DUBAI: Time was when spending long hours in the office was equated by company management with employee dedication, while telecommuting was regarded as the province of homebodies and slackers.
That was before the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 transformed the world of work, proving almost overnight that many kinds of traditional office-based tasks could be performed equally efficiently from home. White-collar workers across the world, including the Middle East, quickly adapted to social-distancing rules and lockdown conditions, making the term “WFH” (work from home) more popular than ever.
The emergence and widespread acceptance of remote working led to an explosion in the use of advanced communication technologies, including video conferencing apps, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams and FaceTime, which all but seamlessly replaced in-person meetings, thereby slowing the spread of the highly contagious virus.

The emergence and widespread acceptance of remote working led to an explosion in the use of advanced communication technologies, including video conferencing apps, such as Zoom. (Shutterstock)
“Throughout the pandemic, individuals, organizations, communities and nations have encountered tremendous hurdles, and video communications have helped maintain a sense of normalcy and continuity in life’s essential tasks,” Sam Tayan, head of Zoom’s Middle East and North Africa division, told Arab News.
More than two years on, the transition from full-time in-person to partial remote interaction seems unstoppable, with workplaces, educational institutions, health professionals, business partners, families and individuals all dependent, to varying degrees, on communication applications.
For Melissa Whitehead, a Dubai resident who works in public relations, remote working has been a game-changer, allowing her to save on fuel, parking and commuting time.
“Not having to sit in traffic twice a day for over an hour has, overall, improved people’s mental well-being and even contributed to a greener environment by reducing automobile exhaust,” she told Arab News.

Many businesses are now beginning to see distributed workplaces as a transition from geo-specific workspaces to one that's more people-driven. (Getty Images)
But what employees such as Whitehead see as an open-and-shut argument, many employers see as a recipe for empty offices, less face-to-face interaction and productivity risks.
Since the easing of pandemic restrictions, companies and government departments have been eager — some of them impatient — to bring staff back into the office setting. Indeed, new studies show that the demand for office space in countries such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE is now on the rise.
Findings by 6Wresearch, a global market research and consulting firm, show that almost 32 million square feet of office space is being built in Saudi Arabia’s capital, Riyadh, to accommodate the many multinational corporations now relocating to the Kingdom.
 The figures reflect the success of the Kingdom’s Program HQ campaign, which aims to encourage at least 500 foreign corporations to relocate their regional headquarters to Riyadh by 2030 as part of the drive toward diversifying the Saudi economy.
The figures reflect the success of the Kingdom’s Program HQ campaign, which aims to encourage at least 500 foreign corporations to relocate their regional headquarters to Riyadh by 2030 as part of the drive toward diversifying the Saudi economy.
“The flexible office space industry is clearly all set to grow in the Kingdom in the coming years as a rising number of newer firms and well-established corporations opt to employ serviced workspaces,” Ali Rao, CEO of Dubai-based Elixir Establishments, told Arab News.
Rao estimates that the flexible office space market in Saudi Arabia will see a compounded annual growth rate of more than 6 percent over the next five years.
Post-pandemic demand for office space is also booming in the UAE, surging to a five-year high amid an influx of foreign companies looking to expand or relocate to the Gulf’s commercial hub, Dubai. In the first quarter of 2022, office units with a combined 480,000 square feet were delivered, bringing the city’s supply to 107 million square feet, according to 6Wresearch.
Rao attributes the improved business environment and upbeat mood to the immense success of Expo 2020 Dubai (October 2021-March 2022) and a series of reforms the UAE made to corporate, employment and visa rules.
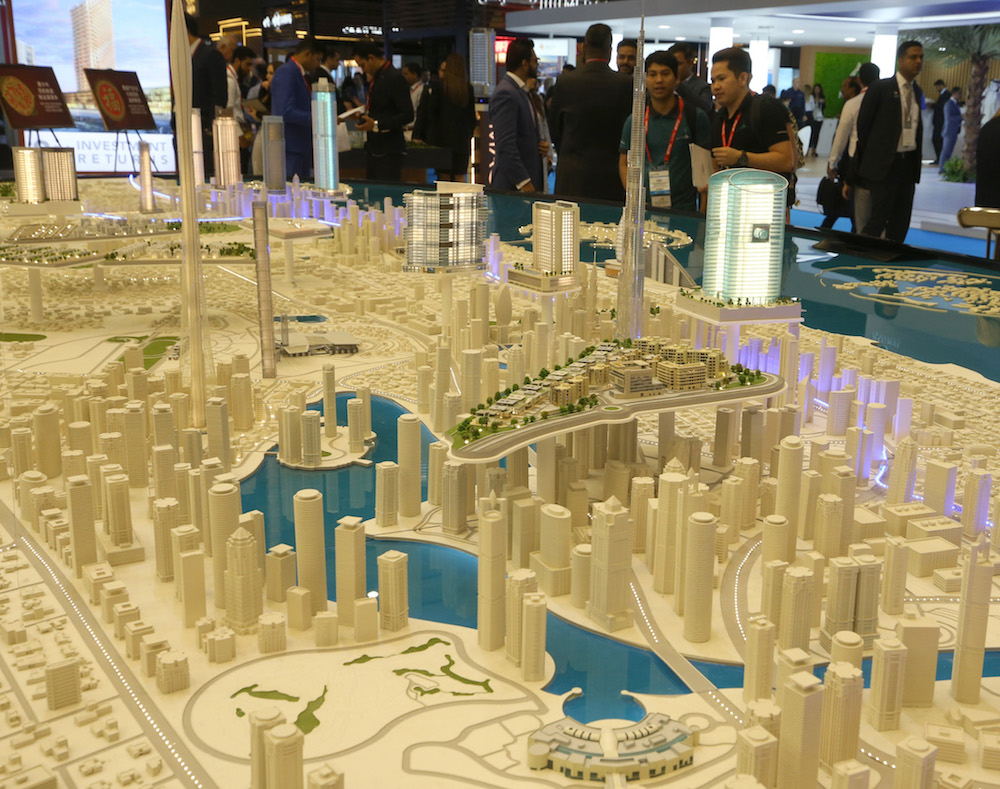

Millions of square feet of new office space is currently being built across the Gulf region. (AFP)
“What’s helping attract new investors and businesses is the slew of new measures introduced by the UAE in recent months, from decriminalizing bounced cheques to announcing long-term five-to-10-year visas, making it far easier and more appealing than ever before for new investors to set up a base here,” he told Arab News.
Tayan, of Zoom’s MENA division, agrees that changes in laws have contributed to a much more conducive investment environment.
“Economic reforms implemented by both the UAE and Saudi Arabia, such as 100 percent foreign ownership, new remote working visa initiatives, and the government’s push to increase investment, are driving demand for commercial office space,” he said.
So, could the Middle East be witnessing the end of the era of WFH?
Soaring demand for office space, according to Tayan, does not necessarily mean that remote working is a thing of the past. In fact, many companies are embracing the hybrid work model, promoting a better work-life balance for their employees.
“Working from home and hybrid working have become commonplace, as 58 percent of UAE firms offer variations of these, and, in most cases, it has become a necessity,” he said.
The picture is not uniform, even beyond the Middle East. According to a study by real-estate services company Savills, 80 percent of workers in Dubai on average are back in the office in some capacity, while in Chinese cities the figure is as high as 90 percent.

Elixir Establishments CEO Ali Rao. (Supplied)
Meanwhile, in the City of London, less than 40 percent of workers have returned to the office, while in North America the figure is below 50 percent
According to Savills, variations between countries and regions depend on factors such as the length of local lockdowns, commuting times, ease of mobility and the average working age
Young workers appear more likely to seek interaction and mentorship in an office environment. For instance, in Mumbai, where 50 percent of the working-age population is under 35, the shift to hybrid working has been notably slower.
Other factors include the cost of renting office space, local workplace culture and the size of employees’ homes, as larger properties are more likely to have dedicated space for home working.
A common concern of many company executives around the world is that remote working reduces productivity. However, according to Tayan, the opposite may well be the case.
A study commissioned by Zoom and conducted by Forrester Consulting found that the composite model organization using Zoom could add up to 53 minutes of productivity per employee per week, while also reducing the need for company travel, potentially saving firms millions.
A separate Stanford University study found that working from home increased productivity by as much as 13 percent. The increase in staff performance was attributed to a quieter and more convenient working environment, which allowed staff to work more minutes per shift with fewer breaks and sick days.

Could the Middle East be witnessing the end of the era of “working from home,” popularly known as WFH? (Supplied)
“It’s hard to say what exactly is responsible for any data pointing toward an increase in productivity in a work-from-home environment, but it’s likely a combination of various factors such as work-life balance, lack of distractions, and employee satisfaction,” said Tayan.
This was also reflected in a survey by ConnectSolutions, which found employees following the hybrid model had increased productivity, with 30 percent doing more work in less time and 24 percent doing more work in the same period of time.
The business establishment appears to be taking notice of what the data suggests, but seems reluctant to embrace an entirely remote model of work.
Priyabrata Rath, commercial investment manager at Powerhouse Real Estates, believes the trend of remote and hybrid forms of working will outlive the pandemic, but not eclipse office work entirely.
“During the pandemic, it helped all of us cope with the changing times,” he told Arab News. “But it is unlikely that it will replace traditional offices permanently.”
Whether in the Middle East or at a global level, the general consensus seems to be that the pandemic has had a lasting impact on attitudes to remote and hybrid forms of work, ushering in an era of continued office space expansion alongside the widespread acceptance of greater workplace flexibility.
“It is definitely the beginning of a new era that is set to see hybrid work arrangements,” Rao, of Elixir Establishments, told Arab News.
“Many businesses are now beginning to see distributed workplaces as a way to transition from geo-specific workspaces to one that’s more people-driven.”















