JEDDAH: Since the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution in 1970 calling on economically advanced countries to contribute at least 0.7 percent of their gross national income to developing countries in aid, the worldwide need for humanitarian and development assistance has moved in only one direction: Upward.
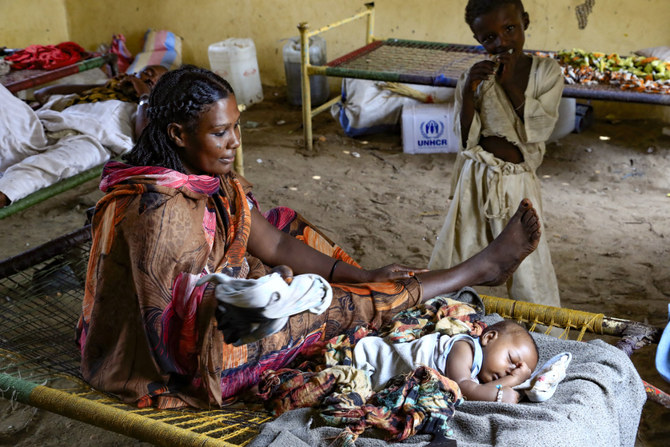
The latest Global Humanitarian Overview notes that 235 million people are in need and face an uncertain future, and that the COVID-19 pandemic has triggered “the deepest global recession since the 1930s.”
Looking on the bright side, however, the past two decades have seen many aid conferences and fund-raising events being organized and a steady increase in the number of aid providers. The humanitarian and development assistance provided by Saudi Arabia alone is a testament to the significant impact that foreign aid, in combination with clear policies, efficiency and accountability, has been making on the lives of people in the recipient countries.
In 2020, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs financial tracking service showed that Saudi Arabia ranked sixth among the world’s most generous donors, providing 3 percent of global humanitarian aid. In October 2021, the Kingdom ranked third among the world’s top donors, its share of humanitarian assistance having risen to 5 percent.
For quite some time, the assistance provided by Saudi Arabia neither received the media recognition it merited nor found prominence in international aid platforms. The Kingdom itself did not publicize data or reports related to foreign aid, opting to keep a low profile in keeping with Saudi culture and the Islamic practice of preserving the dignity of the recipient during charitable giving.
But now, a research paper titled “Why the World Needs Partnership with Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabia’s Global Humanitarian and Development Aid,” has shed light on how assistance provided by Saudi Arabia to developing countries worldwide has contributed significantly to their well-being.
FASTFACT
$5,211,331,962
Financial support from Saudi Arabia to different UN agencies
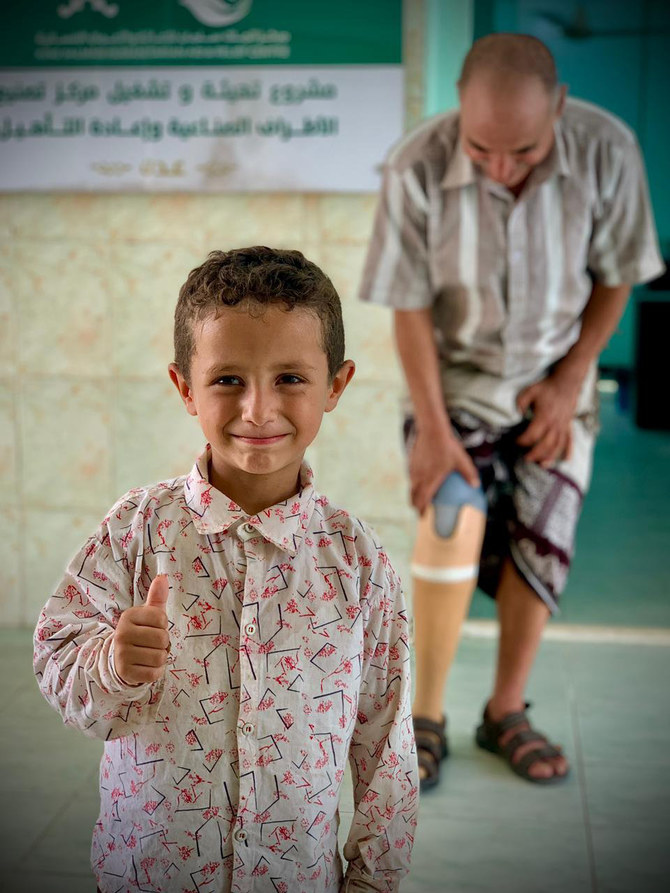
Published by the King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies, the paper unpacks the Kingdom’s humanitarian and development agenda, outlining the various categories of aid, where it is disbursed (by country and region), the targeted sectors and how it has evolved over time. It also highlights Saudi assistance to developing countries in their efforts to meet the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, the response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and support provided to in-country refugees.
The author of the paper, Makki Hamid, who is the director of research and information at King Salman Humanitarian Aid and Relief Centre, said the Saudi Fund for Development, the Kingdom’s primary development aid provider, has generously financed projects in different fields — notably health, agriculture, irrigation, electricity and transportation — over the years in a large number of countries.
“Saudi development aid has been provided in forms of grants and concessional loans and has provided significant funding as budget and deposits in central banks of many low- and middle-income countries,” he told Arab News. “Such budget support and deposits contribute to strengthen and enhance the economy of these countries.”
As the paper notes, Saudi Arabia has an extensive history of providing aid to developing countries affected by natural disasters and countries in need of immediate assistance. It was reporting its aid data to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development–Development Assistance Committee for many years as an aggregated data set, until in 2018, when it became a participant member of the OECD–DAC, represented by KSRelief.
KSRelief began collating data from the Kingdom’s different aid providers to proceed with overseas aid via the UNOCHA Financial Tracking Services, the OECD-DAC and the International Aid Transparency Initiative.
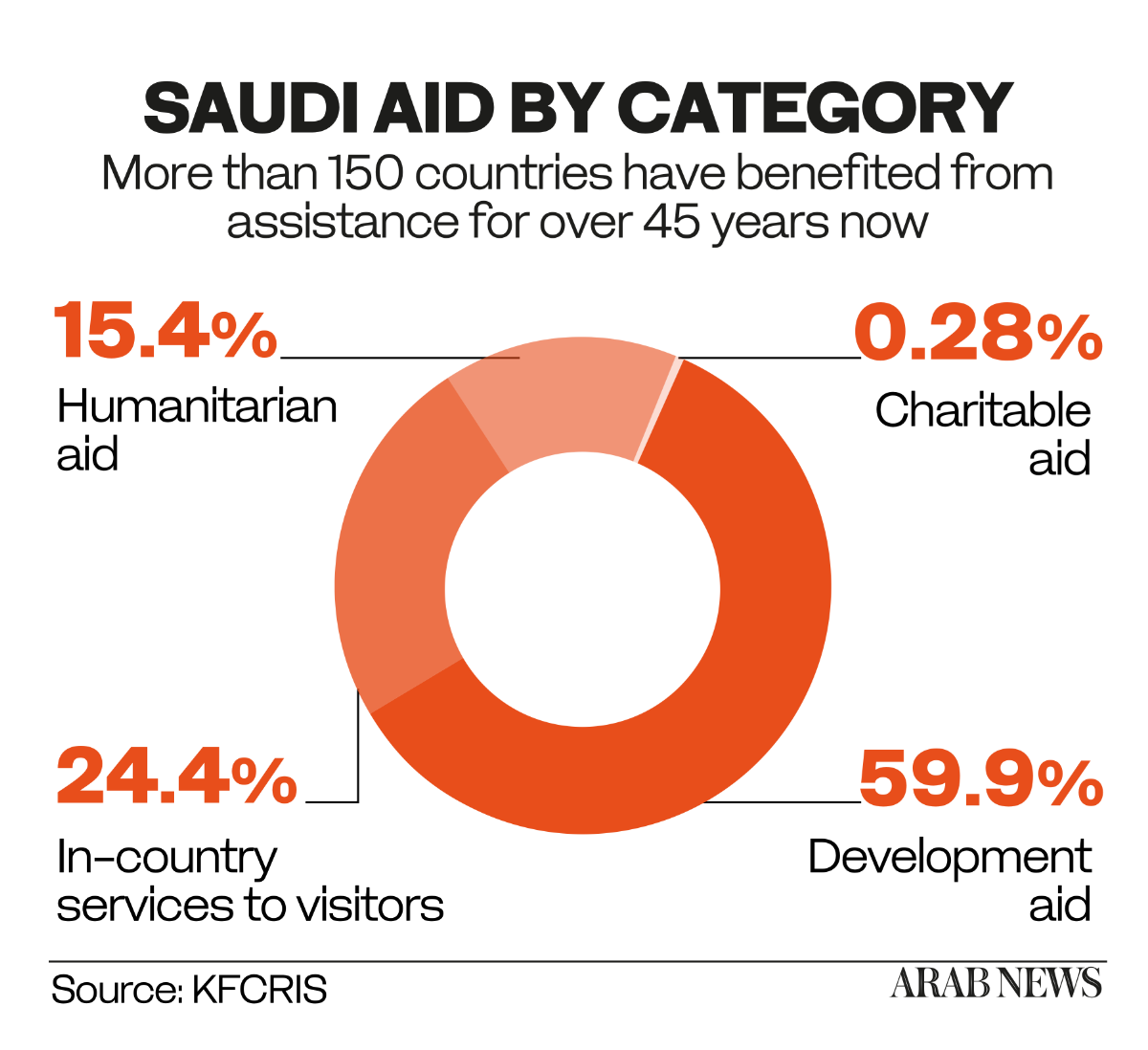
Currently, Saudi Arabia provides several categories of Official Development Assistance — namely, humanitarian aid (given during emergencies), development aid (for improving the economic and social well-being of developing countries), and charitable aid (which is provided for cultural or religious purposes, such as building mosques or supporting Hajj pilgrims).
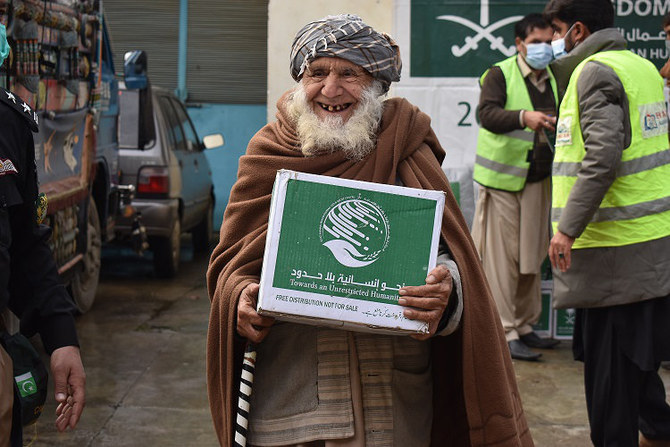
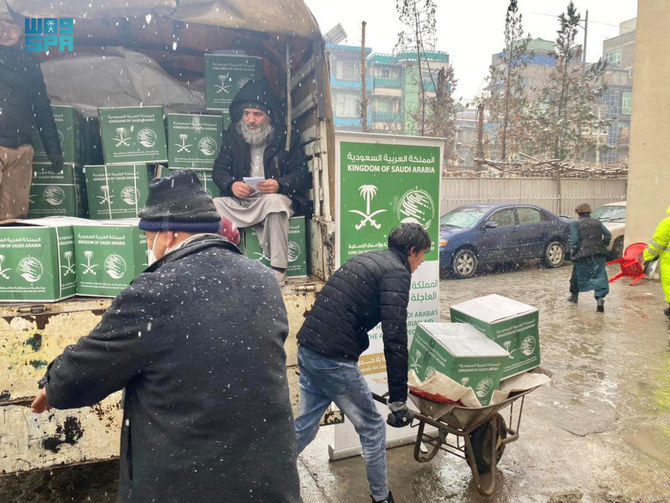
Saudi ODA is provided as financial assistance or in-kind assistance in the form of goods or services to a recipient’s organization or country. It can include food aid, vehicles, logistic support, medical supplies, medicines and equipment. The assistance is delivered through the Saudi Fund for Development, KSRelief and other donor entities registered under a unified database, the Saudi Aid Platform, established by a royal decree in 2018.
Additionally, Saudi Arabia provides aid bilaterally through governments, national non-governmental organizations, international NGOs, and multilaterally through institutions such as the UN agencies concerned and the Red Cross and Red Crescent organizations.
Through strategic partnerships, Saudi Arabia, a founding member of the UN, has provided financial aid totaling $5.2 billion to different UN agencies, with the World Food Program receiving the most ($1.9 billion), followed by the UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East ($955.5 million).
“Saudi Arabia provides bilateral aid based on a vigorous needs assessment to the countries and institutions eligible to receive such aid. Humanitarian and development projects are carefully identified and risk assessment is done before funding is dispatched,” Hamid told Arab News.
THE LIST
Top 10 ODA recipient countries between 1975-2021:
Yemen
Syria
Palestine
Pakistan
Sudan
Lebanon
Egypt
Morocco
Tunisia
“Funding is also paid in installments linked to clear outcomes. Monitoring and evaluation is carried out during the project implementation period to ensure that aid reaches the beneficiaries and makes the impact intended to achieve.”
Among its many achievements, Saudi Arabia played a prominent role in 2015 in the framing of the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which primarily aims to reduce poverty by at least 50 percent by 2030. From 2016 to October 2021, the Kingdom gave $24.04 billion to low- and middle-income countries to enable them to achieve the UN’s sustainable development goals.
A 2016 report by the UN Development Program noted that assistance provided by Saudi Arabia between 2005-2014 accounted for 1.9 percent of its ODA/GNI, breaking a record for the highest percentage achieved by a single donor.
In November 2020, as the chair of the G20 summit in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia succeeded in mobilizing donors to commit sizable funding to respond internationally to the COVID-19 pandemic. According to Hamid’s report, the Kingdom’s COVID-19 international response amounted to over $825 million managed by KSRelief, including vaccines, medical supplies and medical equipment for 33 countries.
A further $10 million in financial support to the World Health Organization’s Solidarity Response Fund and about $300 million for vaccine research were provided by the Kingdom.
Overall, records show that Saudi Arabia, which has derived policy from Islamic teachings since its foundation, has contributed significantly to the well-being of over 150 countries for more than 46 years (1975-2021) through aid totaling $65.7 billion.
INNUMBERS
IN-COUNTRY ASSISTANCE TO “VISITORS”
Exemption from immigration fees $6.68 billion
Education support $4.96 billion
Free healthcare $4.37 billion
“The Kingdom is not a new donor. It has been providing significant humanitarian and development assistance to many countries around the world,” Hamid said, putting Saudi Arabia’s outsized contribution as an aid donor in perspective.
“However, in recent years, aid provided by Saudi Arabia has been systematically documented and registered in international aid platforms. Also, there is significant increase in aid provided by the Kingdom to combat the pandemic and for emergencies to countries such as Yemen, Somalia, Syria and Palestine. These are the factors that have contributed to the rise of Saudi Arabia’s global humanitarian ranking.”
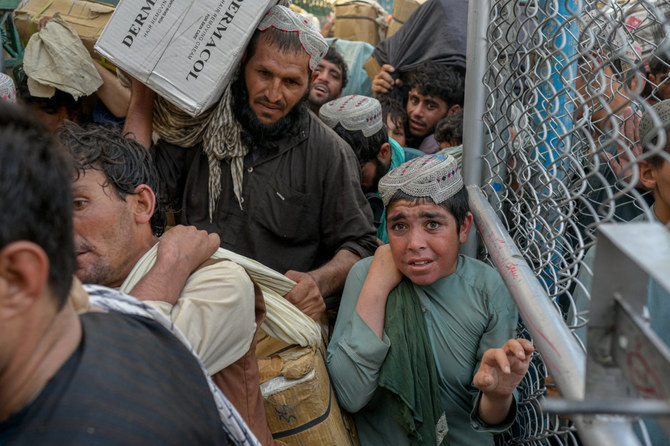
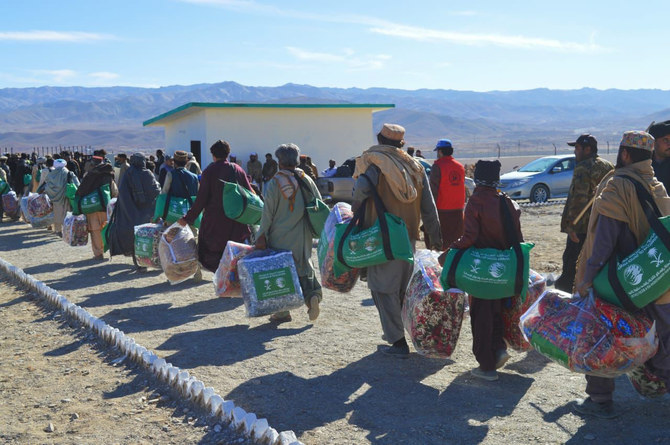
Last but not least, as the paper notes, Saudi Arabia is home to the sixth-largest population of refugees worldwide. The 1.07 million refugees hosted by the Kingdom in recent years are equivalent to 5.5 percent of its population.
Unlike other countries that keep refugees in special camps, Saudi Arabia regards them as visitors, grants them an exemption from immigration fees, provides free healthcare and education for their children and gives them permission to work.
Such assistance and support, contributing to the financial stability of the visitors, amounted to $16.01 billion from 2011 to 2020.