ZAATARI REFUGEE CAMP, Jordan: For Um Ali, a 73-year-old Syrian woman living in a refugee camp in Jordan, being vaccinated against COVID-19 was a moment of overwhelming emotion.
“I really feel more secure now from the corona that has added a lot to our burdens,” the mother-of-five said, her eyes filling with tears. “For an old woman of my age, receiving the vaccine was such a great blessing. Thank you Jordan.”
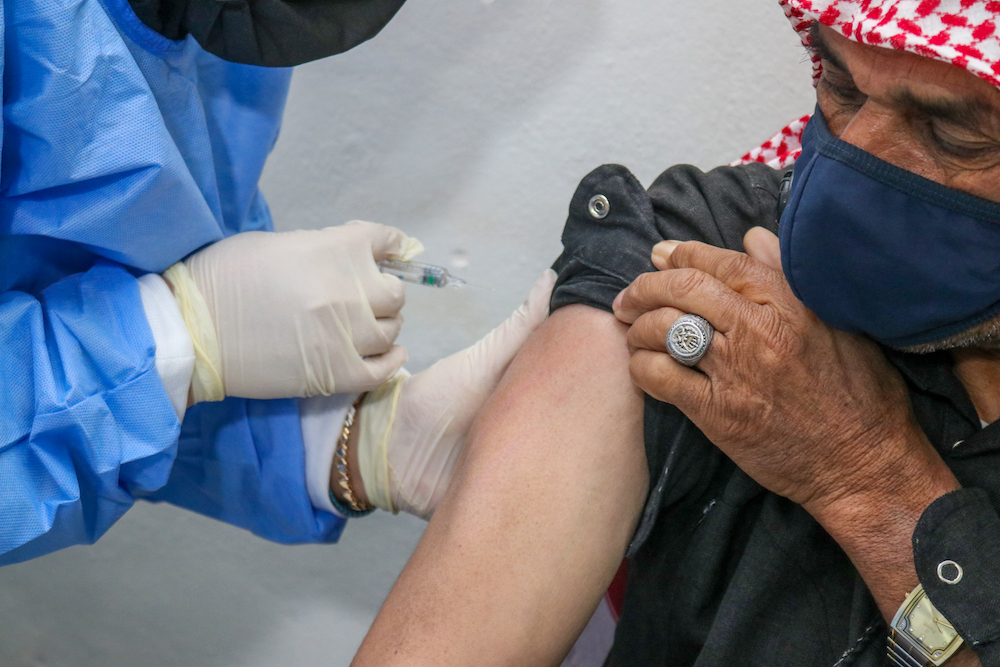
Um Ali was vaccinated against the disease on Monday at the sprawling Zaatari refugee camp, which is on Jordan’s border with Syria. Her jab was part of an inoculation drive that got underway this week at the camp, which is home to 80,000 displaced Syrians.
As the world’s wealthy countries race ahead with vaccinating their populations, Jordan has begun delivering the jab to some of the most vulnerable, those driven from their homes by the turmoil that has shaken parts of the Middle East in the last 10 years.
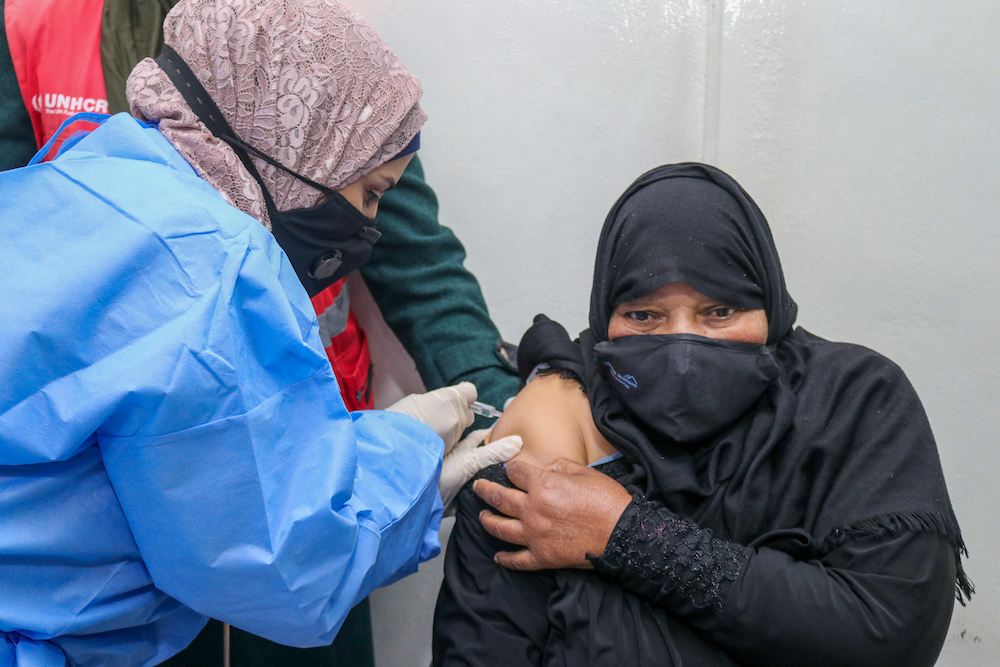

Zaydeh, 64, a Syrian refugee living in Zaatari camp receives her COVID-19 jab. (Raed Omari)
“Jordan is the first country in the world to include refugees in its nationwide COVID-19 vaccination drive,” Mohammad Hawari, spokesman in Jordan for the UN’s refugee agency (UNHCR), told Arab News. “The vaccination centre in Zaatari is also the first in the world at a UN-administered refugee camp.”
Jordan started vaccinating its population on Jan. 13 and, within three days, Raia Al-Kabasi, an Iraqi living in Jordan’s second largest city of Irbid, became the first refugee in the kingdom to receive the jab.
In a country which has, throughout its history, become home to huge refugee populations, it was a moment of great significance.
“We just want life to be back to normal,” Al-Kabasi said. “The vaccine is the right way of doing this.”
Ibrahim, 72, a Syrian refugee living in Zaatari camp receives her COVID-19 vaccine. (Raed Omari)
Hawari said that a total of 52 Syrian refugees were vaccinated on Monday and another 44 on Tuesday. He said the drive was going smoothly.
The camp, one of the world’s largest, has recorded around 2,000 COVID-19 infections since the start of the pandemic.
Hawari added that 2,000 Syrian refugees had signed up with the government to receive the jab. Of these, 1,200 qualified under the kingdom’s priority system for the elderly, health workers, and those with chronic health conditions.
The vaccines were administered by Jordanian health authorities and the National Center for Security and Crisis Management, with the UN providing logistical and administrative support.
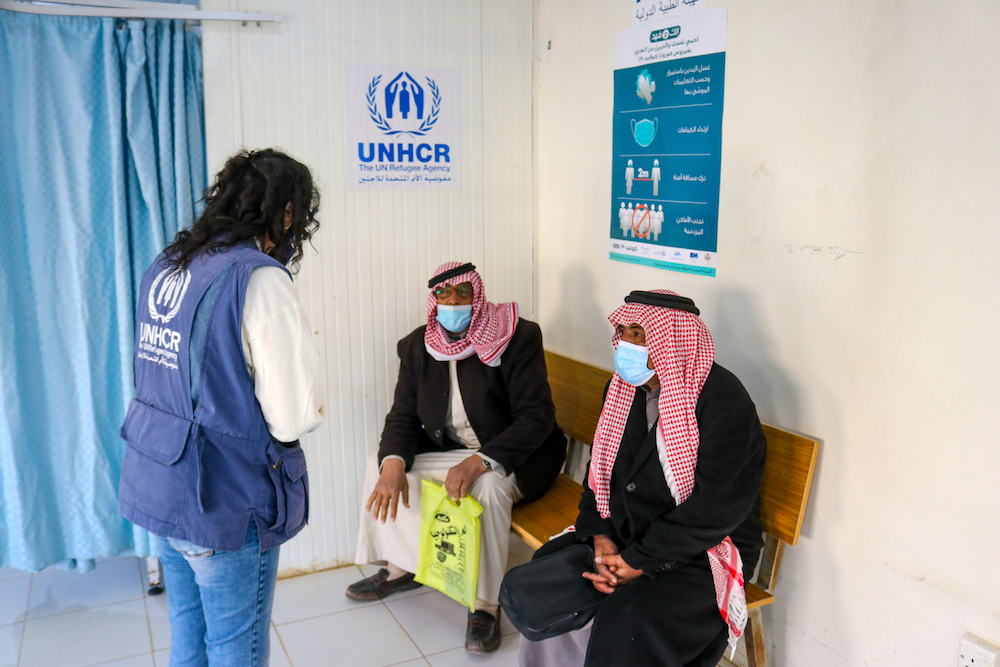

A UNHCR worker talks with two elderly Syrian men at the camp. (Raed Omari)
Despite spending another cold winter in the camp, refugees spoke of their relief and gratitude for being able to receive the jab.
Ibrahim Elhamad, 69, arrived in Jordan in 2012 as the conflict in Syria was unfolding.
“I feel really privileged to receive the vaccine in a refugee camp when other people in advanced countries are unable to,” he told Arab News.
Jordanian officials have said that everyone living on Jordanian soil, including refugees and asylum seekers, are entitled to receive the vaccine for free. It plans to immunize 20 percent of its 10 million population by the end of the year.

Yahya, 65, a Syrian refugee living in Zaatari Camp has his temperature taken before receiving his COVID-19 vaccine. (Raed Omari)
Hawari said that Syrian refugees in urban centers in Amman, Zarqa, Irbid and Ramtha would also receive COVID-19 vaccines.
“In fact, the vaccines will be given to all refugees and asylum seekers of different nationalities living in Jordan.”
According to the UNHCR, around 10 percent of Jordan’s population are refugees.
Among them are 655,000 Syrians, 67,000 Iraqis, 15,000 Yemenis, 6,000 Sudanese and 2,500 refugees from 52 other nations. More than 80 percent of them live outside refugee camps, in cities and towns.

Omar, 65, a Syrian refugee living in Zaatari Refugee Camp receives his COVID-19 vaccine. (Raed Omari)
“In also vaccinating refugees, Jordan has again proved that humanity is at the heart of its policies and decisions, especially when it comes to refugees' lives and dignity,” Hawari said.
Last month, the UN High Commissioner for Refugees Filippo Grandi said Jordan had set an example of how tackling the coronavirus “should be done if we are to keep everyone safe.”
Jordan has included refugees in its national response plan since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
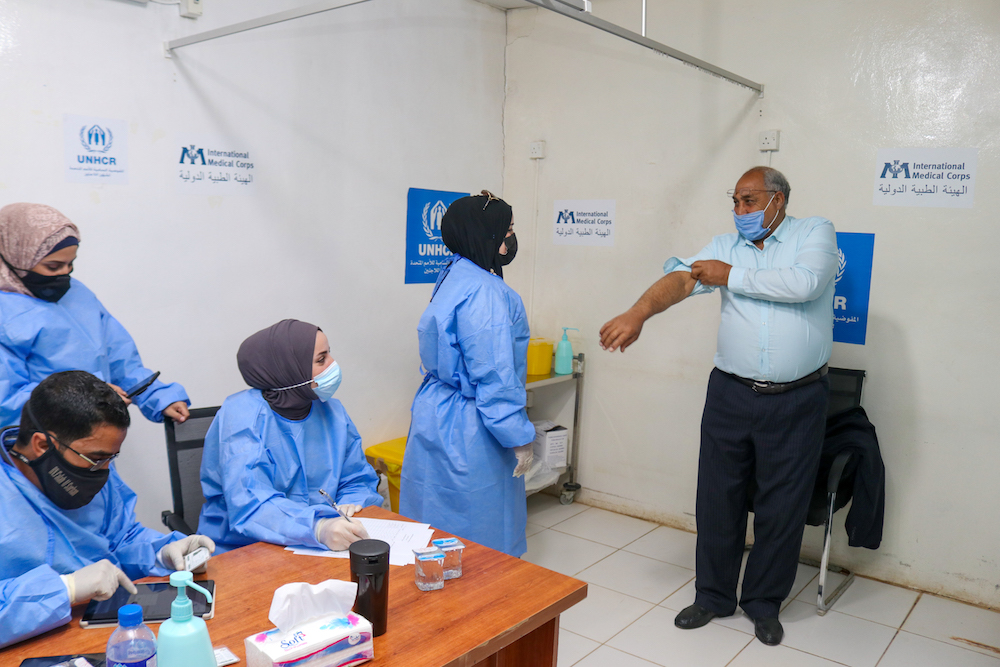

Doctors and nurses help refugees prepare to receive their COVID-19 vaccine in Zaatari camp. (Raed Omari)
Dominik Bartsch, the UNHCR’s representative to Jordan, recently said: “Reducing the spread of COVID-19 now necessitates that the most vulnerable people in our society and around the world can access vaccines, no matter where they come from.”
This year UNHCR Jordan is appealing for $370 million to help refugees, to cope with the additional challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.













