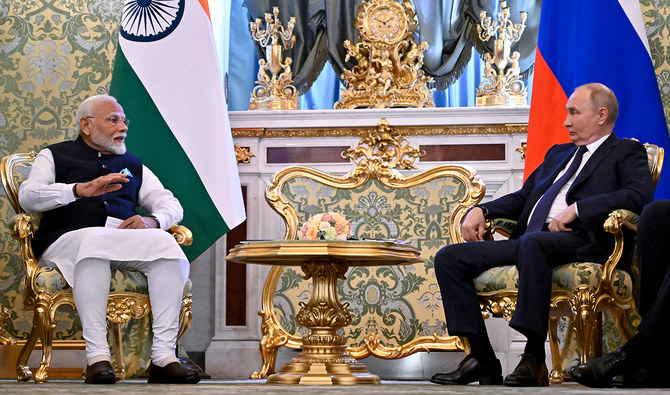
MOSCOW: Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi told Russian President Vladimir Putin on Tuesday in Moscow that peace was “of utmost importance” and that “war cannot solve problems.”
“As a friend, I have also said that for the brighter future of our next generation, peace is of utmost importance,” Modi said in a speech in Hindi, sitting alongside Putin.
“When innocent children are murdered, one sees them die, the heart pains and that pain is unbearable.”
Modi said he and Putin had discussed Russia’s campaign in Ukraine during his visit to Moscow.
“As a true friend, we were together and chatted on a range of issues,” Modi said.
“And I was happy that on Ukraine, we could both express our views openly and in detail.”
Modi landed in Moscow on Monday, hours after Russia launched a massive barrage targeting cities across Ukraine that killed more than three dozen people and heavily damaged a children’s hospital in Kyiv.
It sparked condemnation from governments in Europe and North America.
“I know that war cannot solve problems, solutions and peace talks can’t succeed among bombs, guns, and bullets,” Modi added. “And we need to find a way to peace through dialogue.”
Russia is a vital supplier of cut-price oil and weapons to India, but Moscow’s isolation from the West and growing ties with Beijing have impacted its partnership with New Delhi.
Western powers have in recent years also cultivated stronger relations with India as a hedge against China and its growing influence across the Asia-Pacific, while pressuring New Delhi to distance itself from Russia.
India PM Modi tells Putin ‘war cannot solve problems’
https://arab.news/z47ct
India PM Modi tells Putin ‘war cannot solve problems’

- Modi landed in Moscow on Monday, hours after Russia launched massive barrage targeting cities across Ukraine
- The latest Russian attack killed more than three dozen people and heavily damaged a children’s hospital in Kyiv
Russia committed ‘crimes against humanity’ in deporting Ukrainian children: UN inquiry

- The inquiry said Russia had deported or transferred “thousands” of children from occupied areas of Ukraine, of which it had so far confirmed 1,205 cases
- “Four years on, 80 percent of the children deported or transferred in the cases investigated by the commission have not returned,” it said
GENEVA: Moscow’s deportation and forcible transfer of children from Ukraine to Russia amounts to a crime against humanity, a United Nations team of investigators said Tuesday.
The UN’s Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine said it had collected evidence leading it to conclude that “Russian authorities have committed the crimes against humanity of deportation and forcible transfer, as well as of enforced disappearance of children.”
The probe was established by the UN Human Rights Council shortly after Moscow launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
The inquiry said Russia had deported or transferred “thousands” of children from occupied areas of Ukraine, of which it had so far confirmed 1,205 cases.
“Four years on, 80 percent of the children deported or transferred in the cases investigated by the commission have not returned,” it said.
Moscow has failed to establish a system facilitating returns, and has instead focused on long-term placement of the children with families or institutions in Russia, while relatives were not informed of their fate.
The commission confirmed its previous finding that Russian authorities had unlawfully deported and transferred children — as a war crime — “and that they have unjustifiably delayed their repatriation, which is also a war crime.”
These measures “were not guided by the best interests of the child,” and have violated international law, the probe found.
- Putin cited -
It said the involvement of Russian President Vladimir Putin, “including through his direct authority over entities that have steered and executed this policy, has been visible from the outset.”
In 2023, the International Criminal Court issued a war crimes arrest warrant against Putin, accusing him of “unlawfully deporting” Ukrainian children.
The issue is highly sensitive in Ukraine and remains central to negotiations for a potential peace agreement between Kyiv and Moscow.
According to Kyiv, nearly 20,000 Ukrainian children have been forcibly removed since Russia’s full-scale invasion.
Russia insists it has moved some Ukrainian children from their homes or orphanages to protect them from hostilities.
As for Russian trials in the context of its invasion of Ukraine, the commission found that Russian authorities have “systematically fabricated evidence” and “systematically violated a range of fair trial guarantees,” while judges “have not acted with independence and impartiality.”
- ‘Extreme violence’ -
The commission also probed the situation of nationals from 17 countries who were recruited — either voluntarily or through deception — to fight with Russian troops in Ukraine.
They included men from Azerbaijan, Belarus, Brazil, Cuba, Egypt, Ghana, India, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Nepal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkiye and Yemen.
“After training, usually lasting between one week and 30 days, they were forced to serve on frontlines in Ukraine, often assigned extremely dangerous duties,” the commission said in its report.
Commanders arbitrarily imposed “extreme violence” as punishment for refusing orders that meant almost certain death, with soldiers describing being treated like “cannon fodder,” sent on “meat assaults” without training or necessary equipment, and “forced to advance at all costs.”
“The evidence collected demonstrates abusive behavior, cruelty, humiliation, inhuman treatment, and a total disregard for human life and dignity, perpetrated with a sense of impunity,” the report said.
Regarding Ukraine, the report voiced concern about the overly broad definition and sometimes distorted interpretation of the crime of “collaboration.”
The commission also said reports regarding violent treatment of conscientious objectors during Ukrainian mobilization were “a source of concern.”
The report will be presented at the Human Rights Council in Geneva on Thursday.
Moscow does not recognize the commission and does not answer its requests for access, information and meetings.