MISSOURI, USA: On Aug. 2, 1990, the Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein ordered his army to invade and capture Kuwait. This ill-fated decision forever changed Iraq and the lives of all Iraqis and the first coalition war against Iraqi began on Jan. 16, 1991.
Some 30 years later, we are still assessing the consequences of the invasion of Kuwait. As part of its special coverage of the Gulf War, Arab News has done a deep dive into the topic to produce a multimedia feature titled Desert Storm: 30 years on.
Iraq between 1991 and 2003 suffered tremendously under international sanctions. Although the “Oil for food” UN program was designed to make sure no Iraqis went hungry under the sanctions, Saddam’s regime prevented food and medicine from reaching dissident populations still under his control (particularly Shiites).
As a result, some 500,000 Iraqi children are estimated to have died preventable deaths during this period. The brutal dictatorship that terrorized all Iraqis finally fell in the 2003 installment of the Gulf War. For a brief moment it seemed life would get better for the citizens of a country with one of the world’s largest proven oil reserves.
The successful coalition military campaign quickly degenerated, however, into a disastrous occupation. One event in particular came to symbolize everything the Americans did wrong in their occupation of Iraq: the scandal surrounding American treatment of Iraqi prisoners in the infamous Abu Ghraib prison near Baghdad.
First came the very fact that the Americans chose the Abu Ghraib prison to house close to 4,000 prisoners (mostly Sunni Arabs suspected of participating in the post-2003 insurgency against the coalition occupation regime). Abu Ghraib had been infamous during Saddam’s reign, akin to Iran’s Evin prison in Tehran. Long before 2003, “getting sent to Abu Ghraib” stood out as one of the worst fates someone could face in Iraq.
Follow our special coverage of Iraq
Instead of assuaging already suspicious Iraqis and reassuring them that post-Saddam Iraq would be different, the Americans simply took over Abu Ghraib and began using it much as Saddam had. Coalition forces likewise installed themselves in Saddam’s palaces (including the “Green Zone” in Baghdad), turning them into their new administrative headquarters for the occupation.
For many Iraqis, the message seemed clear: The Americans were the new Saddam, except this time Sunnis would take the place of Shiites and Kurds as Iraq’s oppressed groups. Just in case anyone remained unsure about Iraq’s new dictators, the Abu Ghraib scandal broke in April of 2004.
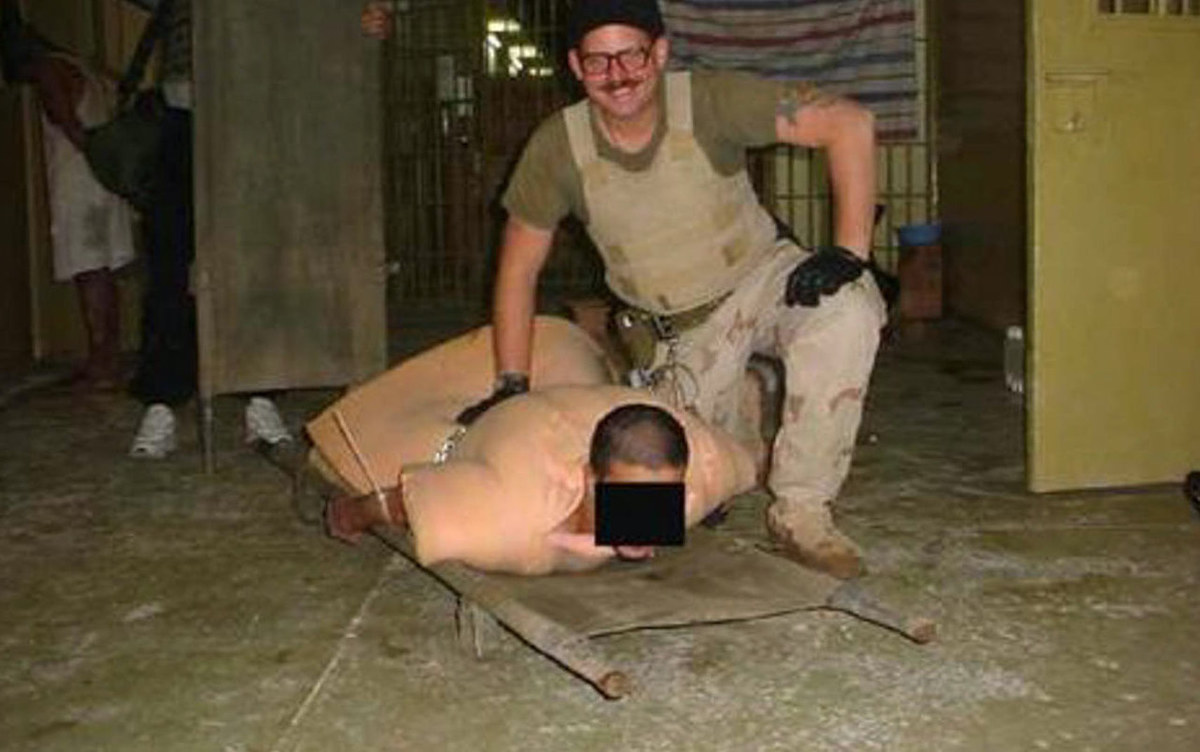

The evidence of the torture and humiliation of Iraqis swelled the ranks of militant groups and fueled the insurgency in the country. (Alamy Stock Photos)
It began with the death of an Iraqi detainee being interrogated at the prison. Soon after, a US soldier discovered a CD-ROM disc in the prison with photos of prisoner abuse. He reported this to his superiors, who began an investigation (as is standard operating procedure for such reports).
The news program “60 Minutes” soon obtained the graphic photos of detainees being tortured by their American guards and broadcast a story on the matter.
The photos of the abuse of prisoners at Abu Ghraib shocked the world. CNN summarized the types of abuse as follows:
- Punching, slapping and kicking detainees; jumping on their naked feet.
- Videotaping and photographing naked male and female detainees.
- Forcibly arranging detainees in various explicit positions for photographing.
- Forcing detainees to remove their clothing and keeping them naked for several days at a time.
- Forcing naked male detainees to wear women’s underwear.
- Photographing and videotaping groups of male detainees in humiliating acts.
- Arranging naked male detainees in a pile and then jumping on them.
- Positioning a naked detainee on a box, with a sandbag on his head, and attaching wires to his fingers, toes and other extremities to simulate electric torture.
- Writing “I am a Rapest (sic)” on the leg of a detainee accused of rape, and then photographing him naked.
- Placing a dog chain or strap around a naked detainee’s neck and having a female soldier pose for a picture.
- A male military police guard violating a female detainee.
- Using military working dogs (without muzzles) to intimidate and frighten detainees, and in at least one case biting and severely injuring a detainee.
- Taking photographs of dead Iraqi detainees.
Although most people think of Iraq as a very hot country, much of this torture occurred in December 2003 — when temperatures in an unheated prison get quite cold and damp. Keeping the prisoners naked under such conditions, in addition to various forms of humiliation, stress positions, sleep deprivation, cold-water, high-pressure hoses, physical abuse and psychological abuse, certainly amounted to torture.
By early May of 2004, George W. Bush, then US president, appeared before news cameras around the world disavowing the abuse of prisoners and his regret “for the humiliation suffered.” The damage had already been done, however, as the evidence of torture and humiliation of Iraqis swelled the ranks of militant groups and fueled the insurgency in the country.

Former US President George W. Bush
If the torture of prisoners in Abu Ghraib was intended to save coalition lives by forcing prisoners to divulge information about the Iraqi insurgents, it had very much the opposite effect. Responsibility for the whole sorry episode never ended up reaching very high up the American chain of command.
Although Donald Rumsfeld, who was secretary of defense at the time, testified before the US Congress and Senate, neither he nor President Bush or Vice-President Cheney were ever really blamed.
The narrative that emerged instead was one of a few “bad apples” on the night guard shift at Abu Ghraib. Low-level soldiers and civilian contractors received demotions, reprimands and prison sentences of a few months. The highest official sanctioned for the abuse was Janis Karpinski, the brigadier general in charge of several prisons in Iraq. She was rotated out of Iraq and demoted to colonel.
Follow our special coverage of Iraq
For a country that prides itself on its human-rights standards and frequently chides foreign leaders from a moral high ground, this looked like a hypocritical outcome. Many thought it unlikely that higher level officers and government officials did not know what was going on in Abu Ghraib prison.
At the very least, President Bush, Vice-President Cheney and Defense Secretary Rumsfeld created the kind of standard operating procedures and climate that allowed Abu Ghraib to occur. They insisted on calling captured militants “enemy combatants” rather than “prisoners of war” so that they could send them to Guantanamo Bay without formal charges or Geneva Convention protections.

Former US Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld
On other occasions they sent the captured fighters on secret flights to Egypt or secret CIA detention centers in Eastern Europe so they could be tortured there, far from the light of the world. They engaged in various forms of sophistry to classify things like water boarding “enhanced interrogation” rather than torture.
In the end, all of this hurt rather than helped the American cause. Such abuses gave the insurgents in Iraq the oxygen they needed to survive several more years than they should have. Some of the insurgents even eventually morphed into the self-proclaimed Islamic State or Daesh.
To be certain, some of the outcomes from Saddam’s 1990 blunder turned out for the better. Iraqi Kurds in particular found an opportunity to emerge from the ashes of Saddam’s genocidal policies against them in the 1980s.
The unacceptable risk that Saddam’s nuclear weapons program would have posed to the world — a program which was just a few years short of completion in 1990 — receded. However, as with almost all watershed moments in a country’s historical trajectory, the positive changes found themselves weighed down by the bad.
• David Romano is Thomas G. Strong Professor of Middle East Politics at Missouri State University
















