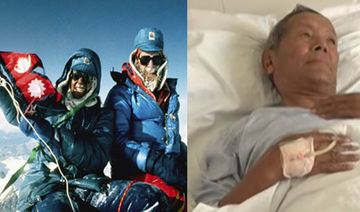
KATMANDU, Nepal: A Swiss climber acclaimed for his rapid ascents — including scaling dozens of peaks in the Alps in a little more than two months — was killed Sunday in a mountaineering accident near Mount Everest in Nepal, expedition organizers said.
Ueli Steck was killed at Camp 1 of Mount Nuptse, Mingma Sherpa of Seven Summit Treks said. Steck’s body has been recovered from the site and been taken to Lukla, where the only airport in the Mount Everest area is located.
Steck’s family said the exact circumstances of his death were still unclear.
“The family is infinitely sad and asks that the media refrain from speculating about his death out of respect and consideration for Ueli,” it said in a statement on Steck’s website. “As soon as reliable information about Ueli Steck’s death becomes available, the media will be informed.”
Steck was planning to climb 8,850-meter (29,035-foot) Mount Everest and nearby Mount Lhotse next month.
He was the first casualty in the spring mountaineering season in Nepal that began in March and will end in May. Hundreds of foreign climbers are on the mountains to attempt scale Himalayan peaks in May when there are a few windows of favorable weather.
The 40-year-old Steck was one of the most-renowned mountaineers of his generation. He was best known for his speed-climbing, including setting several records for ascending the north face of the Eiger, a classic mountaineering peak in the Bernese Alps that he climbed in two hours and 47 minutes without using a rope.
In 2013, he achieved the first solo climb of the Annapurna south face in Nepal after almost losing his life in a fall there in 2007. For that he received the “Piolet d’Or” — considered the Oscar of mountaineering — the following year.
In 2015, Steck decided to climb all 82 peaks in the Alps higher than 4,000 meters (13,100 feet) traveling between mountains by foot, bike and paraglider only. He completed the feat in 62 days, helping cement his reputation as the “Swiss Machine.”
Steck once said he considered himself an “outsider” in the mountaineering scene because athletic achievement was more important to him than adventure.
In a recent post on his website, Steck mused about the transience of success in mountaineering and the inevitable decline that comes with age.
“A record is broken again and again, and the world keeps on turning,” he wrote. “You are getting older and there comes a time when you have to adjust your projects to your age.”
Steck suffered a setback during his last trip to Everest, in 2013, when he became involved in a violent altercation with a group of local guides. On his return this year, he aimed to perform a quick climb of Everest and Lhotse, including an overnight stop at more than 8,000 meters, an altitude that’s known as the “death zone” because the human body’s performance is reduced to 20 percent of its normal rate.
Asked about the upcoming expedition, Steck told Swiss daily Tages-Anzeiger in an interview last month: “When I’m on Everest I can stop at any point. The risk is therefore quite small. For me it’s primarily a physical project. Either I get through, or I don’t have the strength for the whole traversal.”
“Of course I want to climb Everest and Lhotse,” Steck told the paper when asked about his measure of success. “But that’s a very high goal. Failure for me would be to die and not come home.”
___
Frank Jordans reported from Berlin.
Famed Swiss climber killed near Mount Everest in Nepal
Famed Swiss climber killed near Mount Everest in Nepal

Three-year heatwave bleached half the planet’s coral reefs: study

PARIS: A study published on Tuesday showed that more than half of the world’s coral reefs were bleached between 2014-2017 — a record-setting episode now being eclipsed by another series of devastating heatwaves.
The analysis concluded that 51 percent of the world’s reefs endured moderate or worse bleaching while 15 percent experienced significant mortality over the three-year period known as the “Third Global Bleaching Event.”
It was “by far the most severe and widespread coral bleaching event on record,” said Sean Connolly, one the study’s authors and a senior scientist at the Panama-based Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute.
“And yet, reefs are currently experiencing an even more severe Fourth Event, which started in early 2023,” Connolly said in a statement.
When the sea overheats, corals eject the microscopic algae that provides their distinct color and food source.
Unless ocean temperatures return to more tolerable levels, bleached corals are unable to recover and eventually die of starvation.
“Our findings demonstrate that the impacts of ocean warming on coral reefs are accelerating, with the near certainty that ongoing warming will cause large-scale, possibly irreversible, degradation of these essential ecosystems,” said the study in the journal Nature Communications.
An international team of scientists analyzed data from more than 15,000 in-water and aerial surveys of reefs around the world over the 2014-2017 period.
They combined the data with satellite-based heat stress measurements and used statistical models to estimate how much bleaching occurred around the world.
No time to recover
The two previous global bleaching events, in 1998 and 2010, had lasted one year.
“2014-17 was the first record of a global coral bleaching event lasting much beyond a single year,” the study said.
“Ocean warming is increasing the frequency, extent, and severity of tropical-coral bleaching and mortality.”
Australia’s Great Barrier Reef, for instance, saw peak heat stress increase each year between 2014 and 2017.
“We are seeing that reefs don’t have time to recover properly before the next bleaching event occurs,” said Scott Heron, professor of physics at James Cook University in Australia.
A major scientific report last year warned that the world’s tropical coral reefs have likely reached a “tipping point” — a shift that could trigger massive and often permanent changes in the natural world.
The global scientific consensus is that most coral reefs would perish at warming of 1.5C above preindustrial levels — the ambitious, long-term limit countries agreed to pursue under the 2015 Paris climate accord.
Global temperatures exceeded 1.5C on average between 2023-2025, the European Union’s climate monitoring service, Copernicus, said last month.
“We are only just beginning to analyze bleaching and mortality observations from the current bleaching event,” Connolly told AFP.
“However the overall level of heat stress was extraordinarily high, especially in 2023-2024, comparable to or higher than what was observed in 2014-2017, at least in some regions,” he said.
He said the Pacific coastline of Panama experienced “dramatically worse heat stress than they had ever experienced before, and we observed considerable coral mortality.”