JAKARTA: Indonesian families whose children were offered free school meals are joining non-profit groups calling for the flagship government program to be suspended after thousands of students fell ill from the food.
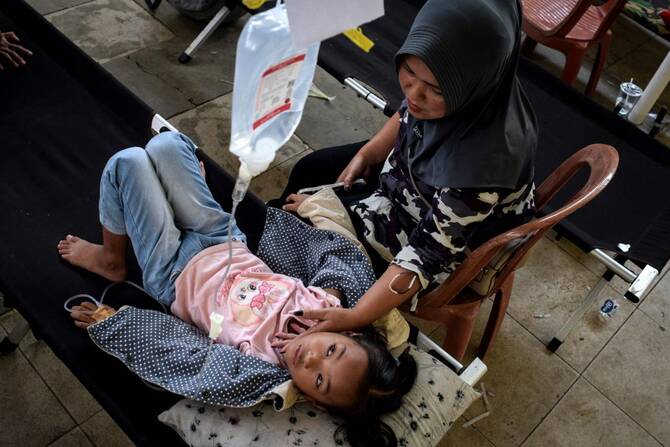
Cases of food poisoning spiked last week in West Bandung, a district of Java island, when more than 1,300 children were rushed to health clinics after suffering from breathing difficulties, nausea and diarrhea, local media reported.
President Prabowo Subianto’s initiative was touted as a way to tackle a child nutrition crisis but the government has instead had to suspend dozens of production kitchens.
“This program should be stopped and replaced with cash,” said 50-year-old grandmother Aminah, who goes by one name and whose seven-year-old grandson got sick after a free meal.
“I’d rather the kids bring their own lunch from home.”
The disastrous rollout comes as Prabowo is working to move on from violent anti-government protests fueled by deep inequality in Indonesia, where stunting spurred by malnutrition affects more than 20 percent of children.
But nine months after the program began, food poisoning cases have affected thousands of people, prompting mounting calls from non-profit groups for a temporary halt to the multi-billion-dollar scheme.
In West Bandung, students wailed in pain as they were hooked up to oxygen tanks in a temporary health clinic set up by local government to handle the surge in food poisonings, an AFP journalist saw.
The National Nutrition Agency (BGN), which is responsible for the initiative, reported 70 food poisoning incidents since the program began in January until late September.
More than 6,400 people are affected, the agency said in an update on Wednesday.
The reported cases were the “tip of the iceberg,” said Diah Satyani Saminarsih, founder of the non-profit Center for Indonesia’s Strategic Development Initiatives.
“The actual number of cases could be higher because the government has not yet provided a publicly available reporting dashboard,” Diah said.
Part of the problem was the government’s rapid expansion of the program, she added.
Rapid expansion
The government initially aimed to deliver meals to almost 83 million people by 2029, including students, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers, but now says the target will be reached by the end of 2025.
The nutrition agency expanded the number of production kitchens from around 1,000 in April to more than 9,600 by late September.
The number of beneficiaries grew from three million to 31 million over the same period.
The agency did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Dadan Hindayana, chair of the nutrition agency, said in a statement on Sunday that most of the cases occurred in newly operating kitchens where cooks lacked experience.
The food poisoning incidents were also caused by the quality of raw materials, water and violations of operational standards, he said.
Prabowo’s administration has allocated 62 cents per meal and set a budget of 71 trillion rupiah ($4.2 billion) for 2025.
Finance Minister Purbaya Yudhi Sadewa said last week that the government had prepared an additional budget of 28 trillion rupiah requested by the agency, local media reported.
Prabowo defended the program in a televised speech on Monday, saying cases of food poisoning incidents were long a small percentage of the number of meals served.
“We calculated from all the food that went out, the deviation, or shortcoming or error is 0.00017 percent,” he said.
He added that all kitchens involved in the program were ordered to test foods before distribution.
Calls for suspension
It was “very urgent” for the program to be suspended given the number of people who fell ill, said Izzudin Al Farras, a researcher at the Institute for Development of Economics and Finance.
Ubaid Matraji, a researcher at the Network for Education Watch, said the program should be suspended before matters worsen.
“We stress that we will no longer wait until we have thousands more victims — we cannot let death happen,” he said.
The nutrition agency suspended 56 kitchens allegedly responsible for “food safety incidents,” it said in a statement Monday.
Nanik S. Deyang, the agency’s deputy chair, said the suspension was part of a “comprehensive evaluation” to prevent similar incidents from recurring.
“The safety of the people, especially children who receive the free nutritious meals, is our top priority,” she said.
Indonesia free meals program under fire after thousands sickened
https://arab.news/gnt47
Indonesia free meals program under fire after thousands sickened

- Indonesian families whose children were offered free school meals are joining non-profit groups calling for the flagship government program to be suspended after thousands of students fell ill
Isolated Kremlin critics lament lost future at Nemtsov memorial

- Hundreds used to flock to the makeshift memorial on the anniversary of his death
- Since Russia ordered troops into Ukraine it has intensified a crackdown on dissent, with almost no opposition to the Kremlin visible on the street
MOSCOW: On a bridge next to the Kremlin on a drizzly Friday morning, a lone Russian police officer stood looking at the half-dozen bunches of flowers laying in memory of slain opposition figure Boris Nemtsov.
The symbolism was almost too much.
Four years into Moscow’s full-scale offensive on Ukraine, which has seen President Vladimir Putin eradicate all forms of dissent and usher in strict military censorship laws that have silenced his critics, few Russians dared, or wanted, to pay tribute.
Nemtsov, a longtime Putin opponent, was shot and killed on February 27 2015, meters from the Kremlin’s red walls. He was 55.
Hundreds used to flock to the makeshift memorial on the anniversary of his death, which came on Friday.
This year, there was barely a trickle. Those who turned up were visibly nervous.
“So few people, they’ve all forgotten,” lamented one elderly man, who refused to give his name.
“Everybody is afraid,” a woman standing nearby added.
Since Russia ordered troops into Ukraine it has intensified a crackdown on dissent, with almost no opposition to the Kremlin visible on the street.
AFP reporters on Friday morning saw only around a dozen mourners alongside Western ambassadors laying red carnations.
“Keep moving, don’t gather in a crowd, don’t block the way for other citizens,” a police officer said through a megaphone.
Three days after Russia launched its offensive on Ukraine in 2022, protesters had staged an impromptu rally against the war at the memorial on the anniversary of Nemtsov’s death.
Nemtsov’s supporters have always accused Chechen leader and key Putin ally Ramzan Kadyrov of ordering his killing.
Kadyrov has rejected the claims.
Five Chechens were convicted of a contract killing but investigators never said who it was ordered by.
- ‘Everything is persecuted’ -
For his followers, Nemtsov is a totemic figure in Russian political life — seen as a once-future leader who might have taken the country on a different path.
“I come here every year,” said 79-year-old scientist Sergei at the bridge on Friday.
“Russia should have had — though unfortunately it didn’t work out — a leader exactly like Nemtsov,” he told AFP, declining to give his surname.
“Right now everything here is suppressed, everything is persecuted, people are sitting in prisons.”
A physicist by education, Nemtsov rose to fame in the 1990s as a young, liberal provincial governor, and was widely tipped to take over from Boris Yeltsin.
He gave his hesitant backing to Putin when the ex-KGB spy was tapped to enter the Kremlin instead, but became an early — and fierce — opponent of what he cast as the Russian leader’s creeping authoritarianism.
He had largely lost popularity and was only a marginal figure in Russian politics when he was killed in 2015. Still, his murder shocked the country and the world.
“The hopes of the whole country were pinned on him — of all the people who wanted it to be free here,” said Olga Vinogradova, a 66-year-old volunteer who tends to the pop-up memorial to Nemtsov on the bridge.
“When this man was killed, naturally, all of us were, we were all just executed at that moment. Because our hopes were destroyed,” she said.
“With this memorial, we remind people that there was a different path for Russia. And that there was a real person who could have led us down this path.”
- ‘Forced out’ -
Nemtsov had strongly opposed Putin’s 2014 annexation of Crimea from Ukraine and Moscow’s military backing for pro-Russian separatists in eastern Ukraine.
He was also a close and early ally of Alexei Navalny, who died in 2024 in an Arctic prison in what his supports say was a poisoning.
Open opposition to the Kremlin is unheard of inside Russia since the first days of the Ukraine offensive — when riot police cracked down hard on the thousands that took to the streets to protest.
All major critics of the Kremlin are in exile, prison or dead.
Those that remain have been silenced.
“Many have been forced out of the country, some have been killed,” said Gleb, a 23-year-old photographer.
A movement or person like Nemtsov was “impossible” to imagine right now, he said.
Still, he held on to a slither of hope.
“But everything can change at any moment.”