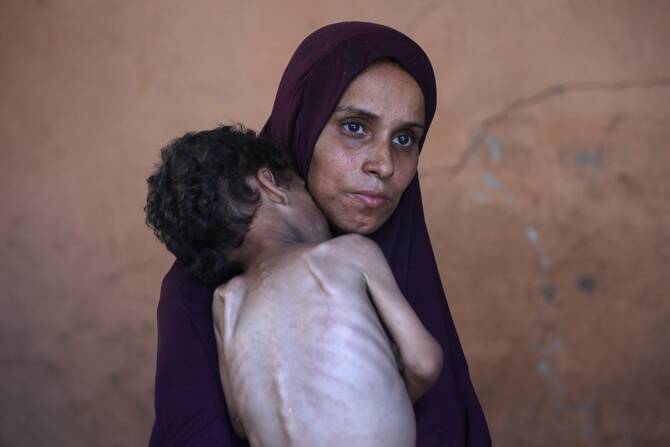
LONDON: British healthcare workers volunteering to treat patients in the Gaza Strip report witnessing harrowing injuries, including severe burns and shrapnel wounds as well as cases of extreme starvation due to Israeli attacks and restrictions on aid.
Sam Sears, a 44-year-old paramedic, told the British tabloid Metro that the range of injuries he has seen at a humanitarian medical tent facility in Al-Mawasi, on the southern coast of Gaza, includes blast injuries, shrapnel wounds, gunshot wounds and polytrauma.
He is volunteering with the UK-Med charity as part of a team responding to starvation in Gaza, following the emergence of distressing images of malnourished Palestinians, including some infants, which have prompted widespread condemnation, including from the UK government.
“It’s unlike anything I’ve seen before,” Sears said.
“Especially like nothing I’ve seen in the UK, and I have worked in other areas like Sierra Leone for Ebola and Ukraine in the war, but this here is completely different. It’s like times ten here.
“We are struggling for food here at the moment, let alone (Palestinian) staff that are working with us who have had to manage this for the last 20 months.”
He said that medical volunteers have been working tirelessly despite limited supplies, including fuel, and it was “very obvious (that) we have got malnourishment in the community.”
“We can buy certain things from the market but it’s very scarce, it’s also costing quadruple or more than what it normally would. A kilogram of sugar at the minute is costing $130, so it’s just extortionate,” he said.
The UK-Med charity operates two field hospitals in Gaza, treating 500 people daily, and includes an operating theater for lifesaving surgical procedures.
“The ceasefire is needed, not just a pause but a permanent end to the hostilities,” Sears said. “The people in Gaza have suffered immensely, they have got nowhere to call home ... They are hungry, malnourished, the conflict needs to stop really.”
“The healthcare and aid needs to come in for the 2.1 million people who it’s needed for here,” he added.
Dr. Tom Potokar, a veteran British plastic surgeon who has volunteered in various Palestinian hospitals and has visited Gaza 16 times since 2018, said that the healthcare system is overwhelmed with severe burn victims from Israel’s military actions.
Dr. Potokar told the Telegraph newspaper that he had been operating on 10 to 12 patients suffering burns from blasts each day, with three-quarters of those cases being women or children. “That’s taking the top-10 priority, but there’s still plenty more behind that that needed operating,” he said.
He volunteered nearly two years ago during the initial six weeks after Israel began its attacks on the Gaza Strip in late 2023. He is the founder of the medical charity Interburns, established in 2006, which addresses the lack of burns expertise in poorer nations and war zones. When he arrived for the first time in Gaza in 2018, he discovered that there were only two fully qualified plastic surgeons, one of whom was partially retired.
His most recent visit, with the Ideals international aid charity, was in May and June, during which he witnessed terrible injuries from explosions.
“I saw many cases of bilateral or triple limb amputations, huge open wounds on the back, on the chest, with the lung exposed. Really horrendous blast injuries from shrapnel, and as I say, a lot of them combined with burns as well,” he said.
The most devastating cases involved children, with some cases sustaining about 90 percent burns.
“There’s nothing you can do. Even if there was not a conflict there, in that country, in that scenario, a 90 percent burn (case) when it’s almost all full thickness is not going to survive,” he said.
“But then you are talking about a nine-year-old and some end-of-life dignity, and unfortunately they don’t die in a couple of hours, it takes four or five days, so you see this patient every four or five days, knowing full well that there’s absolutely nothing you can do.”
Dr. Potokar described treating patients who are “skin and bone” due to Israeli aid restrictions leading to mass starvation in Gaza.
“Wounds are just stagnating because they are just not getting food.”
He said that he lost 11 kg during his recent trip, despite bringing food with him. His Palestinian medical colleagues appeared increasingly fatalistic, he said, as more than 100 human rights organizations warned this week that some staff members have become too weak to continue their work due to food shortages.
Dr. Potokar described Gaza as the “world’s first televised genocide” and said that there was a lack of response to end the war in the coastal enclave.
“We are putting plasters on a haemorrhaging aneurysm. The problem is the political initiative, the total lack of global, moral, ethical insight into this and desire to stop it,” he said.