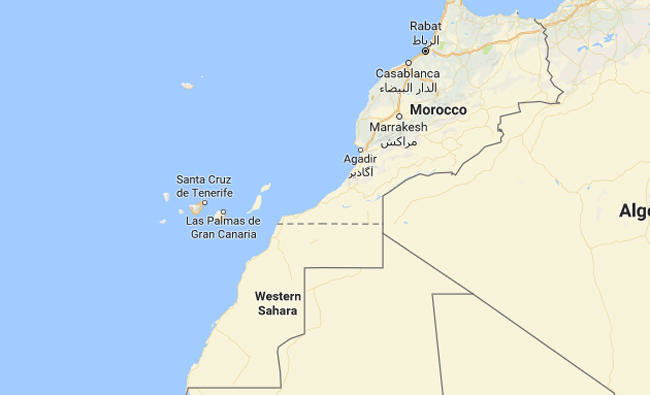
ALGIERS/RABAT: The UN Security Council unanimously backed attempts to restart talks between Morocco and the Polisario independence movement over the Western Sahara conflict, and extended its peacekeeping mission there for another year.
The resolution came after the UN mission confirmed the Polisario had withdrawn troops from the Guerguerat area of the territory, a vast swath of desert bordering the Atlantic Ocean that has been contested since 1975.
They had faced off in Guerguerat since 2016 with Morocco, which pulled its forces back earlier this year.
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres earlier this month called for Morocco and the Polisario Front, which fought a war over the region until a 1991 cease-fire, to enter new negotiations that would include proposals from both sides.
“This action should improve the prospects of creating an environment that will facilitate early implementation of Mr. Guterres’s determination to relaunch the negotiating process,” the UN spokesman said in a statement, noting Morocco’s early pullback and confirming Polisario’s withdrawal.
Morocco claimed Western Sahara after colonial Spain left, but Polisario fought a guerrilla war for independence for the Sahrawi people there until the UN-backed cease-fire.
UN talks have long failed to broker an agreement on how to decide on self-determination. Morocco wants an autonomy plan under Moroccan sovereignty. But Polisario wants a UN-backed referendum including on the question of independence.
The UN resolution on Friday extended the UN peacekeeping mission, known as MINURSO, until April 30, 2018 and called on the parties to resume a fifth round of talks.
Against a backdrop of decades of past political failures and mistrust, the resolution noted Morocco’s 2007 autonomy proposal and welcomed Rabat’s “serious” efforts to progress.
It also emphasized Polisario’s 2007 proposal, which calls for a referendum between independence, integration with Morocco and self-governance.
Past attempts to broker a deal have been fallen apart over details mostly on referendum terms, including who should be allowed to vote.
Morocco’s Foreign Ministry said in a statement the kingdom was satisfied with the resolution, and hoped for a “real process” toward a solution, which it said should be the autonomy initiative.
Morocco also called for neighboring Mauritania as well as Algeria, which backs Polisario and maintains tense relations with Rabat, to be involved in negotiations.
“All parties must assume their responsibilities, Algeria must assume its responsibility,” Foreign Minister Nacer Bourita told reporters in Rabat. “Algeria is the missing key.”
UN Security Council backs new Western Sahara talks push
UN Security Council backs new Western Sahara talks push
Families mourn those killed in a Congo mine landslide as some survivors prepare to return

GOMA, Congo: After a landslide last week killed at least 200 people in eastern Congo at a rebel-controlled coltan mine, families of the deceased and survivors are mourning their lost loved ones, and some survivors prepared to head back to the reopened mines.
On Wednesday, following heavy rains in eastern Congo, a network of hand-dug tunnels at the Rubaya mining complex collapsed, killing at least 200 artisanal miners and trapping an unknown number who remain missing. The mine, located around 25 miles (40 kilometers) to the west of the regional capital of Goma, has been under the control of Rwandan-backed M23 rebels since early 2024 and employs thousands of miners who work largely by hand.
Family members grieve
In the Mugunga neighborhood in Goma, the family of Bosco Nguvumali Kalabosh, 39, mourned his death Monday.
Since last Thursday, relatives, neighbors and loved ones have been gathering at the family home, sitting around a photograph of him placed up against a wall.
“He was supposed to return to Goma on Thursday,” said his older brother, Thimothée Kalabosh Nzanga.
Kalabosh had been a miner for more than 10 years. He owned his own mines on the site and came from a family where artisanal mining — mining for minerals using basic hand tools — had been passed down from generation to generation. He leaves behind a widow and four children, the eldest of whom is 5 years old.
Survivors head back to Rubaya
For survivors trickling back into town, the pressure to return to the mines is clear — despite the constant danger.
Tumaini Munguiko, a survivor of the collapse, came to offer his condolences to Kalabosh’s family. “Seeing our peers die is very painful. But despite the pain, we are forced to return to the mines to survive,” he said.
Munguiko calmly explained that he had already experienced several similar disasters. “It has almost become normal. We accept it because it is our means of survival. I was saved this time, but I lost five friends and my older brother.”
According to him, landslides are common in Rubaya, especially during the rainy season. “When it rains, the clay soils become unstable. Some take shelter, others perish, others survive, and others watch from afar,” he said.
Miners dig long tunnels, often parallel to one another, with limited support and no safe evacuation route in case of a collapse.
A former miner at the site told The Associated Press that there have been repeated landslides because the tunnels are dug by hand, poorly constructed and not maintained.
“People dig everywhere, without control or safety measures. In a single pit, there can be as many as 500 miners, and because the tunnels run parallel, one collapse can affect many pits at once,” former miner Clovis Mafare said.
“The diggers don’t have insurance,” said Mafare. Of potential compensation for families, he said: “It’s a whole legal process, and it’s very long. They might receive some money for the funerals, but that small amount isn’t compensation.”
Kalabosh’s family has not received compensation for their loss.
However, both Munguiko and Nzanga say they will return to the mines soon despite the risks.
“I have no choice. Our whole life is there,” said Munguiko.
Rare earth minerals
The Rubaya mines have been at the center of the recent fighting in eastern Congo, changing hands between the Congolese government and rebel groups. For over a year now, the site has been controlled by the M23 rebels.
The mines produce coltan — short for columbite-tantalite — an ore from which the metals tantalum and niobium are extracted. Both are considered critical raw materials by the United States, the European Union, China and Japan. Tantalum is used in mobile phones, computers and automotive electronics, as well as in aircraft engines, missile components and GPS systems. Niobium is used in pipelines, rockets and jet engines.
The mines at Rubaya are massive and attract people from across the region. Artisanal miners and workers have been flocking there for years, drawn to the site to earn a steady income in a region plagued by poverty and chronic insecurity. A disaster like this affects people across eastern Congo and the grief has spread to regional hubs like Goma.
For the last two weeks, Rubaya has been virtually cut off from the world. The mining town has no mobile network or Internet connection. Poor infrastructure, coupled with persistent conflict, means cellular service and electricity are unreliable. To communicate with the outside world, residents must pay around 5,000 Congolese francs — just over $2 — for 30 minutes of connection via a private Starlink system.
Congo’s government, in a statement on X, expressed solidarity with the victims’ families and accused the rebels of illegally and unsafely exploiting the region’s natural resources while blaming Rwanda. An M23 spokesperson accused the government of politicizing the tragedy and listed other collapses at government-controlled mines.











