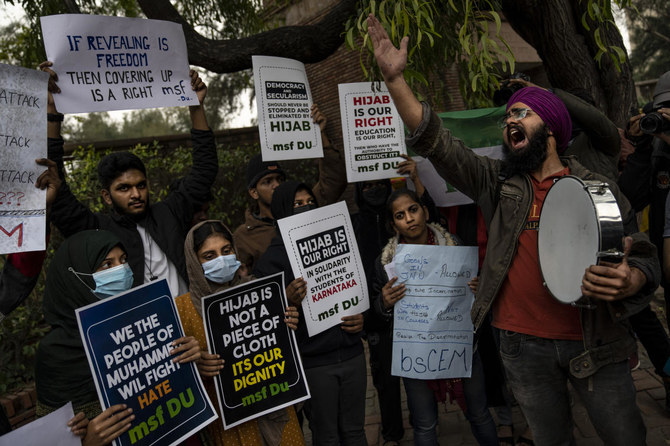NEW DELHI: A court in a southern Indian state told students on Thursday not to wear any religious clothing until it delivers a verdict on petitions seeking to overturn a ban on hijabs, headscarves used by Muslim women.
The court in Karnataka state is considering petitions filed by students challenging a ban on hijabs that some schools have implemented in recent weeks.
“We will pass an order. But till the matter is resolved, no student should insist on wearing religious dress,” the Press Trust of India news agency quoted Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi as saying.
The court also directed the state to reopen schools and colleges which the chief minister had shut for three days as protests over the ban escalated earlier this week.
The issue grabbed headlines last month when a government-run school in Karnataka’s Udupi district barred students wearing hijabs from entering classrooms, triggering protests outside the school gate. More schools in the state followed with similar bans, forcing the state’s top court to intervene.
The uneasy standoff has raised fears among Muslim students who say they are being deprived of their religious rights in the Hindu-majority nation. On Monday, hundreds of students and parents took to the streets to protest the restriction.
The dispute in Karnataka has set off protests elsewhere in India. A number of demonstrators were detained in the capital, New Delhi, on Thursday, and students and activists have also marched in cities including Hyderabad and Kolkata in recent days.
It also captured attention in neighboring Muslim-majority Pakistan. “Depriving Muslim girls of an education is a grave violation of fundamental human rights,” its foreign minister, Shah Mahmood Qureshi, tweeted on Wednesday, calling the situation “absolutely oppressive.”
Nobel Peace Prize laureate and education activist Malala Yousafzai also condemned the ban. “Refusing to let girls to go to school in their hijabs is horrifying,” the 24-year-old Pakistani human rights campaigner tweeted.
For many Muslim women, the hijab is part of their faith and a way to maintain modesty. It has been a source of controversy for decades in some Western countries, particularly in France, which in 2004 banned them from being worn in public schools.
In India, where Muslims make up about 14 percent of the country’s almost 1.4 billion people, they are not banned or restricted in public places and are a common sight.
Some rights activists have voiced concerns that the bans could increase Islamophobia. Violence and hate speech against Muslims have increased under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s governing Hindu nationalist party, which also governs Karnataka state.
India court: No religious clothes until hijab row settled
https://arab.news/zjeaz
India court: No religious clothes until hijab row settled

- The court in Karnataka state is considering petitions filed by students challenging a ban on hijabs
- The uneasy standoff has raised fears among Muslim students who say they are being deprived of their religious rights in the Hindu-majority nation
Kremlin says won’t share ‘specifics’ of Putin, Trump phone call on Iran war

DUBAI: The Kremlin said on Wednesday that it will not disclose the specific proposals by Russian President Vladimir Putin on the current Middle East war which came during an earlier phone call with US President Donald Trump.
During a presser, Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told reporters that Russia will not disclose the “specifics” of the Russian president’s proposals to Trump.
Putin held a phone call with Trump on Monday where they discussed the Ukraine and Iran wars.
Trump hailed the conversation as “positive.”
“He wants to be helpful” on the Middle East, Trump said of Putin.
Russian presidential aide Yury Ushakov told reporters later that day that Putin had a roughly one-hour telephone conversation with Trump at the request of the US side. The two leaders had not spoken over the phone since late December of last year.
Separately, Russia said it is constantly in touch with the Iranian leadership and willing to contribute to efforts to stabilize the region.
“Here I can only say that we are in constant contact with the Iranian side and with the Iranian leadership.”
“As President (Vladimir) Putin has said, Russia is always ready to do what it can to restore peace and stability in the region.”