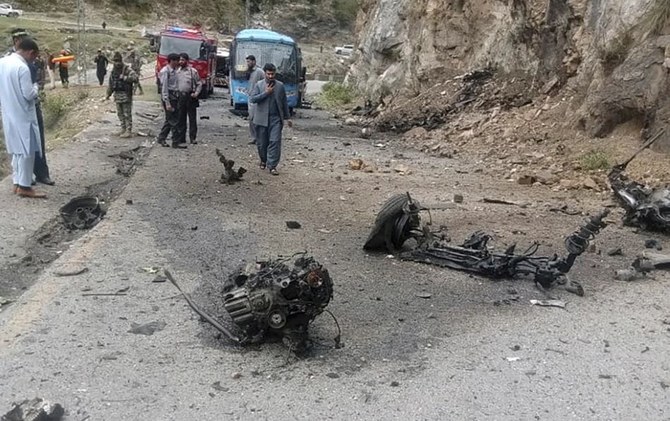
BOGOTA: Colombia’s ELN rebel group was responsible for the car bomb attack against a police academy that killed at least 21 and injured dozens, Defense Minister Guillermo Botero said on Friday.
In Thursday’s attack, which the government described as an act of terrorism, the car broke through checkpoints into the grounds of the General Santander School before it detonated, shattering windows of apartments nearby.
The National Liberation Army (ELN), made up of some 2,000 fighters and considered a terrorist organization by the United States and European Union, began peace talks with the government of former President Juan Manuel Santos February 2017 but they have been put on hold by President Ivan Duque.
The country’s defense ministry had previously reported 11 dead and 65 injured. Colombia’s government declared three days of mourning Thursday after the attack.
The defense ministry said the “terrorist act” was carried out using a vehicle packed with 80 kilograms (around 175 pounds) of explosives.
“All Colombians reject terrorism and we’re united in fighting it,” President Ivan Duque tweeted in the aftermath.
Later in a statement to the nation, he said he had ordered reinforcements to Colombia’s borders and routes in and out of cities.
“I have also requested that priority be given to all the investigations ... to identify the masterminds of this terrorist attack and their accomplices,” he said.
The bomber — who authorities confirmed was killed in the attack — struck at the General Francisco de Paula Santander Officer’s School in the south of Bogota during a promotion ceremony for cadets.
No group has claimed responsibility, but public prosecutor Nestor Humberto Martinez named suspect Jose Aldemar Rojas Rodriguez as the “material author of this abominable crime.”
Martinez said Rojas Rodriguez entered the school compound at 9:30 a.m. driving a grey 1993 Nissan Patrol truck, but gave no details about the explosion.
He said the truck underwent an inspection in July in the Arauco department on the border with Venezuela — a traditional stronghold of ELN Marxist guerrillas.
Ecuador’s President Lenin Moreno said one of the dead was an Ecuadoran cadet, while a second suffered light injuries.
“The brutal act of terrorism in Bogota took the life of a compatriot,” Moreno said on Twitter.
“My sincerest thoughts go to the family, friends and companions of Erika Chico.”
Meanwhile, Panama’s President Juan Carlos Varela said that 45 Panamanian cadets were present during the attack, with two injured.
Fanny Contreras, the Colombian armed forces’ health inspector, told local radio that the truck “entered (the school compound) suddenly, almost hitting the police, and then there was the explosion.”
Carol Oviedo said her brother Jonathan, a cadet, told her on the phone he had been injured, before the connection was cut.
“In two years since he joined the police, he’s never had to face a situation like this,” she said.
Like other families, she was lingering in the vicinity of the academy hoping to hear some news.
United States assistant secretary of state in charge of Latin America, Kimberly Breier condemned the attack and said: “Our condolences and sympathies go to the victims and family members of those killed.”
The US embassy in Bogota offered its “help in investigating this reprehensible attack.”
Rosalba Jimenez, 62, was opening her confectionary store near the school when the bomb went off.
“When we turned to look at the school the sky was grey with smoke. People were running, sirens... horrible, horrible, it seemed like the end of the world,” Jimenez said.
Authorities sealed off the area to the press and increased security service patrols in the south of the city, AFP reporters said.
Right-wing Duque, who assumed power in August, has peddled a tough line against Marxist rebels and drug traffickers in the largest cocaine producer in the world.
Peace talks with ELN guerrillas — who in the past have claimed responsibility for bomb attacks on police — stalled before Duque replaced Juan Manuel Santos as president, and have not been restarted.
Duque has made several demands, including the release of all hostages, as prerequisites to kick-starting the peace process, but the ELN has dismissed those as unacceptable.
After the 2016 peace accord signed by Santos and FARC guerrillas, turning the former rebels into a political party, the ELN is considered the last active rebel group in a country that has suffered more than half a century of conflict.
That cycle of violence has also involved paramilitaries, drug traffickers and other Marxist rebels, including FARC dissidents.
A year ago, six police died and 40 were injured in an attack on a police station in the Caribbean city of Barranquilla that was claimed by the ELN.
In February 2017, the ELN claimed responsibility for an attack on a police patrol in the Macarena neighborhood of Bogota that left one officer dead and several seriously wounded.
In June, three people — including a Frenchwoman — were killed and nine others wounded in an attack on a Bogota shopping mall that authorities blamed on a fringe left-wing group called the Revolutionary People’s Movement.