WASHINGTON: Responding to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the United States, the 27-nation European Union and other Western allies announced a round of punitive measures against Russian banks and leading companies and imposed export controls aimed at starving the country’s industries and military of semiconductors and other high-tech products.
From the US to Western Europe and Japan, South Korea and Australia, nations lined up to denounce the Kremlin as the outbreak of fighting raised fears about the shape of Europe to come. The invasion initially sent stocks slumping and oil prices surging on fears of higher costs for food and fuel.
The latest round of sanctions announced Thursday against Russia purposely spares the energy sector to avoid inflicting pain on the Western allies, but officials say they leave room for escalation.
Washington said the penalties will be severe, and will have lasting impact on Russia’s economy, even though they tried to “mitigate” costs on American and European consumers, who already face rising oil prices.
In the meantime, countries began taking steps to isolate Moscow in hopes of forcing it to pay so high a price that it changes course.
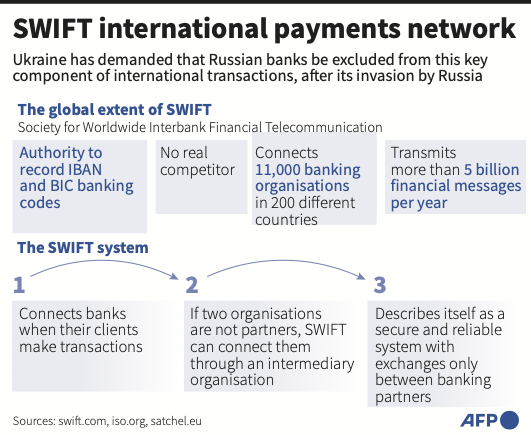
US President Joe Biden, for now, held off imposing some of the most severe sanctions, including cutting Russia out of the SWIFT payment system, which allows for the transfers of money from bank to bank around the globe. Ukraine’s president called for Russia to be cast out of SWIFT, but the US has expressed concern about the potential damage to European economies.
Sanctions target
Here are the highlights of the measures:
The Treasury added five more Russian banks to the sanctions list including country’s the two largest, both majority owned by the government, although each faced penalties with differing severity.
Sberbank, which holds about a third of all bank assets in Russia, will be banned from conducting transactions through the US financial system, through what is known as the Correspondent Account or Payable-Through Account Sanctions (CAPTA) List.
But VTB and three other bank were hit with “full blocking sanctions,” meaning all US-held assets will be frozen.
Asked to explain the rationale behind the differing treatment, a senior administration told reporters the decision was partly due to the fact that VTB “had assets in the United States that we wanted to freeze” denying them to the Kremlin.
On top of previously-announced measures, the official said “the top 10 Russian financial institutions representing nearly 80 percent of Russia’s banking sector and assets value are now under US restrictions.”
However, transactions involving energy, agriculture or medical goods are exempt from the financial prohibitions.
In addition, major state banks and companies, including Gazprom’s oil and natural gas units, were cut off from Western credit markets, joining the debt blockage of the central government announced earlier this week.
Western allies banned exports of key high-tech goods aimed at choking off the Russian military’s capabilities.
The ban targets the defense and aerospace sectors and includes semiconductors, computers, telecommunications, information security equipment, lasers, and sensors.
Washington said the blockade “will cut off Russia’s access to vital technological inputs, atrophy key sectors of its industrial base, and undercut its strategic ambitions.”
The United States, the European Union (EU), Japan, Australia, United Kingdom, Canada, and New Zealand, cooperated on the ban, with more expected to join.
Washington added to the list of Russian oligarchs in government and finance, who officials say “Putin relies on for his wealth and power.”
The officials, including executives at Sberbank and VTB, will have any US assets frozen. The penalties extend to their family members as well, to prevent transferring resources to them.
Isolating Russia’s industry
US Sen. Chris Van Hollen, D-Md., a member of the Foreign Relations Committee, said there was agreement that Congress “stands ready to provide whatever additional resources are needed” as the US supports the Ukraine military and backs the Ukrainian resistance. More funding may be needed from Congress.
Many lawmakers have pushed for the toughest sanctions possible on Russia to stop the invasion. The senator said there’s a recognition “we can continue to build” on those Biden has already announced.
EU leaders held an emergency summit and agreed on sanctions that cover, among other things, the financial, energy and transport sectors and various Russian individuals. In a statement, the leaders said the measures will have “massive and severe consequences” for Russia.
The details will not become available until Friday at the earliest.
“We want to cut off Russia’s industry from the technologies desperately needed today to build the future,” European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said.
Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte said: “It is about the leadership of Russia and being merciless in finances and the economy.”

European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen (center) and European Union leaders gather during a round table meeting at an extraordinary EU summit on Ukraine in Brussels on Feb 24, 2022. (REUTERS)
British Prime Minister Boris Johnson also announced financial restrictions and export controls. In addition, Britain will also prohibit Russia’s flagship airline, Aeroflot, from landing at British airports.
Johnson called the attack on Ukraine “hideous and barbaric” and said of Putin: “Now we see him for what he is — a bloodstained aggressor who believes in imperial conquest.”
Canada imposed sanctions that will target 58 people and entities, including members of Russia’s elite and their families, the paramilitary Wagner Group and major Russian banks. The punitive measures, announced after Prime Minister Justin Trudeau attended a virtual meeting of G-7 industrialized nations, will also cover members of the Russian Security Council, including key cabinet ministers.
In the days before the attack, Germany suspended approval of the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline from Russia.
With Stoltenberg and Johnson, von der Leyen called the invasion a “barbaric” attack on an independent nation that threatened “the stability in Europe and the whole of the international peace order.”
The new US sanctions also targeted the military and financial institutions of Belarus, Ukraine’s neighbor to the north. Russia is using Belarus as a staging ground for troop movements into Ukraine.
Separately, the UN Security Council is expected to vote Friday on a resolution condemning Russia and demanding the immediate withdrawal of all its forces. But Moscow is certain to veto it.
Highlighting a widening rift in superpower relations, China stood alone in failing to condemn the attack and instead accused the United States and its allies of worsening the crisis.
In a clear defense of Moscow, China “called on parties to respect others’ legitimate security concerns.”
Foreign Ministry spokesperson Hua Chunying said that “all parties should work for peace instead of escalating the tension or hyping up the possibility of war” — language China has consistently used to criticize the West in the crisis.
China went further and approved imports of wheat from Russia, a move that could reduce the impact of Western sanctions. Russia, one of the biggest wheat producers, would be vulnerable if foreign markets were closed off.
The possible repercussions extended well beyond economics and geopolitics. The director of the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention worried that the crisis will further distract global attention from helping the world’s least vaccinated continent fight COVID-19.
In New York City, a projection artist is projecting “Stand With Ukraine” and the country’s flag on a wall of the United Nations headquarters. The artist, David Forsee, says he decided to do this because he’s “a concerned person who doesn’t want to be surrounded by nukes.”




















