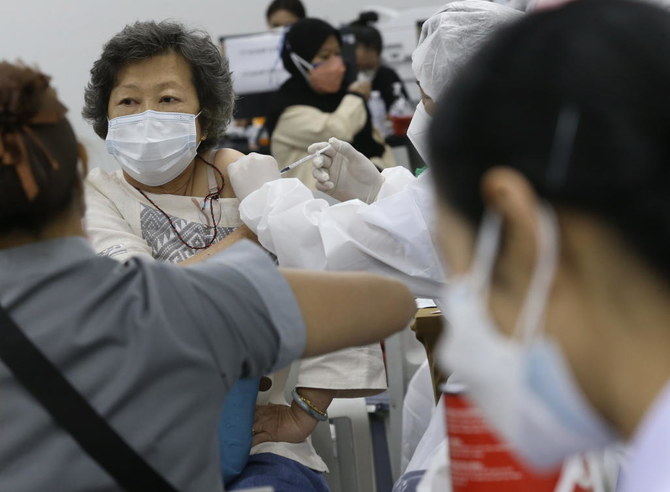
BANGKOK: Thailand will extend the suspension of its quarantine waiver program and bring in new restrictions after a jump in new coronavirus cases linked to the omicron variant, the government’s COVID-19 taskforce said on Friday.
New applications for Thailand’s “Test & Go” quarantine waiver scheme will not be approved until further notice to stem the increase of coronavirus infections, said Taweesin Visanuyothin, the spokesman of the COVID-19 taskforce.
But existing applicants can still enter Thailand without quarantine until Jan. 15, he said.
“We can still make changes if the situation improves, but for now we have to learn more about omicron,” Taweesin said.
Due to concerns over omicron, Thailand had halted the waiver program since Dec. 22 and also most of its “sandbox” schemes, which requires visitors to remain in a specific location for seven days but allows them free movement during their stay, except for the resort of Phuket.
But from Jan. 11, Thailand will allow quarantine-free entry into the country via the previously suspended sandbox schemes of Samui Plus, Phang Nga, and Krabi, Taweesin said.
Thailand would also lift on Jan. 11 an entry ban on people traveling from eight African countries it had designated as high-risk.
To curb local virus transmissions, alcohol consumption in restaurants will be halted after 9 p.m. in eight provinces including the capital Bangkok from Sunday, and banned in the country’s other 69 provinces, Taweesin said.
“Social drinking is the cause of the virus spread. Measures to restrict this will help curb the spread,” he said.
Thailand reported 7,526 cases of the coronavirus on Friday, the highest number since early November and more than double the number on Jan. 1.
“If we just let it happen, cases could reach 30,000 a day by the end of the month,” said Taweesin.


Thailand announces more coronavirus curbs after jump in cases
Short Url
https://arab.news/jwc6v
Thailand announces more coronavirus curbs after jump in cases

- New applications for Thailand’s ‘Test & Go’ quarantine waiver scheme will not be approved until further notice to stem the increase of coronavirus infections
DR Congo city residents forced to adapt during year of M23 rule

- Around one million Goma residents were holed up in their homes on Jan. 26, 2025, when the Congolese army and its allies were forced to pull out of the provincial capital
GOMA, DR Congo: They were caught under a barrage of fire and became trapped with “nowhere to go” after their city in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo fell under the M23 armed group’s control a year ago.
Around one million Goma residents were holed up in their homes on January 26, 2025, when the Congolese army and its allies were forced to pull out of the provincial capital.
Hundreds of Rwandan soldiers had just poured across the border to fight alongside the M23 in a lightning offensive to seize the lakeside city.
Thousands of people were killed in the intense clashes.
Janvier Kamundu, whose name has been changed for security reasons, was sheltering from the fighting at home with his wife and children.
“Suddenly I heard my wife cry out. She fell, hit by a stray bullet,” he recalled.
Neighbors braved the gunfire to come and help, and a vehicle was found to transport his wife to hospital, ultimately saving her life.
Hospitals were overwhelmed with the wounded and bodies covered in white bags piled up at the morgues.
“She is slowly recovering, but it isn’t easy — she has a lot of wounds around her stomach,” Kamundu said.
Oppressive quiet
A year on, Goma residents endure “constant oppression” by the M23 group, government spokesman Patrick Muyaya said.
In the weeks that followed its capture, the streets emptied out at nightfall and the buzz evaporated from the bars that had once offered some respite in a region scarred by three decades of conflict.
Escaped prisoners, militia fighters and soldiers who had evaded capture roamed the city after dark, breaking into homes and threatening residents.
With the police and court system no longer functioning, the M23 eventually began to systematically cordon off neighborhoods in search of criminals.
By late May, several hundred men were sitting on the dark volcanic gravel covering the streets of Murambi village on Goma’s northern outskirts, watched over by members of the M23.
Local leaders and families are ordered to identify those they recognize as upstanding citizens. The others are detained.
Rough justice
But on the street, anyone deemed suspicious looking drew the M23’s ire.
People spoke of those who had been hauled off to the city sports stadium serving as an open-air prison for wearing dirty clothes or having an untidy beard.
An M23 spokesman invited reporters on several occasions to view the results of the operation — detainees separated into categories.
Desperate families crowded at the entrance, pleading to get their relatives released.
Those not cleared by testimony deemed reliable ended up at secret detention sites. NGO reports denounced torture and summary executions.
But, in time, residents and observers agreed that Goma’s streets were returning to relative safety.
With no independent justice system in place, opponents of the M23 faced repression, some accused of being in cahoots with the pro-government militia.
In October, the armed group — whose declared aim is to overthrow the government and end corruption — began appointing magistrates, but observers indicated there was little impartiality.
Despite parallel peace efforts backed by the United States and Qatar, the M23 launched a new offensive on the strategic town of Uvira near the Burundi border in December.
“These events have shown that the Rwandan president is not at all comfortable with peace processes,” Muyaya, the government spokesman, said.
‘Ideological training’
Most civil society representatives and rights campaigners had fled Goma before the M23 entered.
Civilians and former government combatants were forcibly recruited by the M23, which announced it had 7,000 new members in its ranks in September.
At the same time, the group began to impose taxes to finance its war effort but the city, already on its knees, has had no functioning banks for a year after the government ordered their closure to cut off the rebellion’s funding.
The airport remains inaccessible and trade between Goma and areas under government control has dwindled.
Civil servants were among the first to feel the blow of such cuts.
“There were about 200 agents here; around 20 left to work” in government-held areas, urban planning officer Claude Mumbere said.
“The others are here doing nothing,” added the officer, whose name has also been modified for security reasons.
Some had to undergo “ideological training” provided by the M23.
Mother-of-three Madeleine Mubuto’s husband lost his job.
“We had set aside a small amount of money at home that helped us at first, but after a year almost all of it is used up,” she said.
In the absence of cash, Rwanda’s currency is now used at Goma’s markets.
“Many are wondering how long this situation is going to last,” Kamundu said, adding: “We adapt because we have nowhere to go.”
Around one million Goma residents were holed up in their homes on January 26, 2025, when the Congolese army and its allies were forced to pull out of the provincial capital.
Hundreds of Rwandan soldiers had just poured across the border to fight alongside the M23 in a lightning offensive to seize the lakeside city.
Thousands of people were killed in the intense clashes.
Janvier Kamundu, whose name has been changed for security reasons, was sheltering from the fighting at home with his wife and children.
“Suddenly I heard my wife cry out. She fell, hit by a stray bullet,” he recalled.
Neighbors braved the gunfire to come and help, and a vehicle was found to transport his wife to hospital, ultimately saving her life.
Hospitals were overwhelmed with the wounded and bodies covered in white bags piled up at the morgues.
“She is slowly recovering, but it isn’t easy — she has a lot of wounds around her stomach,” Kamundu said.
Oppressive quiet
A year on, Goma residents endure “constant oppression” by the M23 group, government spokesman Patrick Muyaya said.
In the weeks that followed its capture, the streets emptied out at nightfall and the buzz evaporated from the bars that had once offered some respite in a region scarred by three decades of conflict.
Escaped prisoners, militia fighters and soldiers who had evaded capture roamed the city after dark, breaking into homes and threatening residents.
With the police and court system no longer functioning, the M23 eventually began to systematically cordon off neighborhoods in search of criminals.
By late May, several hundred men were sitting on the dark volcanic gravel covering the streets of Murambi village on Goma’s northern outskirts, watched over by members of the M23.
Local leaders and families are ordered to identify those they recognize as upstanding citizens. The others are detained.
Rough justice
But on the street, anyone deemed suspicious looking drew the M23’s ire.
People spoke of those who had been hauled off to the city sports stadium serving as an open-air prison for wearing dirty clothes or having an untidy beard.
An M23 spokesman invited reporters on several occasions to view the results of the operation — detainees separated into categories.
Desperate families crowded at the entrance, pleading to get their relatives released.
Those not cleared by testimony deemed reliable ended up at secret detention sites. NGO reports denounced torture and summary executions.
But, in time, residents and observers agreed that Goma’s streets were returning to relative safety.
With no independent justice system in place, opponents of the M23 faced repression, some accused of being in cahoots with the pro-government militia.
In October, the armed group — whose declared aim is to overthrow the government and end corruption — began appointing magistrates, but observers indicated there was little impartiality.
Despite parallel peace efforts backed by the United States and Qatar, the M23 launched a new offensive on the strategic town of Uvira near the Burundi border in December.
“These events have shown that the Rwandan president is not at all comfortable with peace processes,” Muyaya, the government spokesman, said.
‘Ideological training’
Most civil society representatives and rights campaigners had fled Goma before the M23 entered.
Civilians and former government combatants were forcibly recruited by the M23, which announced it had 7,000 new members in its ranks in September.
At the same time, the group began to impose taxes to finance its war effort but the city, already on its knees, has had no functioning banks for a year after the government ordered their closure to cut off the rebellion’s funding.
The airport remains inaccessible and trade between Goma and areas under government control has dwindled.
Civil servants were among the first to feel the blow of such cuts.
“There were about 200 agents here; around 20 left to work” in government-held areas, urban planning officer Claude Mumbere said.
“The others are here doing nothing,” added the officer, whose name has also been modified for security reasons.
Some had to undergo “ideological training” provided by the M23.
Mother-of-three Madeleine Mubuto’s husband lost his job.
“We had set aside a small amount of money at home that helped us at first, but after a year almost all of it is used up,” she said.
In the absence of cash, Rwanda’s currency is now used at Goma’s markets.
“Many are wondering how long this situation is going to last,” Kamundu said, adding: “We adapt because we have nowhere to go.”
© 2026 SAUDI RESEARCH & PUBLISHING COMPANY, All Rights Reserved And subject to Terms of Use Agreement.