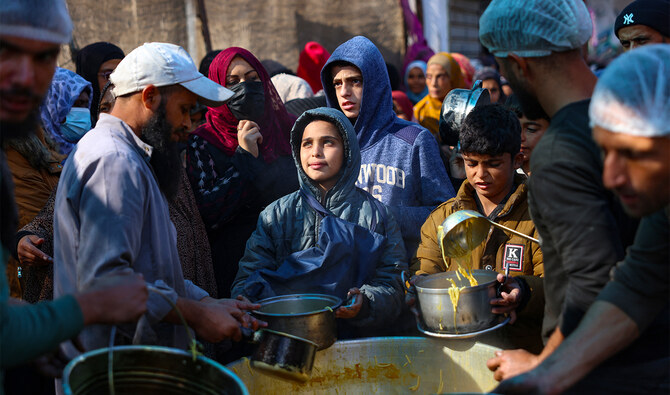The Trump administration’s effort to slash and reshape American foreign aid is crippling the intricate global system that aims to prevent and respond to famine.
Struggling to manage hunger crises sweeping the developing world even before US President Donald Trump returned to the White House, the international famine monitoring and relief system has suffered multiple blows from a sudden cessation of US foreign aid.
The spending freeze, which Trump ordered upon taking office Jan. 20, is supposed to last 90 days while his administration reviews all foreign-aid programs. Secretary of State Marco Rubio has said an exception allows emergency food assistance to continue.
But much of that emergency aid is at least temporarily halted as humanitarian organizations seek clarity about what relief programs are allowed to continue. Compounding the problem is Trump’s move this week to shut the US government’s top relief provider, the US Agency for International Development (USAID).
About 500,000 metric tons of food worth $340 million is in limbo, in transit or storage, as humanitarian organizations wait for US State Department approval to distribute it, said Marcia Wong, a former senior USAID official who has been briefed on the situation.
US-provided cash assistance intended to help people buy food and other necessities in Sudan and Gaza also has been halted, aid workers told Reuters. So has funding for volunteer-run community kitchens, an American-supported effort in Sudan to help feed people in areas inaccessible to traditional aid, these people said.
Humanitarian organizations have hit roadblocks in getting paid for emergency food operations. Questions about what programs have permission to continue have gone unanswered, because the people who normally field such inquiries – officials at USAID – have been placed on leave, at least six sources said.
The Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET), the US entity that produced regular food security alerts meant to prevent famine, also has been shut down. Its loss leaves aid organizations without a key source of guidance on where and how to deploy humanitarian relief
And the US government issued stop-work orders to two major manufacturers of nutritional supplements, diminishing the supply of life-saving food for severely malnourished children around the world.
“We are the one thing that nearly everyone agrees on – that little children who are starving and need emergency aid need help,” said Mark Moore, chief executive officer of Mana Nutrition of Georgia, one of the two suppliers ordered to stop producing supplements. “It is not hype or conjecture or hand wringing or even contested use of stats to say that hundreds of thousands of malnourished children could die without USAID.”
Shortly after this story was published, the US government notified Mana and the other manufacturer, Edesia Nutrition of Rhode Island, that the stop-work orders had been rescinded.
The US State Department did not respond to requests for comment for this story.
STOCKPILES ON HOLD
Conflict is driving large numbers of people into desperate hunger, and the US is the largest single donor of aid. It provided $64.6 billion in humanitarian aid over the last five years. That was at least 38 percent of the total such contributions recorded by the United Nations.
In 2023, almost 282 million people in 59 countries and territories experienced extreme food shortages that threatened their lives or livelihoods, according to the 2024 Global Report on Food Crises.
Even before the pause in US aid, the world’s famine-fighting system was under enormous strain, driven by conflict and political instability, as Reuters detailed in a series of reports last year. The halt in aid creates a two-pronged crisis for humanitarian organizations working to relieve severe hunger. It impairs the programs that aim to prevent mass starvation. More immediately, it hobbles programs meant to respond to crises and save lives.
Among the food aid in limbo around the world is almost 30,000 metric tons meant to feed acutely malnourished children and adults in famine-stricken Sudan, two aid workers there said. Some is sitting in hot warehouses, where it is in danger of spoiling, they said.
The food includes lentils, rice and wheat, one of the workers said – enough to feed at least 2 million people for a month. Some items have a quick expiration date and will be inedible by the end of Trump’s 90-day pause, this person said.
Aid groups are confused about which relief programs qualify for waivers from the spending freeze and if they’ll be able to obtain them – because most USAID staff have been placed on leave.
A LOST STEERING WHEEL
Longer term, the shuttering of FEWS NET stands to cripple the world’s ability to predict, prevent and respond to food insecurity crises.
Created by the US government in 1985 after devastating famines in East and West Africa, FEWS NET is funded by USAID and managed by Washington, D.C.-based Chemonics International. FEWS NET is charged with providing early warning to US policymakers about hunger crises that could require a humanitarian response. It uses data from federal agencies, scientists and other humanitarian organizations to produce a stream of reports on food security. USAID and humanitarian organizations used FEWS NET reports to decide where to send food aid.
Researchers who collect and analyze data on food insecurity and famine say FEWS NET is essential to world efforts to fight hunger. They say it can be more nimble and prolific than its UN-backed counterpart, the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification system (IPC), a global partnership that reports on food insecurity in dozens of lands.
In most areas where it works, the IPC requires consensus on its findings among local government authorities and representatives of other humanitarian bodies. This can result in political attempts to influence its work and can delay and impede its efforts to alert the world to a looming crisis,a recent Reuters investigation found.
FEWS NET doesn’t face those consensus-building requirements, and so is faster and more efficient, researchers say. In 2024, FEWS NET produced more than 1,000 food insecurity outlooks, alerts and other reports covering more than 34 countries. The IPC published 71 reports in 33 countries.
The IPC declined to comment on FEWS NET’s demise. The “implications for the initiative remain unclear,” said Frank Nyakairu, a spokesman for IPC.
On January 27, Chemonics, which manages FEWS NET, received a stop-work order from USAID. Two days later, FEWS NET’s website went dark, eliminating public access to thousands of reports funded by American taxpayers.
“Ending FEWS NET is sort of like taking the steering wheel off the car,” said Andrew Natsios, a professor at Texas A&M University who headed USAID from 2001 to 2006. “Even if the car is working fine, if there’s no steering wheel, you don’t know where the car is going.”
FEWS NET has been a critical player in assessing food insecurity in most of the world’s worst hunger crises. An important conduit of data to the IPC and the global humanitarian system, its reports offered strategic analysis about how conflict and other problems impact food insecurity in specific places. It also pushed the IPC to act when the UN-backed body’s work became bogged down by politics.
Without FEWS NET, “the single most important component of the IPC system is knocked out,” said Alex de Waal, executive director of the World Peace Foundation at Tuft University’s Fletcher School.
In December, Reuters reported that the Sudanese government maneuvered to delay an IPC famine determination in Darfur. FEWS NET, which had already concluded that famine was happening there, pushed for the IPC’s Famine Review Committee to convene, over the objections of Sudanese officials. In the end, the IPC committee agreed to announce that famine had struck Zamzam, a vast camp for internally displaced people in North Darfur.
But FEWS NET’s propensity to issue blunt assessments has also drawn fire in Washington. In December, FEWS NET published a report that projected famine by early 2025 in part of northern Gaza. After the report was issued, Jack Lew, US ambassador to Israel from October 2023 until January, wrote that it was “irresponsible” to issue such a finding. FEWS NET withdrew the report, stating that its alert was “under further review” and that it expected to update the report in January.
With the dissolution of its chief funder, USAID, FEWS NET employees say they are not optimistic about the organization resuming work.
Its apparent death leaves “a gaping hole” in reporting on humanitarian crises, said Chris Newton, an analyst specializing in early warning and food security at International Crisis Group, a Brussels-based think tank. FEWS NET’s loss will hurt efforts to end famine in Sudan and prevent it in other hotspots and could lead to the collapse of a wide network of data providers, all crucial to understanding humanitarian risks globally, he said.
“Famine was disappearing from the world in the 2000s, and now its return will likely accelerate as we become increasingly blind to it, even as it becomes a more common tool of politics and war,” Newton said.