LONDON: When a newspaper headline begins with the prefix “revealed,” most readers are sufficiently familiar with media shorthand to know that they are expected to react to the article that follows with surprise, or perhaps even concern.
But when the UK’s Guardian newspaper ran a story in 2020 headlined “Revealed: Saudi Arabia may have enough uranium ore to produce nuclear fuel,” the real surprise was that the story was getting on for 50 years old.
Saudi Arabia’s plans to develop a nuclear energy industry were not hatched overnight or in secret. The reality is that the Kingdom has been slowly, steadily and responsibly treading the complex regulatory and technical path toward the adoption of peaceful nuclear power for decades.
It is clear that having moved cautiously and prudently, the Kingdom is now ready to embrace a technology that has come of age, in an era when access to clean energy has never been more essential.

IAEA Director General Rafael Mariano Grossi. (AFP)
In February, Rafael Mariano Grossi, director general of the International Atomic Energy Agency, told the delegates at a virtual conference in Riyadh that the IAEA was working closely with Saudi Arabia to help the Kingdom develop the infrastructure for a peaceful nuclear energy program.
In March, Prince Abdullah bin Khalid bin Sultan, the Saudi ambassador to Austria and the Kingdom’s governor to the IAEA, announced the establishment of the Saudi Nuclear Energy Holding Company to “develop, own and operate nuclear assets through affiliate or jointly established companies to produce electricity and desalination of saltwater.”
The 2020 Guardian article appeared to refer to a survey begun in 2017 by Saudi and Chinese geologists who, working alongside colleagues from the Geological Survey of Finland, carried out a two-year exploration of sites in the Kingdom potentially rich in uranium — sites that were, incidentally, first identified 50 years ago.
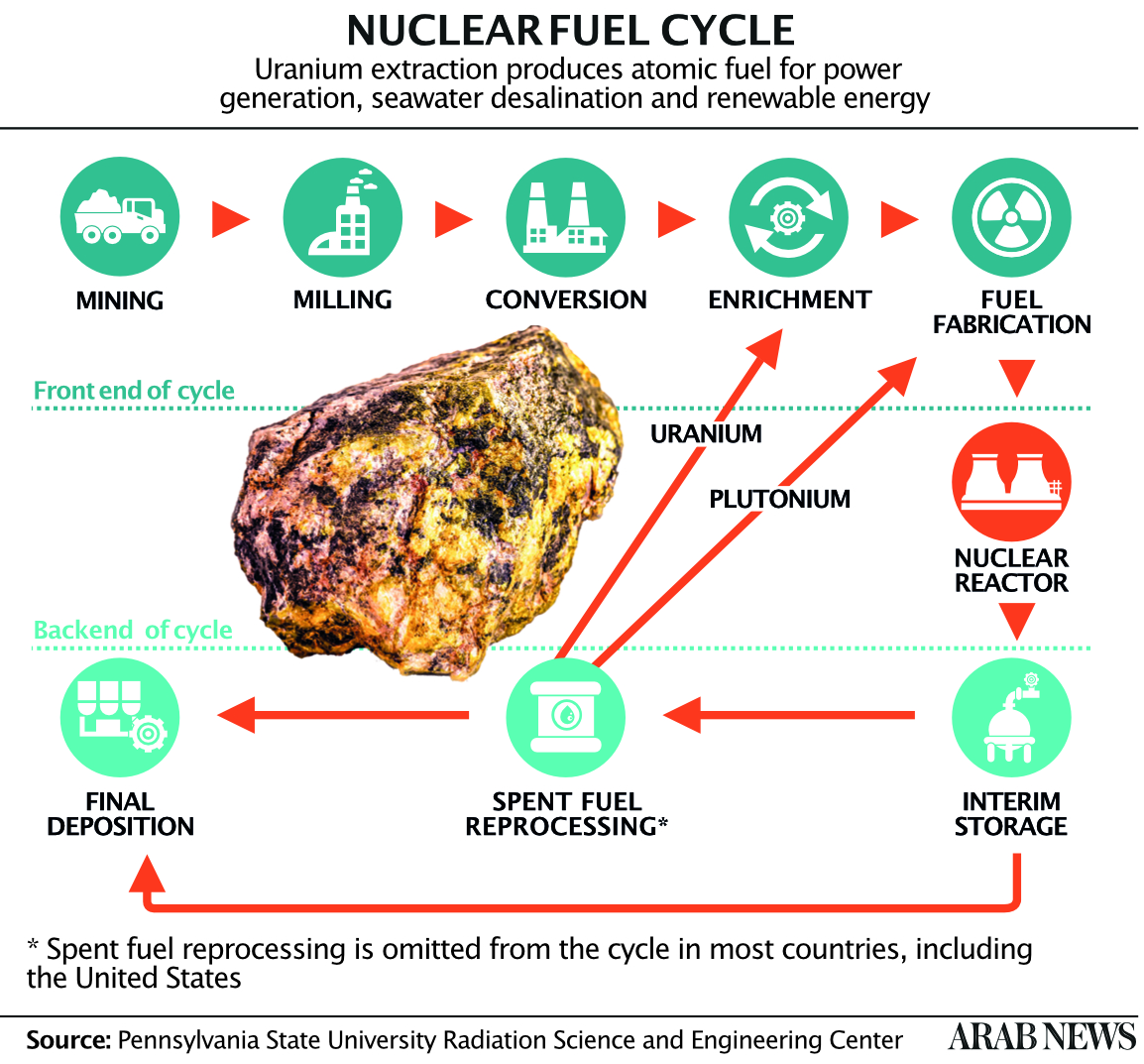
As for what was “revealed” in the story, the details of the research and the findings during its first year were presented openly in a paper delivered to the International Symposium on Uranium Raw Material for the Nuclear Fuel Cycle, which was organized by the IAEA in Vienna in June 2018.
The three co-authors of the paper were all scientists from King Abdullah City for Atomic and Renewable Energy, or K. A. CARE for short. The organization was founded by royal decree in 2010 with “the fundamental aim of building a sustainable future for Saudi Arabia by developing a substantial alternative energy capacity fully supported by world-class local industries.”
Therefore, its creation put the Kingdom firmly ahead of the climate-change curve, with nuclear power among the clean-energy options on the table.
As acknowledged by the creation of K. A. CARE, Saudi Arabia “has a rapidly growing population that places an ever-increasing pressure on the country’s non-renewable hydrocarbon resources.”

It was concluded that “alternative, sustainable and reliable sources of energy for generating power and producing desalinated water should be introduced that will reduce consumption of the nation’s fossil fuel reserves.”
Following “extensive technical and economic analysis,” the decision was taken “to introduce atomic and renewable energy for a significant portion of Saudi Arabia’s future energy mix.”
As the Vienna paper noted in 2018, there has never been any secret about the Kingdom’s uranium stocks, nor its plans to develop self-sufficiency in nuclear fuel for any power-generating reactors the country might build in future.
Geological surveys carried out as early as 1965 suggested the possibility that, alongside the fossil fuels that have so greatly transformed Saudi Arabia since their discovery in the early 20th century, the Kingdom might also be sitting on abundant supplies of the raw nuclear material it would need to continue its economic growth and development in the post-oil era.
It is now 35 years since the Saudi Geological Survey confirmed these vast reserves of uranium, and more than a decade since K. A. CARE was founded in Riyadh to advance the Kingdom’s nuclear agenda, working in close partnership with international bodies. Now those partnerships are close to bearing fruit.

The Saudi Geological Survey confirmed that the existence of vast reserves of uranium in the Kingdom in 1987. (Supplied)
The most important of those bodies is the IAEA, the intergovernmental forum for scientific and technical co-operation in the nuclear field that was set up in 1956 to “accelerate and enlarge the contribution of atomic energy to peace, health and prosperity throughout the world.”
Saudi Arabia has been a member of the IAEA since 1962. In January 2013, Yukiya Amano, at the time the director general of the IAEA, visited the Kingdom to be briefed by Saudi authorities on their plans to introduce nuclear power into their national energy mix.
Since then, the Kingdom has adhered to its commitments and obligations under the IAEA’s “Milestones Approach,” a sequence of three phases beginning with the formal inclusion of nuclear power as an element in a nation’s energy strategy, and culminating in the construction, commissioning and operation of a nuclear plant.
Saudi Arabia has completed phase one, which involved a series of feasibility studies, and phase two, which included the establishment of key organizations along with legal and regulatory frameworks.
Now it has embarked on phase three, during which “activities to contract, license and construct the first nuclear power plant are undertaken,” ending in milestone three: “Ready to commission and operate the first nuclear power plant.”
A commitment to forge ahead with the development of nuclear power was enshrined in the National Energy Program launched in 2016 as part of Saudi Vision 2030’s National Transformation Program. In July the following year, the government approved the Saudi National Atomic Energy Project, and in March 2018 established the Nuclear and Radiological Regulatory Commission.
In July 2018, at the invitation of the Saudi government, a team of nuclear experts from Brazil, Spain and the UK, led by IAEA staff, carried out a 12-day review of Saudi Arabia’s preparations.
Team leader Jose Bastos, technical lead of the IAEA’s Nuclear Infrastructure Development Section, concluded: “Saudi Arabia is well placed to finalize its plans for construction of its first nuclear power plant.”

The King Abdullah City for Atomic and Renewable Energy in Riyadh. (Supplied)
This Integrated Nuclear Infrastructure Review was a significant step and was welcomed in a statement by Khalid Al-Sultan, the president of K. A. CARE.
“The vision of Saudi Arabia 2030 considers nuclear energy as an important source to support stability and sustainable growth,” he said.
The review was “a valuable tool to pinpoint areas of improvement and ensure that the required infrastructures are in place before signing the contract for building the first nuclear power plant in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia,” he added.
In 2019, plans were unveiled for the foundation of the Saudi Nuclear Energy Holding Company, which was formally launched in March this year.
Behind the scenes, a vast amount of technical preparatory work has been under way. Surveys have been carried out to identify and prepare suitable sites for the first two power-generating reactors that will be built — light pressurized water reactors, which are deemed the most suitable technology for the Kingdom’s initial nuclear needs.
Meanwhile work has also begun on what is perhaps the Kingdom’s most dramatic Vision 2030-related project — its first nuclear reactor, which will be a low power research reactor designed “to support a demanding training and human resources development plan and become a tool for research and development.” The foundation stone for this facility was laid by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman at King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology in November 2018.
Just how close Saudi Arabia might be to building its first full-scale reactor became clear in April 2021, when, during an online training course organized for the Kingdom by the IAEA, 50 nuclear regulators, national guards, customs and port authority agents, and other officials from more than 20 Saudi government agencies learned more about their roles as first responders in the event of a radiological or nuclear emergency.
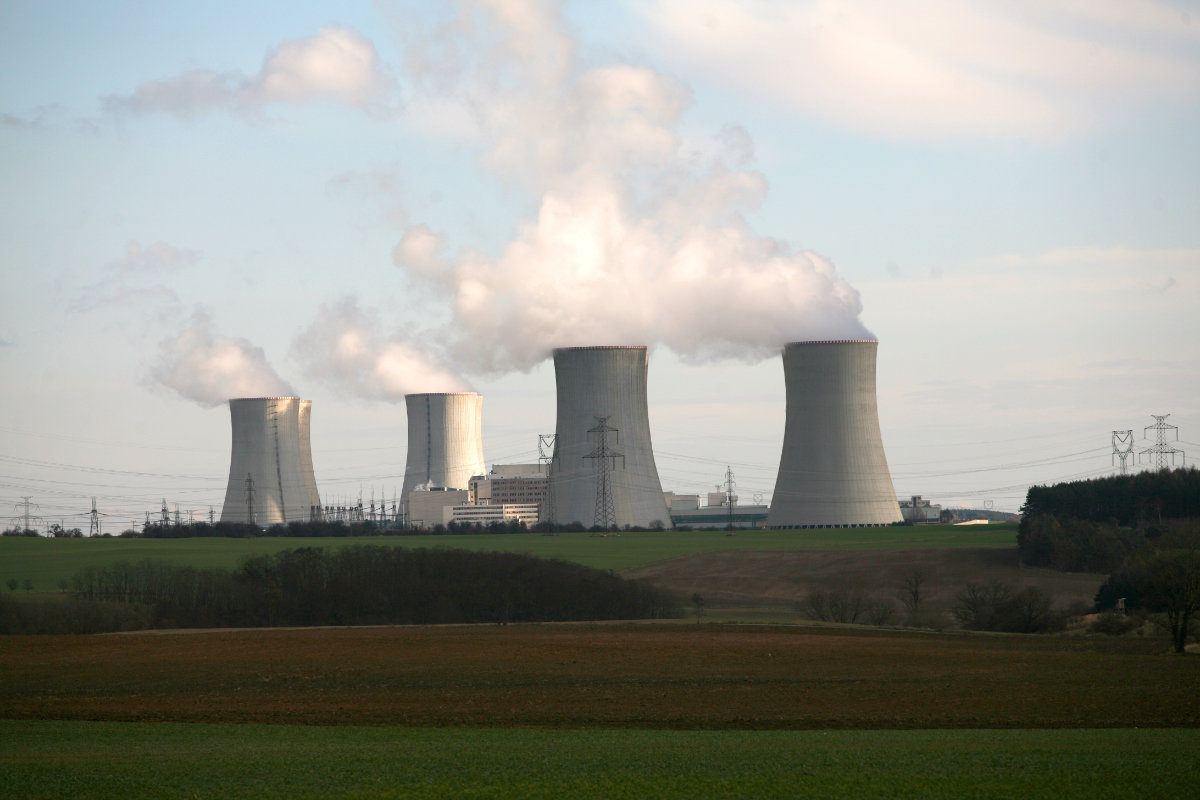

The International Atomic Energy Agency has been informed by Saudi authorities of the Kingdom's plans to introduce nuclear power into their national energy mix. (Shutterstock)
A few months later, in September 2021, Saudi Arabia became the 37th country — and only the third in the region after Egypt and Israel — to join RANET, the IAEA’s Response and Assistance Network. This is a global scheme that allows members to offer and request timely assistance in the event of a nuclear accident or radiological emergency.
Another significant checkpoint was reached in May this year, when UK consultancy firm EY was appointed as “transaction adviser” for Saudi Arabia’s first large-scale nuclear power project — a two-reactor plant that is expected to have a capacity of up to 4 gigawatts, enough to power three million homes.
In keeping with the IAEA’s Milestones Approach, the Kingdom is now ready to invite bids and negotiate contracts for the construction of that plant.
For Saudi Arabia, reaching milestone three — the point at which the first plant can start to operate, pumping clean electricity into the national grid — will be the moment when the nation’s energy-consumption profile will begin to change radically.
And nuclear power can’t come on stream too soon. According to K. A. CARE, at the current rate of growth peak energy demand in Saudi Arabia is expected to exceed 120 gigawatts by 2030, which means there would be a shortfall of 60 gigawatts based on current energy provision.
Nuclear energy is also expected to play an important part in desalination. It is predicted that demand for water by 2030 will be 7 million cubic meters per day, 3 million more than current capacity.
In January, Energy Minister Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman told the World Economic Forum that Saudi Arabia could even use nuclear power to produce hydrogen gas, which burns cleanly but energy is required to extract it from water.

Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman, Saudi Minister of Energy. (Getty Images )
By embracing nuclear power, Saudi Arabia is not only taking steps to head off its own looming energy crisis, it is also contributing to the battle against global warming.
As Sama Bilbao y Leon, the director general of the World Nuclear Association, wrote in her foreword to the World Nuclear Performance Report ahead of the UN Climate Change Conference, COP26, in Glasgow last year: “Anything less (than) achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by the middle of this century … will mean failing to meet the goals set in the Paris Agreement.”
It is, she added, “vital that the contribution made by nuclear generation increases to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels.”
New analysis by the WNA has shown that since 1970, the emission of 72 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide has been avoided through the use of nuclear reactors, compared with the emissions that would have been created had coal-fired generation been used instead.

(Shutterstock image)
Saudi Arabia uses no coal whatsoever to generate power. In 2020 it generated its electricity using a mix of natural gas (61 percent) and oil (39 percent). Of the two, burning gas creates the lower volume of greenhouse gases — and half as much as coal — producing far fewer pollutants in the process.
Nevertheless, both oil and gas contribute significantly to the Kingdom’s carbon footprint, which is why, in January 2021, Prince Abdulaziz said the country is committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2060.
The first major destination on that journey will be reached in 2030, by which time Saudi Arabia aims to source 50 percent of its electricity from renewable sources, including wind, solar and nuclear power.
It is 84 years since the discovery of oil in Dhahran transformed the fortunes of Saudi Arabia. The oil will continue to flow for some years to come, funding the development of the renewable technologies — wind, solar and nuclear — that will eventually consign fossil fuels to history.
But it is uranium — the second gift bestowed, improbably, by the ground upon Saudi Arabia — that will power its economy and light its way into the future.
















