the COP 27 Host Country Agreement by Egyptian FM Sameh Shoukry and UNFCCC Executive Secretary Patricia Espinosa on June 8, 2022 during the Bonn Climate Change Conference. (UN Climate Change photo)
They said their call for a funding facility bankrolled by wealthy nations, to help them cope with the damage caused by extreme weather events and rising sea levels, was blocked by the EU.
“Africa has played almost no role in global warming, yet climate change is having a disproportionate impact, with droughts, flooding, and natural disasters driving famine, instability, and conflict,” Ghada Fathi Waly, director-general of the UN Office on Drugs and Crime, told delegates at the Aswan Forum in Cairo in June.
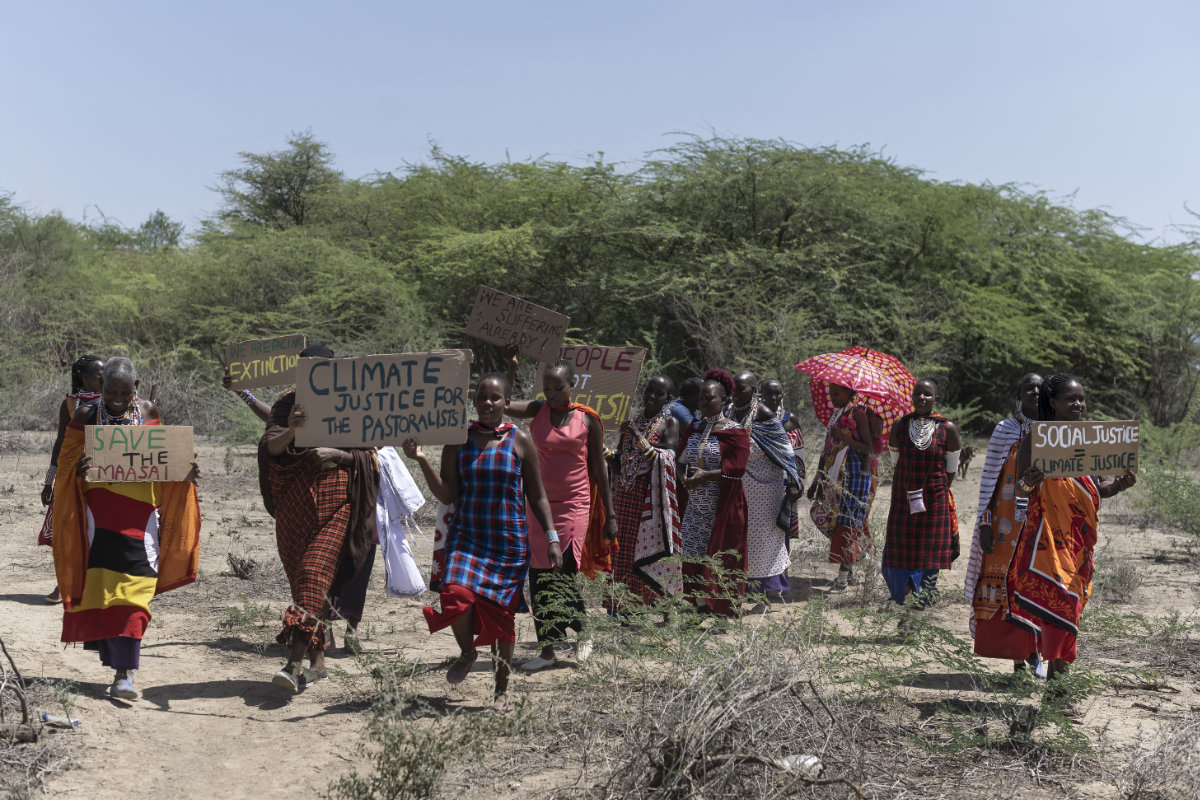

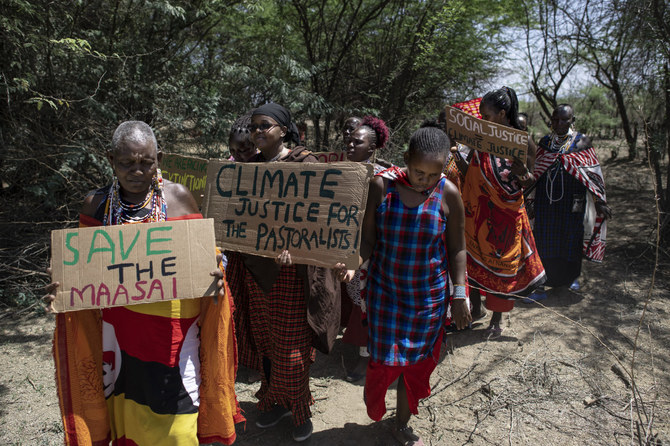
Women from Kenya's Masai community take part in a Global Climate Strike on March 25, 2022 to demand climate reparations and action from world leaders and take genuine climate action. (AFP)
It is hoped that this imbalance can be addressed at COP27. If recent climate research has taught world leaders anything, it is that all nations — whether rich or poor — will pay a far greater price if they fail to collectively take action now.
“The IPCC has warned about the urgency of climate change and the need to take climate action,” Ould-Dada told Arab News. “The costs of inaction would be higher than the costs of action.”






















