DUBAI: More than 100 years on, Armenians and experts alike remember the brutal atrocities and forced exodus from what is now Turkey, which left up to 1.5 million Armenians dead.
DUBAI: More than 100 years on, Armenians and experts alike remember the brutal atrocities and forced exodus from what is now Turkey, which left up to 1.5 million Armenians dead.
April 24 marks the start, in 1915, of the Armenian Genocide. “Every Armenian is affected by the repeated massacres that occurred in the Ottoman Empire as family members perished,” said Joseph Kechichian, senior fellow at the King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies in Riyadh.
“My own paternal grandmother was among the victims. Imagine how growing up without a grandmother — and in my orphaned father’s case, a mother — affects you,” he added.
“We never kissed her hand, not even once. She was always missed, and we spoke about her all the time. My late father had teary eyes each and every time he thought of his mother.”
Every Armenian family has similar stories, said Kechichian. “We pray for the souls of those lost, and we beseech the Almighty to grant them eternal rest,” he added.
“We also ask the Lord to forgive those who committed the atrocities and enlighten their successors so they too can find peace,” he said. “Denial is ugly and unbecoming, and it hurts survivors and their offspring, no matter the elapsed time.”
Donald Miller, professor of religion and sociology at the University of Southern California, said: “The ongoing denial of the genocide by the government of Turkey pours salt into the wound of the moral conscience of Armenians all over the world. On April 24, the genocide will be commemorated all over the world.”
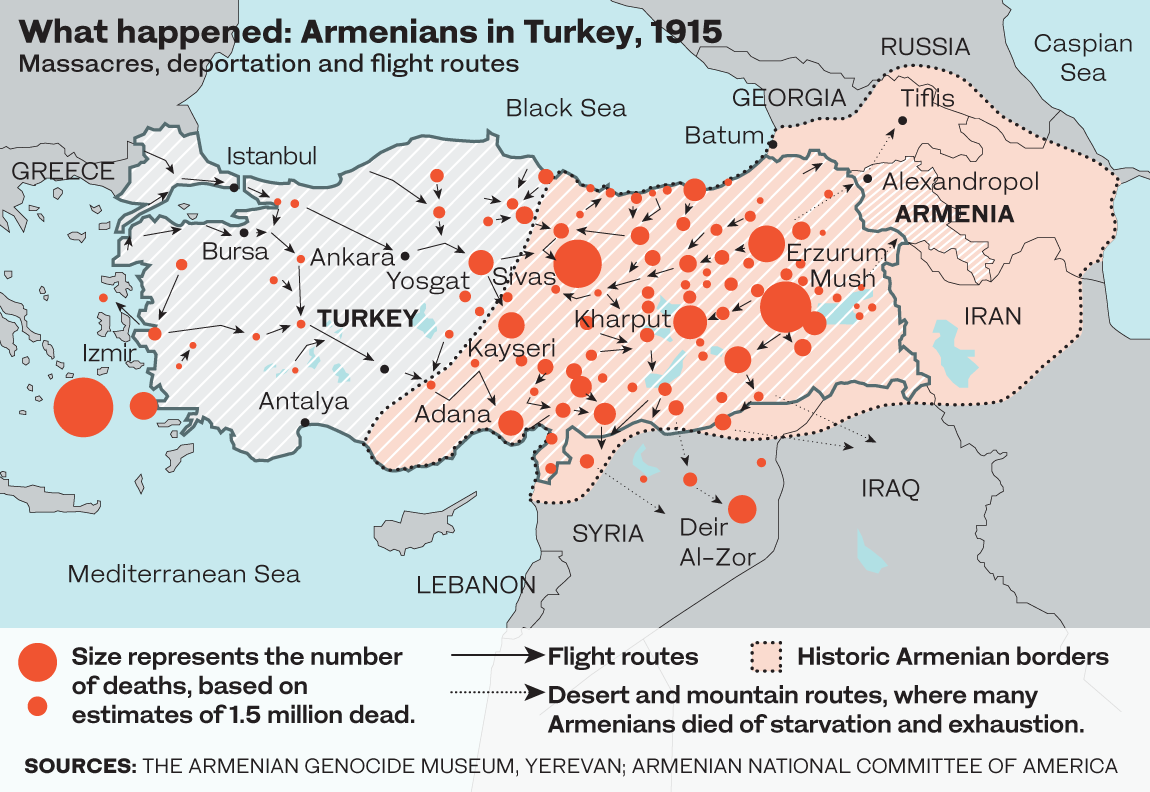
On that day, the Ottoman government arrested and executed several hundred Armenian intellectuals.
Ordinary Armenians were then turned away from their homes and sent on death marches through the Mesopotamian desert without food or water.
Ottoman killing squads massacred Armenians, with only 388,000 left in the empire by 1922 when the genocide ended, from 2 million in 1914.
Many were deported to Syria and the Iraqi city of Mosul. Today they are scattered across the world, with large diasporas in Russia, the US, France, Argentina and Lebanon.
To date, only 28 countries have officially recognized the tragedy as a genocide. The only Arab country that has done so is Lebanon, although a bill is pending in Egypt’s Parliament to do so as well, while Muslim clerics in Iraq have called on Turkey to end the denial.
“The other significant consequence of the Armenian Genocide is the denial that successive Turkish governments have practiced, even though the last Ottoman rulers acknowledged it and actually tried a number of officials who were found guilty,” Kechichian said.
“Denial translates into a second genocide, albeit a psychological one. Eventually, righteous Turks — and there are a lot of them — will own up to this dark chapter of their history and come to terms with it, but it seems we’re not there yet.”
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
For some 3,000 years, Armenians had made their home in the Caucasus, with Christianity their official religion. During the 15th century it became a part of the Ottoman Empire, whose rulers were Muslim.
Soon enough, Armenians were viewed as “infidels,” having to pay higher taxes than Muslims and with very few political and legal rights.
Despite this the Armenian population thrived, causing great resentment among their Turkish neighbors.
And shortly after World War I began, atrocities against Armenians started taking place, with crucifixions, drownings, live burnings and mass murders.
 Some children were kidnapped, converted to Islam and given to Turkish families. Meanwhile, women were raped and forced to join Turkish “harems” or work as slaves, and Armenian properties were seized.
Some children were kidnapped, converted to Islam and given to Turkish families. Meanwhile, women were raped and forced to join Turkish “harems” or work as slaves, and Armenian properties were seized.
“The Armenian Genocide was the first major calamity that hit an entire nation in the 20th century,” Kechichian said.
“Although the term genocide wasn’t in use at the time — it was coined by Raphael Lemkin in his 1944 book ‘Axis Rule in Occupied Europe’ — the Polish attorney applied it to the Armenian case.”
Turkey still denies the persecution of Armenians after World War I. But Hamdan Al-Shehri, a political analyst and international scholar in Saudi Arabia, said: “We know that the genocide happened. The Ottoman Empire in that era conducted many massacres against many people, including Arabs and Armenians.”
He compared the situation to that of Turkey today, with its President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. “We still see that he wants to have his empire again,” Al-Shehri said. “He thinks he’s the sultan of that empire.”
Al-Shehri also drew a parallel with Iran and the Persian Empire. “They (Iran) want to control the whole region, so they’re living with that era in their mind and (trying) to apply it on the ground,” he said.
“This is the difference between us and them — they don’t want to leave countries alone, and this is what we’re facing with Iran.”
Dr. Theodore Karasik, senior advisor at Gulf State Analytics, said the Armenian Genocide remains a “contentious” issue because of “the acrimonious debate over how to define genocide, particularly from the Turkish point of view. Ankara doesn’t recognize genocide because of many reasons, all of them extremely poor.”