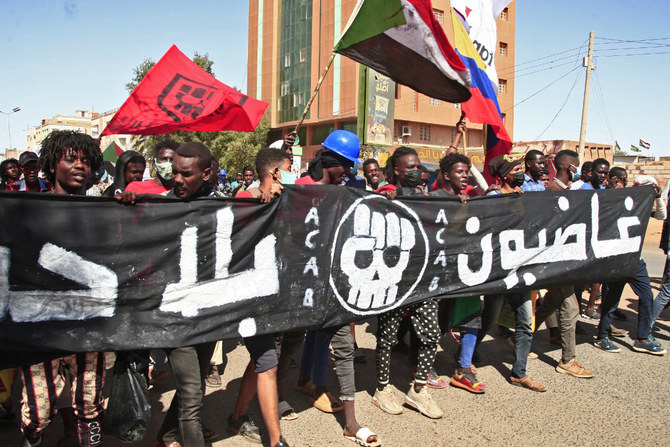
DUBAI: Photographer and activist Lana Haroun, 34, was in Khartoum in 2019, at the epicenter of the revolution in Sudan. She helped to document the rage and optimism of the movement that brought an end to the 30-year rule of dictator Omar Bashir in April that year.
Like thousands of Sudanese people who had long dreamed of political change, Haroun was hopeful as the country subsequently began a difficult transition to democratic civilian rule. Those hopes soon turned to despair.
Abdalla Hamdok, a respected UN diplomat who was appointed prime minister in August 2019, offered a vision of peace and prosperity. But with the economy in crisis, Sudan soon began to run short of food, fuel and medicine.
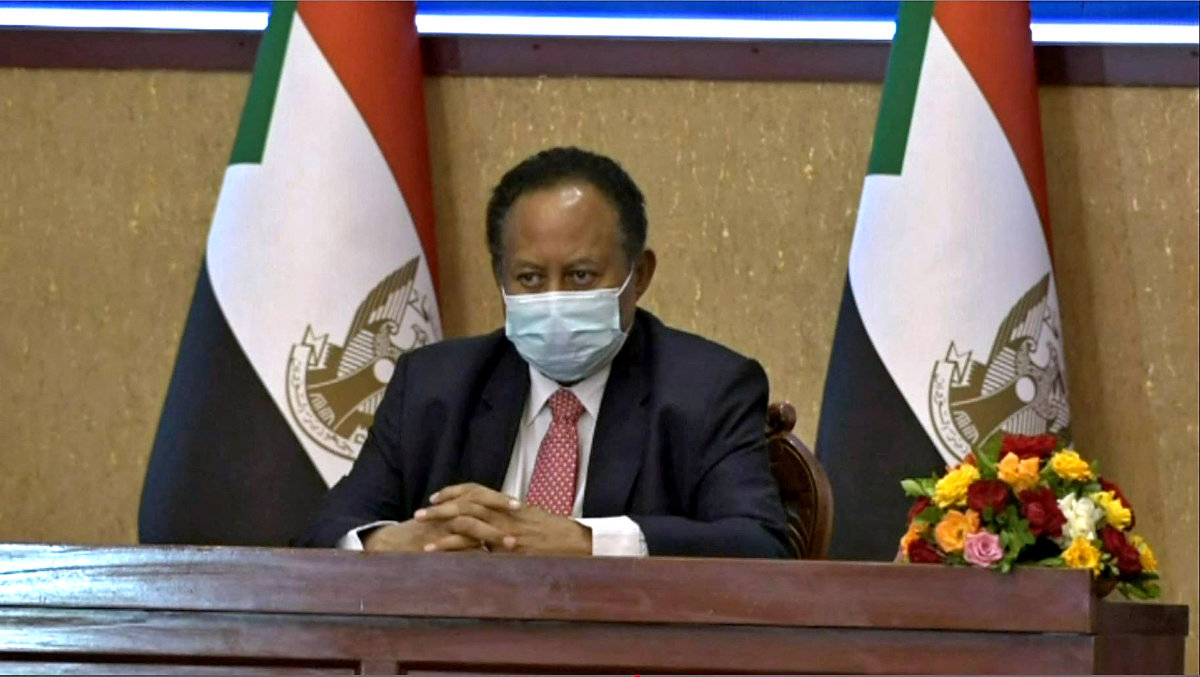

Sudanese Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok. (AFP file photo)
He acknowledged the hardship arising from the austerity measures he had adopted, but expressed hope that their positive impact would be felt very soon.
However, as daily street protests became increasingly violent, Haroun decided it was time to leave the country. In November 2020, she and her family packed up and moved to Dubai, where she now works for a petroleum company.
“The economic situation was very bad in Sudan and there are many things I want to do in my life,” she told Arab News. “I had to leave.”
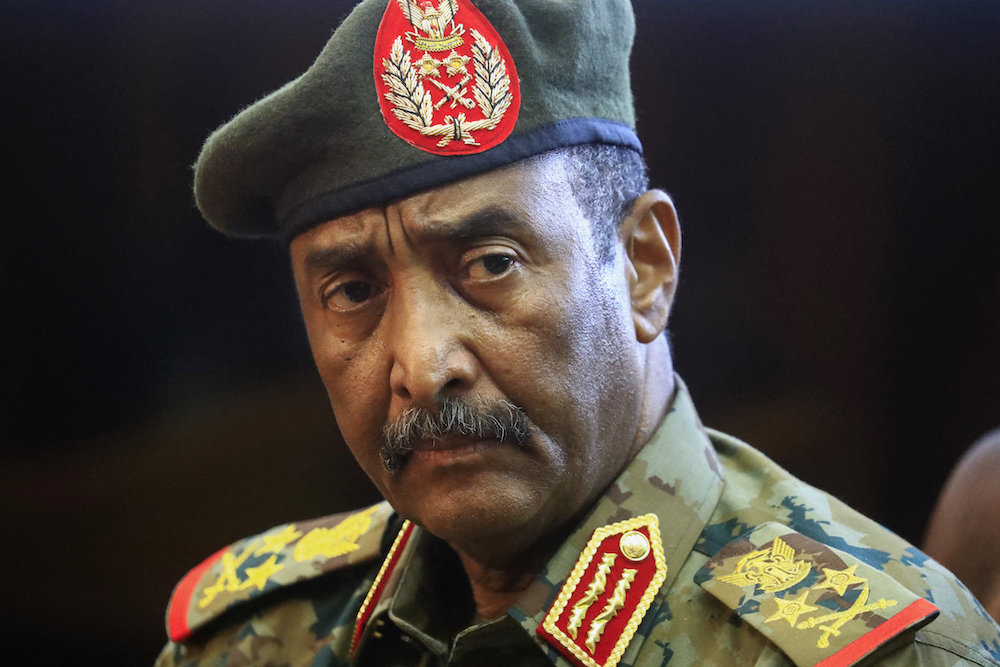

General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan. (AFP)
Sudan’s democratic transition stalled in October 2021 when military chief Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan staged a coup, toppling the civilian government and removing Hamdok from office.
In response to the international condemnation that followed, the military proposed a power-sharing deal and reinstated Hamdok as prime minister in November. The agreement proved unpopular with pro-democracy groups, however, leading Hamdok to resign on Jan. 2.
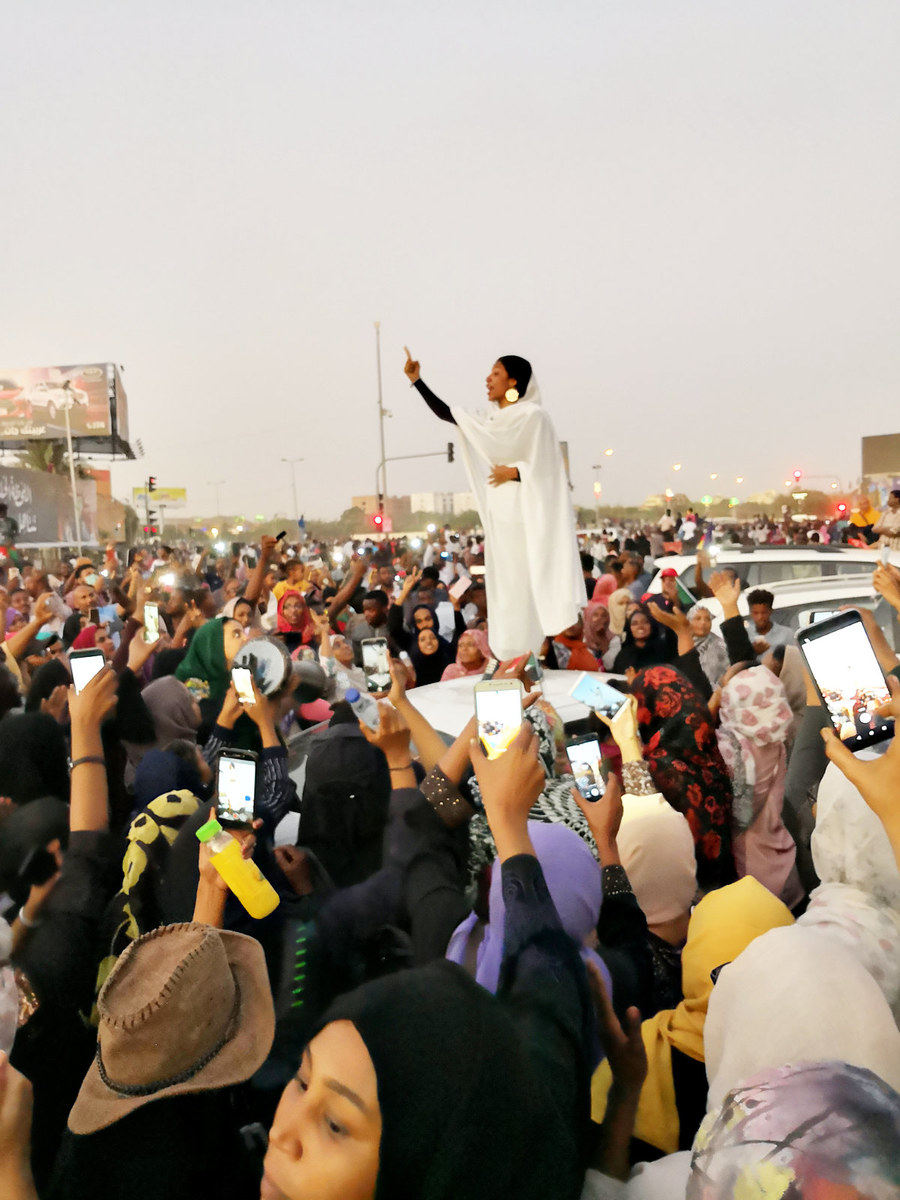

Lana Haroun’s photograph of Sudanese protesters during the 2019 uprising against long-time ruler Omar al-Bashir. (Photo courtesy of Lana Haroun)
“No one knows what will happen now,” Haroun said. “Many people are leaving Sudan because they are afraid to lose their lives, not just because there is no food or money but because they are afraid of being killed.
“Sudan is now worse than in Bashir’s time. We don’t have what we need to live normal lives and more people are being killed than ever before.”
 In a televised address following his resignation, Hamdok said the country was at a “dangerous turning point that threatens its whole survival.” This was no exaggeration; with rising inflation, shortages of basic goods, and deadly unrest in Khartoum, the outlook has seldom been gloomier.
In a televised address following his resignation, Hamdok said the country was at a “dangerous turning point that threatens its whole survival.” This was no exaggeration; with rising inflation, shortages of basic goods, and deadly unrest in Khartoum, the outlook has seldom been gloomier.
“Sudan has unfortunately fallen from the grace of being a rare positive story in the Horn of Africa into the hands of another military regime,” Mohamed Osman, a Sudanese former journalist and an independent specialist on the region, told Arab News.
“This is history repeating itself for the third time since the country’s independence. But this time it’s a poignant combination of tragedy and farce.”
One major challenge for international observers is the lack of reliable information from inside Sudan, in large part because of frequent internet blackouts.
FASTFACTS
A number of former govt. officials and activists have been detained by Sudan’s new military rulers.
Among those targeted are members of The Committee to Dismantle the Regime of June 30, 1989.
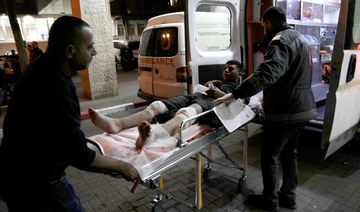
As a result, responsibility for the killings of protesters — whether the result of factional infighting, criminality or deliberate targeting by the feared Rapid Support Forces — is hard to ascertain.
“No one knows who is doing the killing in the streets,” said Haroun, who tries to follow the events as best she can from her self-imposed exile in Dubai.
“It’s crazy. But for sure this killing is from the military themselves because they are running the show in Sudan now.”
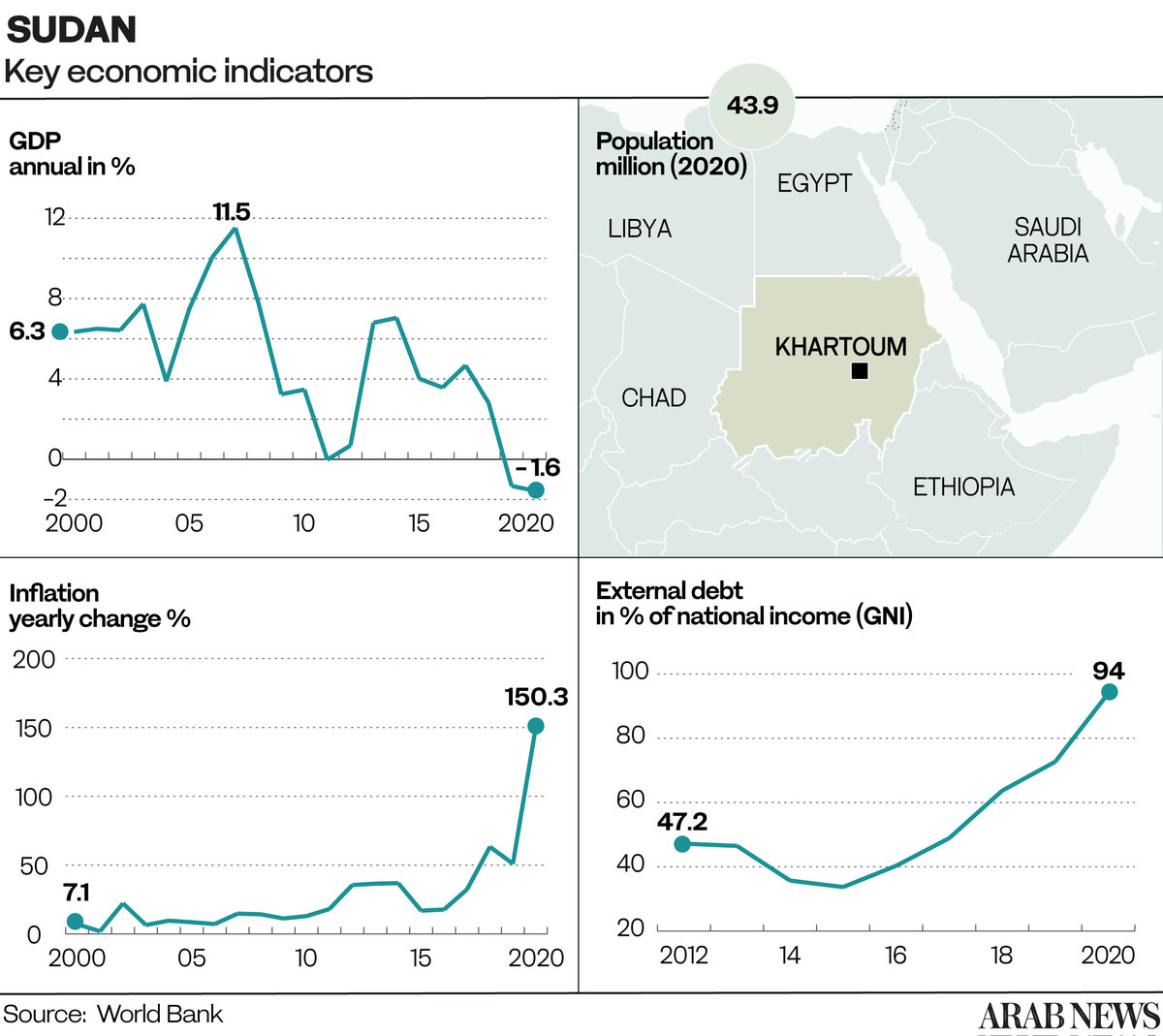
Since October, the value of the Sudanese pound has depreciated alarmingly, compounding inflationary pressure. Sudan’s removal from the US State Sponsors of Terrorism list in 2020 was expected to stimulate financial flows that could benefit growth. By all accounts, the advantage has been squandered.
“The economy was already struggling to recover,” said Osman. “Now this coup has worsened its situation, making life in Khartoum very hard. Many people are running out of money and trying to leave the country.”
According to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, about 14.3 million people in Sudan, almost one in three of the population, will need humanitarian assistance this year — about 0.8 million more than last year.
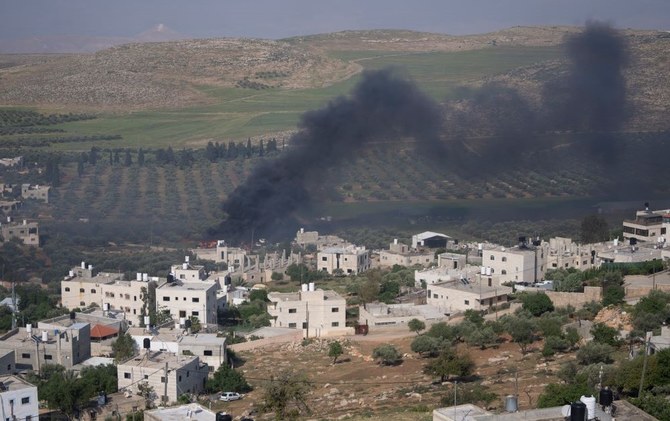
Further complicating matters, disputes over land, livestock, access to water and grazing since October 2021 have triggered a spike in tribal clashes, lootings and rape in the vast, arid Darfur region.
The World Food Programme has suspended operations following looting at its warehouses in North Darfur state, an act which "robbed nearly two million people of the food and nutrition support they so desperately need," the agency said.
Though the main Darfur conflict has subsided, the parts of Darfur bordering Chad are awash with guns and home to most of Sudan’s three million displaced people.
“The situation in the short-to-medium term is very bleak,” Rashid Abdi, a Horn of Africa analyst at Nairobi-based think tank Sahan Research, told Arab News. “The army, digging in, has refused all ideas about a resolution. They want a solution on their own terms.
“I think they understand that they are not going to continue the strategy of Bashir and hope that a military government will be acceptable in the long term.”
But Abdi believes the public in Sudan will not accept this status quo, so army chiefs probably want to install a civilian administration that is weak, that they can control. If that is the military’s game plan, he said, it is unlikely to fly with the Sudanese public.
“Their hope was that Hamdok would be the person to steer the country to better days,” he said. “I think he became trapped by the military and could not maneuver and did the decent thing, which was to resign.”
On Jan. 26, the splits in Sudanese society appeared to widen further when thousands of pro-military protesters gathered outside the Khartoum office of the UN Integrated Transition Assistance Mission in Sudan demanding an end to “foreign interference” and for the UN’s special representative for Sudan, Volker Perthes, to “go back home.”
Perthes, who was appointed head of UNITAMS in January 2021, has been trying to bring Sudanese stakeholders to the negotiating table to discuss a peaceful political solution and get the democratic transition back on track.
He has said that the UN itself “is not coming up with any project, draft or vision for a solution.” But Sudan’s military-led government has rejected his efforts, arguing that he should be working as a “facilitator and not a mediator.”
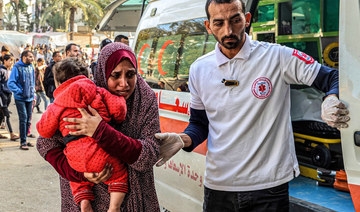
Meanwhile, Sudan’s overwhelmingly young anti-coup protesters have continued to march in the streets of Khartoum, where they routinely clash with security forces amid a ferocious crackdown on dissent. Since the coup, at least 79 people have been killed and hundreds more injured.

Supporters of the Sudanese army rally outside the office of the United Nations mission, west of Sudan's capital Khartoum, on Feb. 5, 2022. (AFP)
The daunting task of restoring the democratic transition has fallen on a population fed up with unending internal conflict, displacement and impoverishment.
“The protests are not just in Khartoum but also in Darfur and other parts of the country,” Erika Tovar Gonzalez, communication and prevention coordinator at the International Committee of the Red Cross, told Arab News from the Sudanese capital.
“There’s a humanitarian crisis, there’s armed and criminal violence and tribal clashes that continue to displace thousands of people. The youth are depressed. Some even have suicidal thoughts. They feel they have no future.”
The result is two seemingly irreconcilable visions, with the nation’s fate hanging in the balance.
“Even the Sudanese political parties that would have been willing to give Al-Burhan the benefit of the doubt for pragmatic reasons are more careful now,” said Abdi, the analyst.
“Because once they get into bed with the military, they damage their credibility and won’t get any support from the public. Al-Burhan has become more toxic as an ally.”
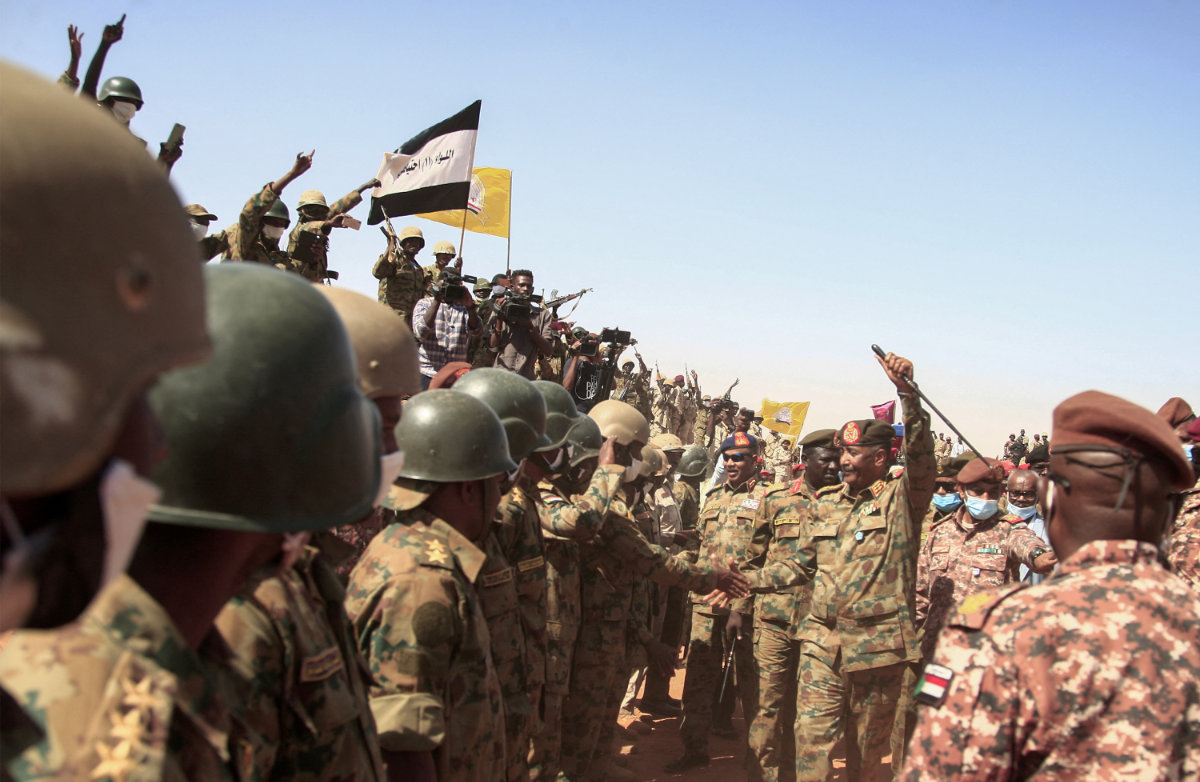

Sudan's top general Abdel Fattah al-Burhan greets soldiers during military exercise in the Maaqil area in the northern Nile River State on Dec. 8, 2021. (Photo by Ebrahim Hamid / AFP)
Analysts therefore believe it is unlikely that Al-Burhan and the military will be able to maintain their grip on power.
“I don’t think the military (strategy) has clarity,” said Abdi. “One speculation is that the military is aware that it is not going to be accepted but what they are trying to do is to buy more time to make good their promise of exit.”
Osman thinks the military badly miscalculated how events would play out after it launched last October’s coup.
“Who will give them money now?” he asked. “Western assistance is suspended. Gulf countries won’t give them enough cash. You cannot stabilize a regime without money. The military shot itself in the foot. The economic situation can only get worse as they move forward with this coup.
Osman added: “There can be no hope for a political compromise unless the military stops its deadly crackdown on protests first.”