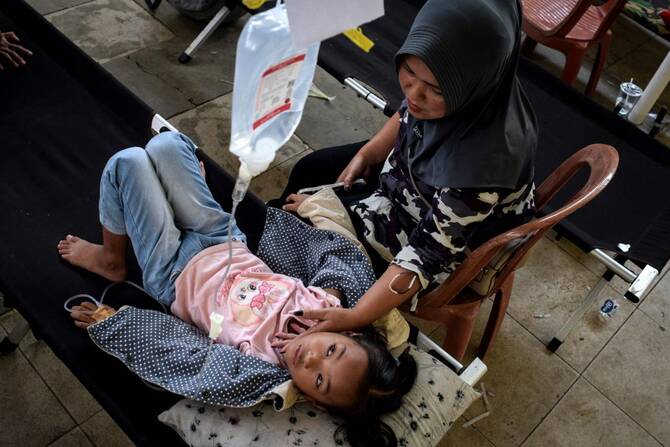
JAKARTA: Indonesian families whose children were offered free school meals are joining non-profit groups calling for the flagship government program to be suspended after thousands of students fell ill from the food.
Cases of food poisoning spiked last week in West Bandung, a district of Java island, when more than 1,300 children were rushed to health clinics after suffering from breathing difficulties, nausea and diarrhea, local media reported.
President Prabowo Subianto’s initiative was touted as a way to tackle a child nutrition crisis but the government has instead had to suspend dozens of production kitchens.
“This program should be stopped and replaced with cash,” said 50-year-old grandmother Aminah, who goes by one name and whose seven-year-old grandson got sick after a free meal.
“I’d rather the kids bring their own lunch from home.”
The disastrous rollout comes as Prabowo is working to move on from violent anti-government protests fueled by deep inequality in Indonesia, where stunting spurred by malnutrition affects more than 20 percent of children.
But nine months after the program began, food poisoning cases have affected thousands of people, prompting mounting calls from non-profit groups for a temporary halt to the multi-billion-dollar scheme.
In West Bandung, students wailed in pain as they were hooked up to oxygen tanks in a temporary health clinic set up by local government to handle the surge in food poisonings, an AFP journalist saw.
The National Nutrition Agency (BGN), which is responsible for the initiative, reported 70 food poisoning incidents since the program began in January until late September.
More than 6,400 people are affected, the agency said in an update on Wednesday.
The reported cases were the “tip of the iceberg,” said Diah Satyani Saminarsih, founder of the non-profit Center for Indonesia’s Strategic Development Initiatives.
“The actual number of cases could be higher because the government has not yet provided a publicly available reporting dashboard,” Diah said.
Part of the problem was the government’s rapid expansion of the program, she added.
Rapid expansion
The government initially aimed to deliver meals to almost 83 million people by 2029, including students, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers, but now says the target will be reached by the end of 2025.
The nutrition agency expanded the number of production kitchens from around 1,000 in April to more than 9,600 by late September.
The number of beneficiaries grew from three million to 31 million over the same period.
The agency did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Dadan Hindayana, chair of the nutrition agency, said in a statement on Sunday that most of the cases occurred in newly operating kitchens where cooks lacked experience.
The food poisoning incidents were also caused by the quality of raw materials, water and violations of operational standards, he said.
Prabowo’s administration has allocated 62 cents per meal and set a budget of 71 trillion rupiah ($4.2 billion) for 2025.
Finance Minister Purbaya Yudhi Sadewa said last week that the government had prepared an additional budget of 28 trillion rupiah requested by the agency, local media reported.
Prabowo defended the program in a televised speech on Monday, saying cases of food poisoning incidents were long a small percentage of the number of meals served.
“We calculated from all the food that went out, the deviation, or shortcoming or error is 0.00017 percent,” he said.
He added that all kitchens involved in the program were ordered to test foods before distribution.
Calls for suspension
It was “very urgent” for the program to be suspended given the number of people who fell ill, said Izzudin Al Farras, a researcher at the Institute for Development of Economics and Finance.
Ubaid Matraji, a researcher at the Network for Education Watch, said the program should be suspended before matters worsen.
“We stress that we will no longer wait until we have thousands more victims — we cannot let death happen,” he said.
The nutrition agency suspended 56 kitchens allegedly responsible for “food safety incidents,” it said in a statement Monday.
Nanik S. Deyang, the agency’s deputy chair, said the suspension was part of a “comprehensive evaluation” to prevent similar incidents from recurring.
“The safety of the people, especially children who receive the free nutritious meals, is our top priority,” she said.


Indonesia free meals program under fire after thousands sickened
Short Url
https://arab.news/gnt47
Indonesia free meals program under fire after thousands sickened

- Indonesian families whose children were offered free school meals are joining non-profit groups calling for the flagship government program to be suspended after thousands of students fell ill
Russia awaits an answer from the US on New START as nuclear treaty ticks down

- Russian leader Vladimir Putin has proposed keeping the treaty’s limits
- US President Donald Trump has said Putin’s proposal sounded ‘like a good idea’
MOSCOW: Russia on Wednesday said it was still awaiting a formal answer from Washington on President Vladimir Putin’s proposal to jointly stick to the last remaining Russian-US arms control treaty, which expires in less than two months.
New START, which runs out on February 5, caps the number of strategic nuclear warheads that the United States and Russia can deploy, and the deployment of land- and submarine-based missiles and bombers to deliver them.
Putin in September offered to voluntarily maintain for one year the limits on deployed strategic nuclear weapons set out in the treaty, whose initials stand for the (New) Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty.
Trump said in October it sounded “like a good idea.”
“We have less than 100 days left before the expiry of New START,” said Sergei Shoigu, the secretary of Russia’s powerful Security Council, which is like a modern-day politburo of Russia’s most powerful officials.
“We are waiting for a response,” Shoigu told reporters during a visit to Hanoi. He added that Moscow’s proposal was an opportunity to halt the “destructive movement” that currently existed in nuclear arms control.
Nuclear arms control in peril
Russia and the US together have more than 10,000 nuclear warheads, or 87 percent of the global inventory of nuclear weapons. China is the world’s third largest nuclear power with about 600 warheads, according to the Federation of American Scientists.
The arms control treaties between Moscow and Washington were born out of fear of nuclear war after the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis. Greater transparency about the opponent’s arsenal was intended to reduce the scope for misunderstanding and slow the arms race.
US and Russia eye China’s nuclear arsenal
Now, with all major nuclear powers seeking to modernize their arsenals, and Russia and the West at strategic loggerheads for over a decade — not least over the enlargement of NATO and Moscow’s war in Ukraine — the treaties have almost all crumbled away. Each side blames the other.
In the new US National Security Strategy, the Trump administration says it wants to reestablish strategic stability with Russia” — shorthand for reopening discussions on strategic nuclear arms control.
Rose Gottemoeller, who was chief US negotiator for New START, said in an article for The Arms Control Association this month that it would be beneficial for Washington to implement the treaty along with Moscow.
“For the United States, the benefit of this move would be buying more time to decide what to do about the ongoing Chinese buildup without having to worry simultaneously about new Russian deployments,” Gottemoeller said.
New START, which runs out on February 5, caps the number of strategic nuclear warheads that the United States and Russia can deploy, and the deployment of land- and submarine-based missiles and bombers to deliver them.
Putin in September offered to voluntarily maintain for one year the limits on deployed strategic nuclear weapons set out in the treaty, whose initials stand for the (New) Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty.
Trump said in October it sounded “like a good idea.”
“We have less than 100 days left before the expiry of New START,” said Sergei Shoigu, the secretary of Russia’s powerful Security Council, which is like a modern-day politburo of Russia’s most powerful officials.
“We are waiting for a response,” Shoigu told reporters during a visit to Hanoi. He added that Moscow’s proposal was an opportunity to halt the “destructive movement” that currently existed in nuclear arms control.
Nuclear arms control in peril
Russia and the US together have more than 10,000 nuclear warheads, or 87 percent of the global inventory of nuclear weapons. China is the world’s third largest nuclear power with about 600 warheads, according to the Federation of American Scientists.
The arms control treaties between Moscow and Washington were born out of fear of nuclear war after the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis. Greater transparency about the opponent’s arsenal was intended to reduce the scope for misunderstanding and slow the arms race.
US and Russia eye China’s nuclear arsenal
Now, with all major nuclear powers seeking to modernize their arsenals, and Russia and the West at strategic loggerheads for over a decade — not least over the enlargement of NATO and Moscow’s war in Ukraine — the treaties have almost all crumbled away. Each side blames the other.
In the new US National Security Strategy, the Trump administration says it wants to reestablish strategic stability with Russia” — shorthand for reopening discussions on strategic nuclear arms control.
Rose Gottemoeller, who was chief US negotiator for New START, said in an article for The Arms Control Association this month that it would be beneficial for Washington to implement the treaty along with Moscow.
“For the United States, the benefit of this move would be buying more time to decide what to do about the ongoing Chinese buildup without having to worry simultaneously about new Russian deployments,” Gottemoeller said.
© 2025 SAUDI RESEARCH & PUBLISHING COMPANY, All Rights Reserved And subject to Terms of Use Agreement.