RIYADH: Although the Arab League’s plan for Gaza, announced at the Cairo summit on March 4, has faced outright rejection by the US and Israel, it still plays a crucial role in keeping negotiations alive, according to renowned Saudi columnist and political analyst Abdulrahman Al-Rashed.
Appearing on the Arab News current affairs program “Frankly Speaking,” Al-Rashed provided a candid assessment of the Arab League’s plan for postwar Gaza, how it stacks up against rival proposals, and the evolving political landscape in Lebanon, Syria, and Saudi Arabia.
The Arab League’s extraordinary summit took place last week in response to US President Donald Trump’s controversial suggestion that the US could take over Gaza, displace its Palestinian population to Egypt and Jordan, and redevelop the land as a leisure resort.
By contrast, the Arab League plan, which has won the backing of European leaders, calls for Gaza to be governed temporarily by a committee of independent experts and for international peacekeepers to be deployed to the territory.
The committee would be responsible for overseeing humanitarian aid and temporarily managing Gaza’s affairs under the supervision of the Palestinian Authority. The territory would be rebuilt at a cost of $53 billion without the need to displace the population.
“I think this leaves us with three plans now,” Al-Rashed told “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen.

Abdulrahman Al-Rashed provided a candid assessment of the Arab League’s plan for postwar Gaza, how it stacks up against rival proposals, and the changing political landscape in Lebanon and Syria. (AN photos)
“One is the Arab League plan, which says people stay in Gaza and reconstruction should be done in five years. And the Israeli plan, which is basically occupation and probably continuation of military activities.
“And, of course, we have the Trump plan, which is ‘the riviera,’ two million people should leave, and reconstruction of the whole area to make it livable. I don’t know whether the two million will come back or not. But the three plans are now on the table.
“I am not really sure if the Cairo summit has succeeded in convincing the White House, but at least we have a plan. This is the point here — to negotiate.”
Despite concerns that the Israeli and Trump-backed proposals could amount to ethnic cleansing, Al-Rashed argued that the Cairo plan is essential in providing a framework for continued diplomatic engagement.
“This is really just a way to negotiate, to keep the momentum, so it’s not just Trump saying, ‘let’s have the two million people out’ and we have chaos in Egypt, Jordan, and the Middle East,” he said.
Al-Rashed admitted he was slightly cynical about the plan when he recently tweeted that Arab League Secretary-General Ahmed Aboul Gheit should present the proposals to Trump himself at the White House — even if it meant risking a public spat similar to that which erupted between Trump and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky in the Oval Office.
A handout picture provided by the Egyptian Presidency shows a group picture during the Arab League summit on Gaza, in Cairo, on March 4, 2025. (AFP)
“Mr. Aboul Gheit, in my opinion, should take the plan and take it directly to the Americans and talk to the Americans,” Al-Rashed said.
“We will have two possibilities. One, either they will negotiate and probably will reach an agreement, or probably Trump will do exactly what he did with Zelensky and say no, he will not accept it, he will push the Arab League to change the plan and come up with something more practical. So this is what I meant, actually.”
One of the primary objections to the Arab League’s plan stems from the role Hamas might play in Gaza’s future governance, particularly as Israel, the US, and many Western countries consider it a terrorist group, not least for its Oct. 7, 2023, attack on southern Israel.
Asked if he believes that Hamas’s endorsement of the Cairo plan makes it harder to sell, Al-Rashed said the group has already shown willingness to step aside.
“Actually, Hamas made a statement almost close enough to say they accept the plan and they almost said that they are willing to accept whatever all Palestinian parties will agree to run Gaza, to manage Gaza,” he said. “So, I believe Hamas is getting closer to saying yes.”
However, he noted that while Hamas might agree to relinquish political control, the group has yet to commit to full disarmament.

Abdulrahman Al-Rashed provided a candid assessment of the Arab League’s plan for postwar Gaza, how it stacks up against rival proposals, and the changing political landscape in Lebanon and Syria. (AN photos)
Recent reports that the Trump administration has been in direct talks with Hamas came as a surprise to many observers. The US has issued an ultimatum, demanding the release of all remaining hostages held by Hamas in exchange for a lasting ceasefire.
While Al-Rashed sees this as a positive development, he criticized Hamas, which has been reticent about such a deal, for appearing to prioritize its public image over the well-being of Gaza’s population.
“I think we are right now on the edge of the second phase of the war,” he said. “So we will see, probably, more Israeli tanks roll into Gaza. And probably the warning might work like magic — probably Hamas will release most of the hostages or the remaining hostages in the coming weeks.”
He added: “I think the issue right now for Hamas is some sort of face-saving plan, something that will make Hamas look victorious, but they will not be in Gaza. I’m not really sure how it’s going to happen, but this is what is missing right now. It’s the Hamas image rather than, really, the lives of the two million Gazans or the remaining hostages.”
One positive, however, is that Egypt and Qatar have influence over Hamas, which could ease the process. “We have a window, a real window of solution this time, much more than before, after the conference,” Al-Rashed said.
“And I think the Egyptians and the Qataris have the leverage now. They can really pressure Hamas. And Hamas, if they accept the idea, will release all the rest of the hostages, they will have a safe passage from Gaza and they will live somewhere else, maybe Algeria or somewhere else. And the Palestinians, mainly the PA, rules Gaza.
“If this scenario happens — and I bet my money on it more likely — yes, we will have an end to hostility. I think Israelis will have some sort of supervision of Gaza. We will have the Palestinians finally at peace and we will have a new chapter start in the Middle East.”
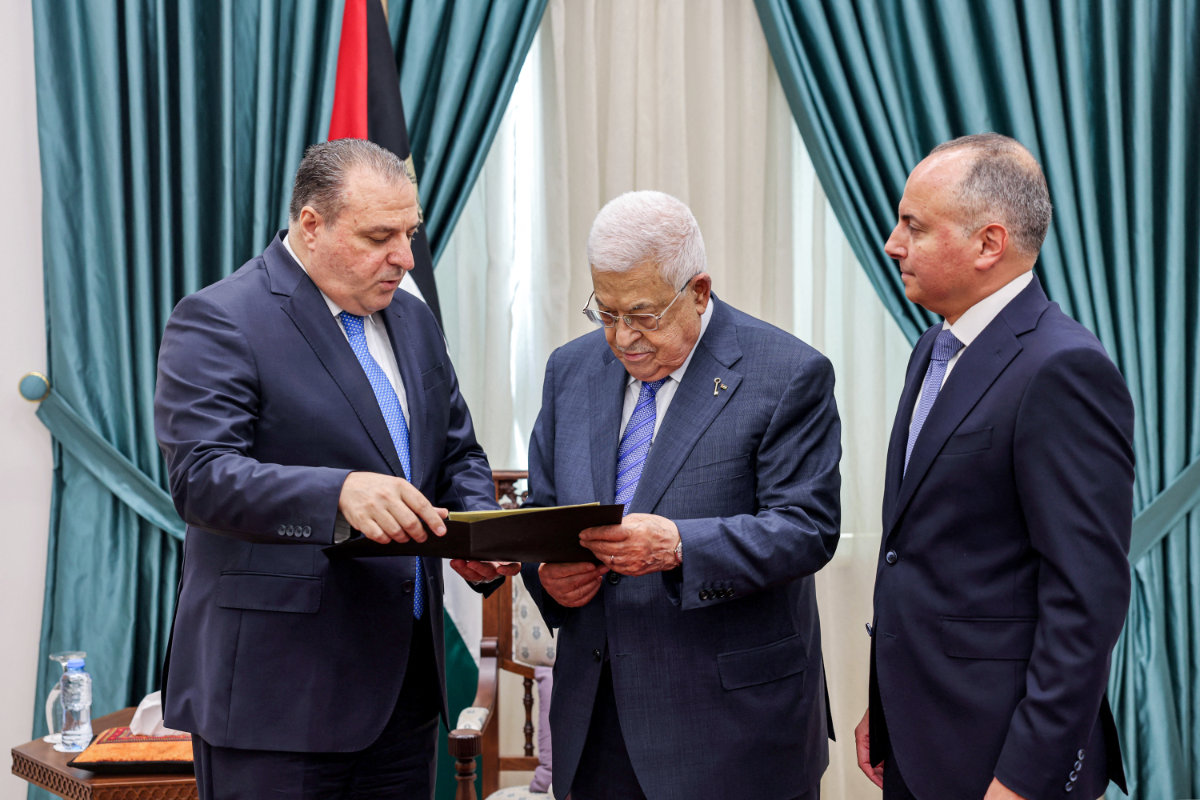

Al-Rashed says Israel's objection to a role for the Palestinian Authority in post-war Gaza is not practical. PA President Mahmud (shown here meeting with the ambassadors of Egypt and Jordan) is widely recognized as the leader of the Palestinian nation. (AFP)
However, Al-Rashed also criticized Israel’s refusal to consider a role for the Palestinian Authority or even the UN Relief and Works Agency in the governance of postwar Gaza.
“Right now, nothing will work unless we have a practical solution,” he said. “Trying to push two million people out is not a practical solution. It’s not going to happen. If it happens, it’s just, everybody will lose, including the Israelis.”
Al-Rashed insisted that the Palestinian Authority remains the most legitimate governing body for Gaza, despite its unpopularity in the West Bank.
“I think in terms of legitimacy, it is not Hamas, it is the PA,” he said. “The PA, the Palestinian Authority, is the one who has the legitimacy and is being recognized by everybody, including Western countries.”
Although events are hard to predict, Al-Rashed said he supports the view of Arab News columnist Hassan Yassin, who suggested in a recent op-ed that Trump’s unconventional style could help pave the way for a lasting peace in the region.
“I think we need to give President Trump the space and the chance because, look, Trump is not (Joe) Biden, and I think Trump is unique among all American presidents,” he said.
“He does definitely move mountains. And I think there is a great chance for the Middle East ... not only to sort out Gaza, but we can go beyond that to the two-state solution.”
He added: “Trump can convince anyone, to be honest, his own way; he has his own style. I’m sure (Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin) Netanyahu will not dare to treat Trump as he did Biden or (Barack) Obama before.
“Trump can make history and he can win the Nobel Prize. Definitely.”
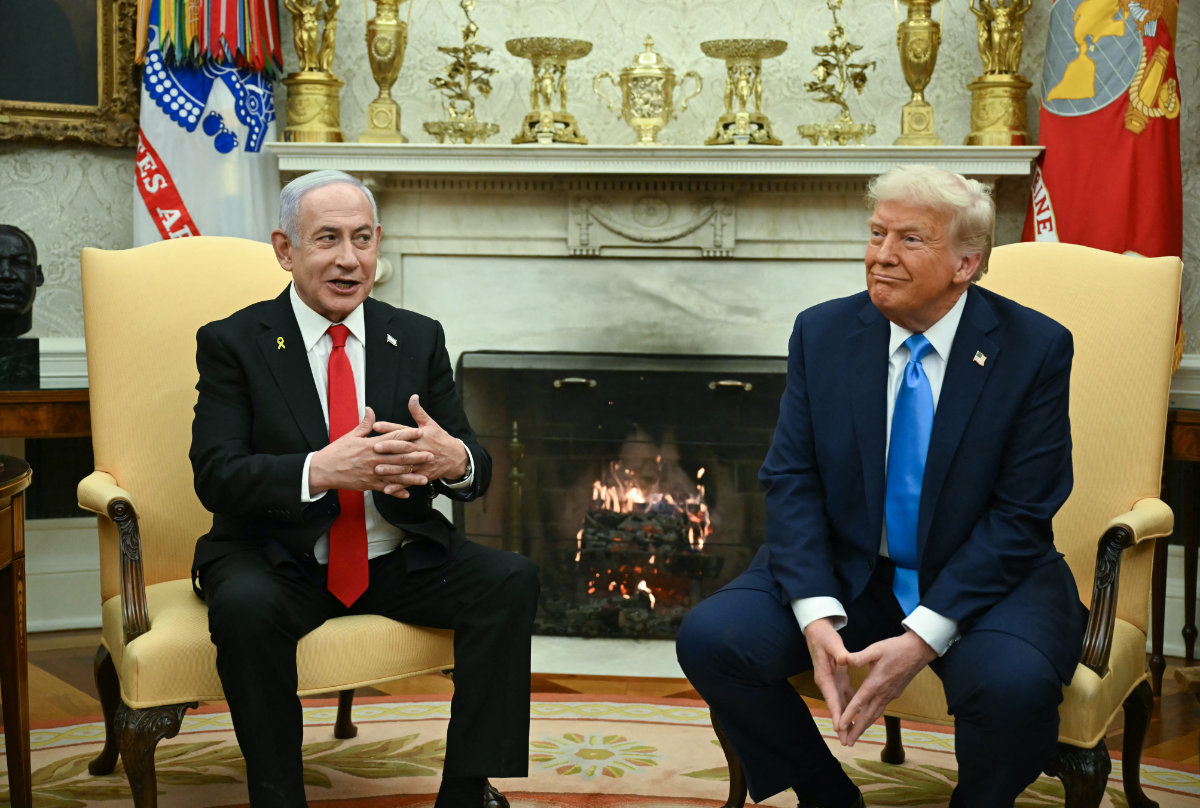

Abdulrahman Al-Rashed says he supports the view that Trump’s unconventional style could help pave the way for a lasting peace in the Middle East and that Netanyahu would not dare defy him. (AFP/File photo)
Al-Rashed dismissed any notion that Egypt and Jordan might fight Israel over the displacement of Palestinians after Ayman Safadi, Jordan’s foreign minister, said such a move would amount to an act of war.
“I don’t think Jordan nor Egypt will go that far. I think these were the two best countries and governments in the region who know how to handle the crisis,” Al-Rashed said.
“They are concerned about the issue of Gaza. It’s just things going really too far in terms of devastation. We have more than 50,000 people killed there. We have Israeli hostages remaining there as well. So we are stuck.
“The issue here is how to get the Israeli hostages out, how to get Hamas out of Gaza, how to have peace in Gaza, and finally how to activate the peace plan. I don’t think what we heard about Egyptian and Jordanian readiness; I don’t take that seriously, honestly.”
Turning to Lebanon, Al-Rashed expressed optimism about the country’s future following the election of former army chief Joseph Aoun as president and former International Court of Justice judge Nawaf Salam as prime minister in January.
Having been trapped in the vortex of a major financial crisis since 2019 and more than two years without a formally recognized government, the country is now on track to make a recovery, not least from the recent conflict on its territory between Israel and Hezbollah.
Al-Rashed said President Aoun’s recent visit to Riyadh was indicative of the reset underway in relations between Saudi Arabia and Lebanon, but warned that Hezbollah — although significantly weakened by the conflict — remains a potentially destabilizing force.
“To a certain degree, the worst is behind us, but we still have problems,” Al-Rashed said. “Even with kitchen knives, Hezbollah could be a problem.”
He added: “Hezbollah, of course, are really facing a lot of problems right now. They have thousands of people who are running out of cash. They have houses destroyed. They have to be rebuilt. They have no routes to Iran anymore. They are disconnected from Iran.”
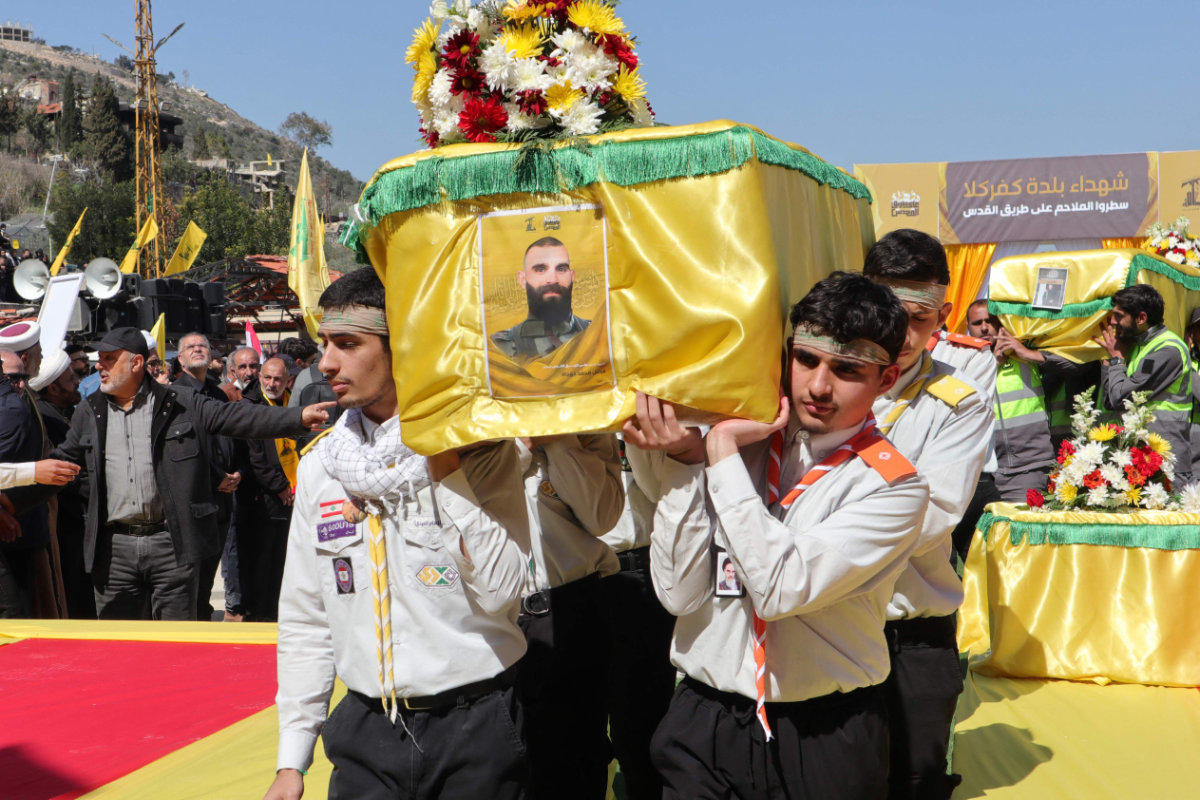

Despite suffering severe beating in its war with Israel, Lebanon's Hezbollah militia remains a potent force, says Abdulrahman Al-Rashed. (AFP photo)
Discussing the downfall of the Bashar Assad regime in December and the rise of Ahmed Al-Sharaa’s transitional government in Syria, Al-Rashed said it was a significant shift for the region.
“I cannot really speak on behalf of Riyadh, but from my understanding, everyone — almost everyone — is extremely happy about the departure of the Assad regime,” he said. “It has been there for half a century. It was a contributor to chaos.”
Clashes between government security forces and suspected pro-Assad factions in the Alawite community escalated last week. The Saudi Ministry of Foreign Affairs has come out in full support of Al-Sharaa.
“Everyone extended their support to President Al-Sharaa, including Saudis,” Al-Rashed said. “He visited Riyadh. He made his first visit. And Saudis, they made sure to welcome him. So no excuse whatsoever that the new regime should be welcomed; of course, it is welcomed as long as it behaves like a normal one in the region.
“Saudi can contribute a lot to the development of Syria, but we need first, of course, to see the sanctions lifted. And this has to do with Washington more than with Riyadh. But yes, this is what we see right now — history in the making, definitely.”
He also warned against Israeli involvement with the Druze community in Syria, suggesting that moves toward creating a breakaway region led by the ethno-religious minority could create further instability.
“Israelis, whatever the objective is, they’re trying, of course, to create a buffer zone by encouraging bordering areas like the Druze area to be protected by them.”
Turning to Saudi Arabia, Al-Rashed reflected on the sweeping reforms implemented under Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman’s Vision 2030 agenda, which have positioned the Kingdom as a leading force for change in the region.

File photo showing Riyadh city's skyline. (SPA photo)
“We are seeing Saudi Arabia not only being developed and Saudi Arabia being moderate also in terms of Islam, but we are seeing a leadership that is trying to spread the word in the region and all over the Islamic world,” he said.
“Saudis will change the Islamic world, not just Saudi Arabia, as is already happening right now.”
Referring to the crown prince’s leadership, Al-Rashed said: “People, individuals make big changes in history. You have the leaders who make a big difference for their own countries. And I think the crown prince has shown his ideas and of course resilience from the beginning.”
Elaborating on the point, he said: “If you have listened to Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman over the past 10 years, when he speaks to local or regional media, he talks about the economy, he talks about the welfare of the people, he talks about the future. These are three subjects which make a big difference.
“Unfortunately, politicians in the region spend 90 percent of their conversation about politics. And I think this is why Saudis have something called 2030, a vision for the future. And that is what everybody’s busy with.”












