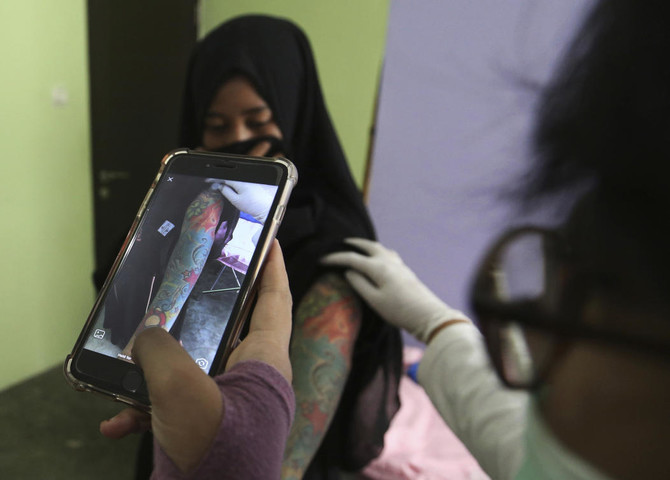
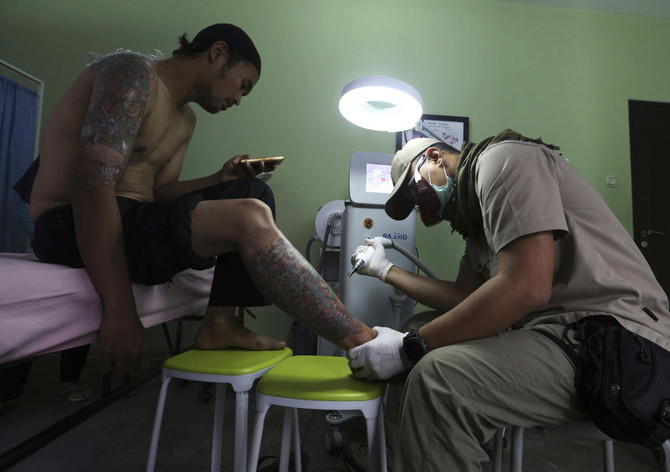
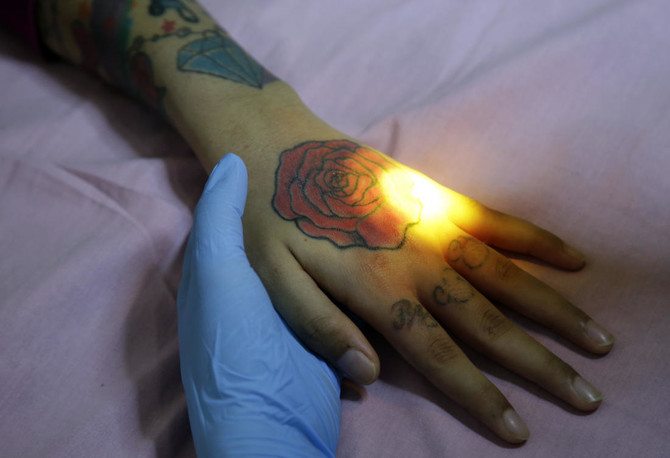
TANGERANG,INDONESIA: Each staccato rat-a-tat-tat of the laser firing an intense beam at the elaborate red, green and black dragon on Taufiq Hidayat’s arm is, he prays, bringing him closer to God.
The shirtless, slender 30-year-old says he got his back, an arm and a leg tattooed to “look cool” back in the day when “I was a gang member, a thug at the market.”
These days, Hidayat has a newfound zeal for Islam that includes the conviction that Muslims should not alter the body that God gave them. He became so desperate to remove the tattoos that he once applied caustic soda, scarring his arm.
Laser removal, which takes repeated treatment and may not be completely successful but is safer than other methods, was out of the question because it costs thousands of dollars for tattoos as extensive as Hidayat’s.
Since his self-mutilation, Hidayat has chanced upon a clinic west of the capital, Jakarta, that is offering laser removal for free, on one condition: While being zapped, patients must read and learn by heart Surah Ar-Rahman, the 55th chapter of the Qur’an about God’s gifts to man.
As a clinic worker aimed the white laser wand at Hidayat’s skin, blasting the color pigments with its penetrating light, he stared intently at his smartphone, reciting some of the 78 Ar-Rahman verses.
“Now I have a wife and a daughter. Sometimes she buys snacks that come with tattoo stickers that she applies to her skin. I said, ‘Don’t do it. It’s not good for you.’ And she replies, ‘But you have a lot of tattoos. I wanna be like Daddy.’ And in that moment I felt sad,” said Hidayat, tears welling in his eyes.
He is among about 1,000 people who have signed up for free tattoo removal, say organizers of the program. About 200 people have finished or are still being treated and others are on a waiting list.
One of the instigators of the program, community activist Ahmad Zaki, first began offering tattoo removal several years ago to young punk rockers in Java who wanted to “berani hijrah” — dare to move closer to God.
Sometimes they had attempted to remove the tattoos in dangerous ways, with chemicals or slashing their skin with razors, he said.
The idea for the clinic in Tangerang grew from a discussion between Zaki and Rizki Sari, a dermatologist who was a high school friend. Zaki said he and other activists collected about $8,000 in donations that helped Sari’s clinic buy two lasers. News about the clinic has spread quickly, thanks in part to a “Dare to Hijrah” Instagram account.
“People with tattoos might think that it’s art, culture or personal identity, but the community thinks otherwise,” said Zaki, who also runs a religious charity sponsored by a local bank. “It’s always false gods, satanic, sexual images, and that’s not good.”
Tattooing has lost much of its stigma in Western societies, becoming more or less mainstream, but in some Asian cultures it remains strongly associated with gangs and criminality. In addition to the religious prohibitions in Muslim-majority Indonesia, ideas about tattoos also reveal oppressive attitudes toward women, who if tattooed can be labeled as promiscuous or disreputable and not worth marrying.
Sri Novianti, who has a large red rose tattooed on one hand, Donald Duck drawings on her fingers and Powerpuff Girls and a ghostly tree on her arms, became a tattooist after graduating from high school because “for me tattoos are like art.”
But the 19-year-old now wears a face-covering veil and all-encompassing clothing and wants her tattoos removed because she feels Indonesian men treat her with respect when she is fully covered.
“I saw the eyes of men and boys no longer looking at me in a disgusting way,” she said. “Suddenly, for the first time I felt respected. I wanted to keep wearing the hijab, and I felt like I was a different person, an honorable woman.”
The tattoos also caused difficulties at her mosque whenever she performed ablutions before praying.
“Many women seem shocked and cannot accept my presence because of my tattoos,” Novianti said.
Sari, the dermatologist, said those accepted for laser treatment are ardent about getting their tattoos removed because the stigma and burden they experience prevents them from fully practicing their religion.
One participant, she said, had tried to iron his own skin in a misguided attempt to remove tattoos.
“Can you imagine the agonizing pain? That’s how badly they want their tattoos removed,” she said.
Fuad Ahmadi said he got his first tattoo — biomechanical images and his father’s birth date — done by friends after he graduated from junior high school. Now 22, he said he’s tried calcium hydroxide and other chemicals to remove that and five other tattoos.
“When I die, I want myself clean,” he said as he waited at the clinic. “God gave me clean skin and I ruined it.”
Indonesia clinic gives relief to Muslims with tattoo regrets
Indonesia clinic gives relief to Muslims with tattoo regrets
Cambodia takes back looted historic artifacts handled by British art dealer

- The objects were returned under a 2020 agreement between the Ministry of Culture and Fine Arts and the family of the late Douglas Latchford, a British art collector and dealer who allegedly had the items smuggled out of Cambodia
PHNOM PENH, Cambodia: Cambodian officials on Friday received more than six dozen historic artifacts described as part of the country’s cultural heritage that had been looted during decades of war and instability.
At a ceremony attended by Deputy Prime Minister Hun Many, the 74 items were unveiled at the National Museum in Phnom Penh after their repatriation from the United Kingdom.
The objects were returned under a 2020 agreement between the Ministry of Culture and Fine Arts and the family of the late Douglas Latchford, a British art collector and dealer who allegedly had the items smuggled out of Cambodia.
“This substantial restitution represents one of the most important returns of Khmer cultural heritage in recent years, following major repatriations in 2021 and 2023 from the same collection,” the Culture Ministry said in a statement. “It marks a significant step forward in Cambodia’s continued efforts to recover, preserve, and restore its ancestral legacy for future generations.”
The artifacts were described as dating from the pre-Angkorian period through the height of the Angkor Empire, including “monumental sandstone sculptures, refined bronze works, and significant ritual objects.” The Angkor Empire, which extended from the ninth to the 15th century, is best known for the Angkor Wat archaeological site, the nation’s biggest tourist attraction.
Latchford was a prominent antiquities dealer who allegedly orchestrated an operation to sell looted Cambodian sculptures on the international market.
From 1970 to the 1980s, during Cambodia’s civil wars and the communist Khmer Rouge ‘s brutal reign, organized looting networks sent artifacts to Latchford, who then sold them to Western collectors, dealers, and institutions. These pieces were often physically damaged, having been pried off temple walls or other structures by the looters.
Latchford was indicted in a New York federal court in 2019 on charges including wire fraud and conspiracy. He died in 2020, aged 88, before he could be extradited to face charges.
Cambodia, like neighboring Thailand, has benefited from a trend in recent decades involving the repatriation of art and archaeological treasures. These include ancient Asian artworks as well as pieces lost or stolen during turmoil in places such as Syria, Iraq and Nazi-occupied Europe. New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art is one of the prominent institutions that has been returning illegally smuggled art, including to Cambodia.
“The ancient artifacts created and preserved by our ancestors are now being returned to Cambodia, bringing warmth and joy, following the country’s return to peace,” said Hun Many, who is the younger brother of Prime Minister Hun Manet.