DUBAI: As representatives of governments and other attendees prepare to gather in Glasgow from Oct. 31 for the 26th UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP26), observers are hopeful that the summit can effect meaningful change.
The conference — under the theme “Uniting the World to Tackle Climate Change” — will include contributions from more than 30,000 delegates from around the globe, including the Arab region.
Along with other GCC countries, Saudi Arabia is accelerating action toward the goals of the Paris Agreement and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
It has unveiled a National Renewable Energy Program — through which it aspires to meet 50 percent of its domestic energy needs from renewable sources by 2030 — and launched the Saudi Green Initiative, a project to plant 10 billion trees in the country to mitigate its CO2 emissions.

Renewables have become the world’s main and cheapest source of power generation. (AFP)
The Kingdom has also pioneered “circular carbon economy,” an integrated strategy for tackling emissions while enabling economic growth that was endorsed by G20 leaders at the summit, under Saudi presidency, last year.
The recent announcement of the Sakaka solar project was another sign of the Kingdom’s ambitions in renewable energy sources. Saudi Arabia is also leading the way in the use of hydrogen, which some energy visionaries see as the fuel of the future. Saudi Aramco shipped the first ever consignment of the fuel last summer.
For its part, the UAE now has more than 2.4 GW of installed renewable energy capacity, as it plans to diversify its energy mix and increase its share of renewables to 44 percent by the middle of the century as part of its National Energy Strategy Plan 2050.
“We all have an important role to play in addressing this global issue, as it affects not only the environment, ecology and biodiversity of our planet but also the natural resources available for future generations,” Dr. Nawal Al-Hosany, permanent representative of the UAE to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), told Arab News.
“Arab countries constitute an integral part of this collective action to further the achievement of COP26 goals of securing global net-zero by mid-century, keeping temperature goals within reach, protecting communities and natural habitats, mobilizing finance, and working together to rise to the challenge and deliver,” Al-Hosany added.
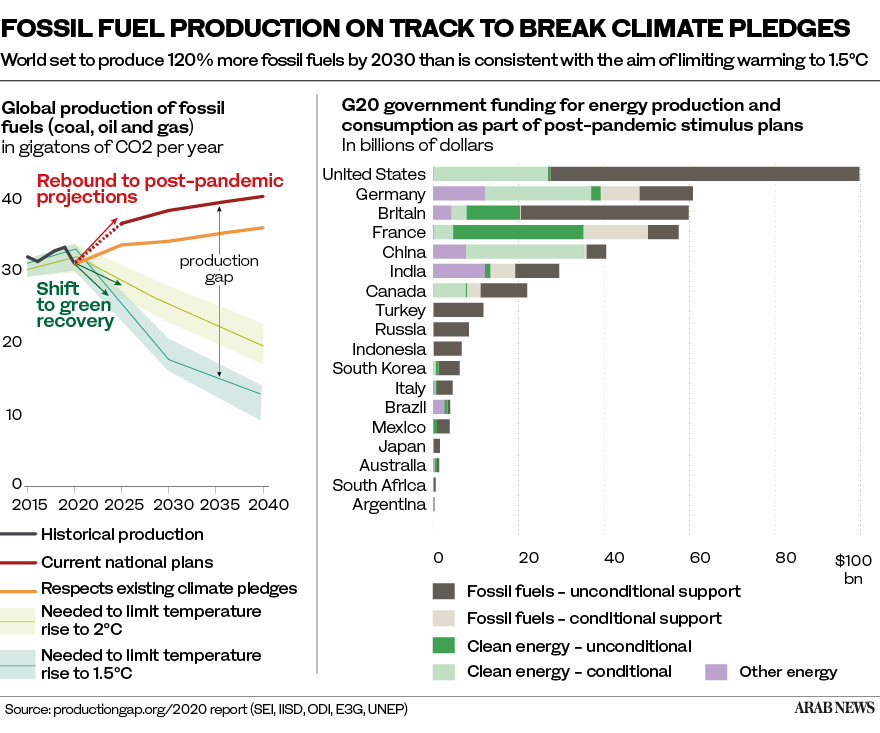
While significant progress has already been made, the UN says nations must do far more if the world is to meet the Paris Agreement target of limiting the rise in global temperatures to 2C — and ideally 1.5C — by the end of the century.
“We hope to see world leaders capitalize on momentum around the Green Recovery to take real and meaningful action on climate change,” Mohamed Jameel Al-Ramahi, CEO of Masdar, a renewable energy company based in Abu Dhabi, told Arab News. “The Arab world faces particularly acute challenges from climate change. Scientists warn that, without immediate climate action, we could witness regular life-threatening heat waves across the region.”

Establishing the policy, regulatory, technical and economic frameworks to enable states to scale up renewables will be indispensable to the world’s collective success. (AFP)
Yet climate change does not always get the attention it deserves in the Middle East, he noted. To address this, he believes the region’s young people — the Arab world’s largest and most important demographic — will have a vital role to play in spreading the message and taking action.
For Daniel Gribbin, corporate sustainability lead at WSP Middle East, recent activity against big oil players by investors and non-governmental organizations will likely have caught the attention of Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) policymakers, as the global impetus towards integrating environmental, social and governance measures and transitioning to low-carbon economies gathers pace.
“We can expect to see these trends highlighted at future COP summits, as world leaders place a higher degree of focus on governments, companies and organizations that are not doing enough to drive adequate climate action,” Gribbin told Arab News.
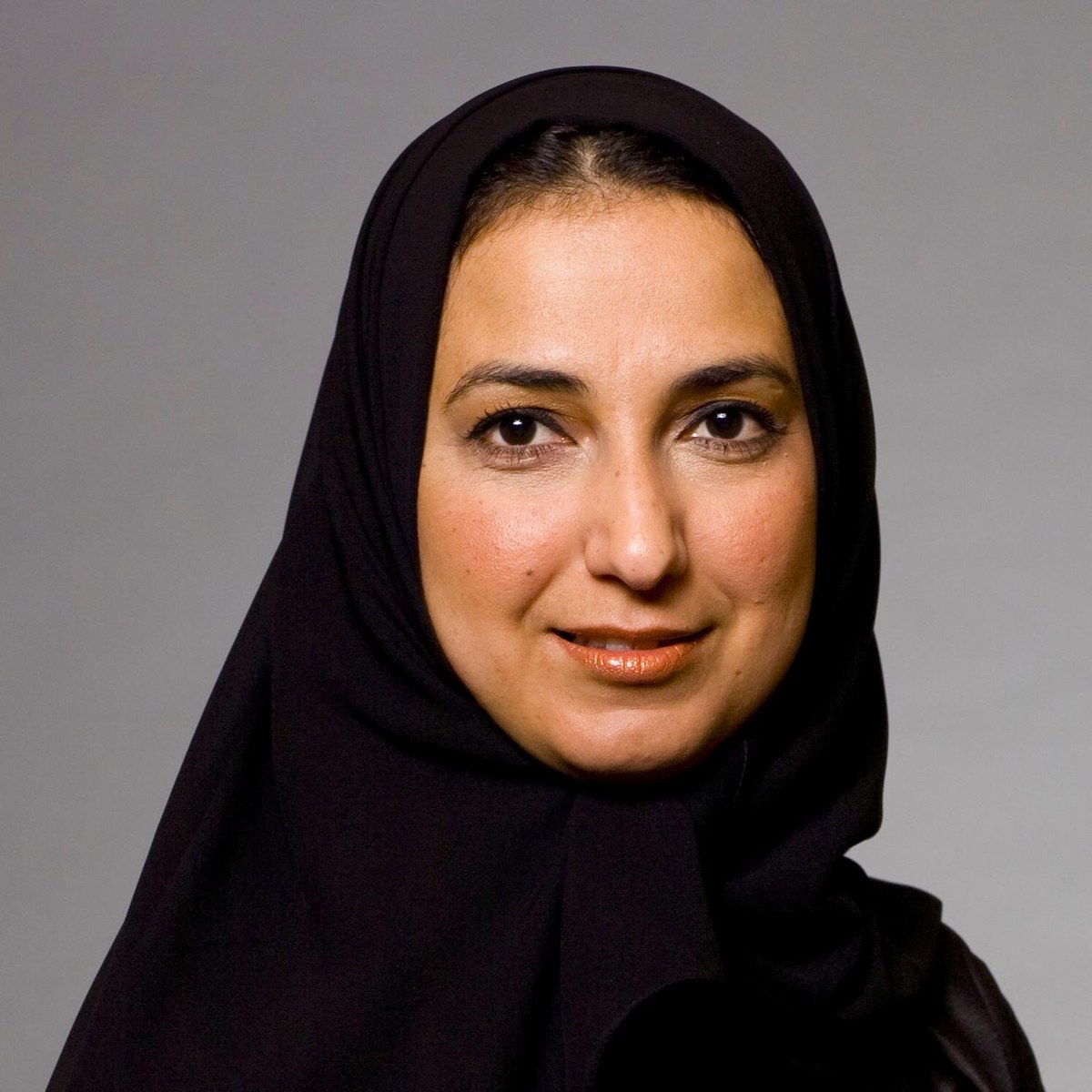

Dr. Nawal Al-Hosany, permanent representative of the UAE to the International Renewable Energy Agency. (Supplied)
“Future COP summits will also place increased pressure on governments, companies and organizations whose strategies, levels of disclosure and transparency are currently lacking in regard to climate-related risks, opportunities and targets.”
This focus on big oil, and how the Middle East is facilitating the transition to low-carbon economies, is firmly on the agenda, particularly with the UAE launching a bid to bring COP28 to Abu Dhabi in 2023.
“There is an expectation that Middle Eastern nations will need to become more transparent about how they manage accelerated climate action in line with their ambitions to transition beyond economic models traditionally reliant on fossil fuels,” Gribbin added.
The Middle East, perhaps more than most, is feeling the effects of climate change, with record temperatures, declining biodiversity, and stress on water resources.
“Specific ecosystems in this region are already very vulnerable, like the hyper-saline Arabian Gulf,” Tatiana Antonelli Abella, founder of the UAE-based green social enterprise Goumbook, told Arab News.
Abella urges collective action to reduce carbon footprints, to work towards an energy transition driven by renewables, and to tackle social and economic disruptions in the region — worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic — through inclusive economic-recovery plans.
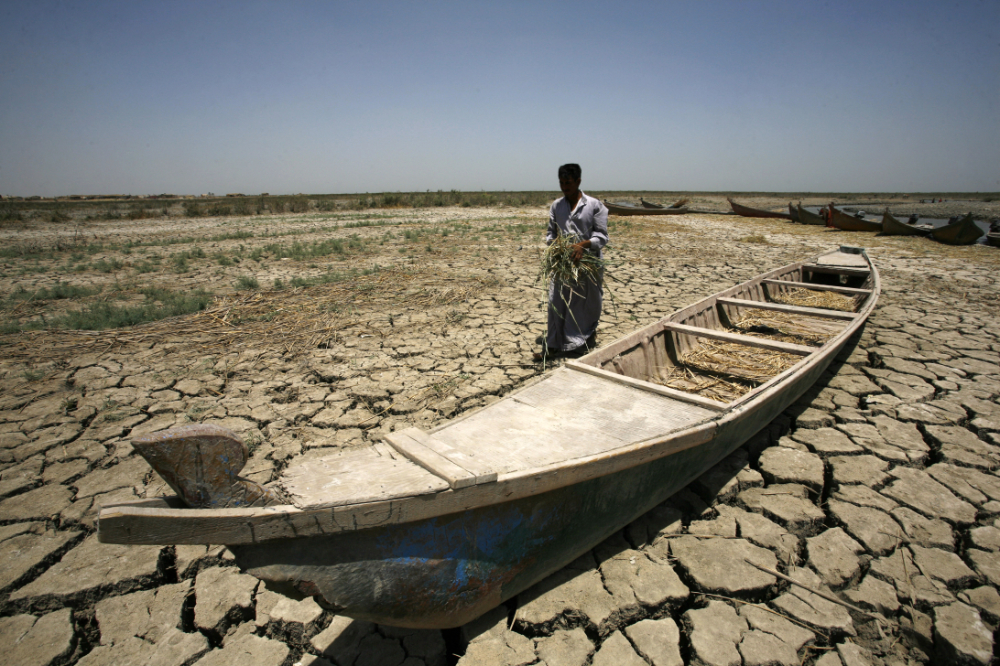

Climate change does not always get the attention it deserves in the Middle East. (AFP)
“We need to cut down on plastic pollution, preserve ecosystems, especially blue carbon, and foster circularity and sustainable economic-growth models,” she said. “Regional collaboration is also needed to address cross-border impacts.”
Climate change is already having a devastating impact on ecosystems, economies and communities around the world due to rising temperatures, desertification, droughts and flooding. To halt this trend, COP26 is urging all countries to set ambitious 2030 targets that align with reaching net-zero carbon emissions by the middle of the century.
“Many of these challenges can be opportunities to make this decade one of energy transformation and sustainable policies that will further increase investment and advance innovation in renewables to help mitigate climate change,” Al-Hosany told Arab News.
“Not only will this help sustainable socioeconomic development in this region, which has great potential for diversifying its energy mix, but it can also help tap into the 42 million renewable-energy jobs that will be available by 2050 per IRENA’s Renewable Energy and Jobs Report.
“If collective action to mitigate climate change is attained, then and only then will these challenges become part of the past.”
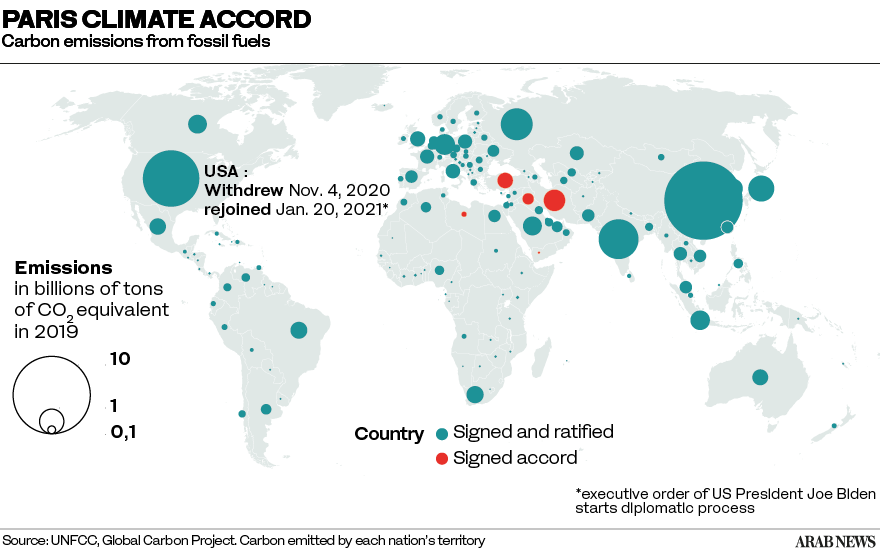
There has been noteworthy progress already. Today, more than 170 countries have renewables targets, which many have included in their Nationally Determined Contributions — non-binding national plans highlighting climate actions set under the Paris Agreement.
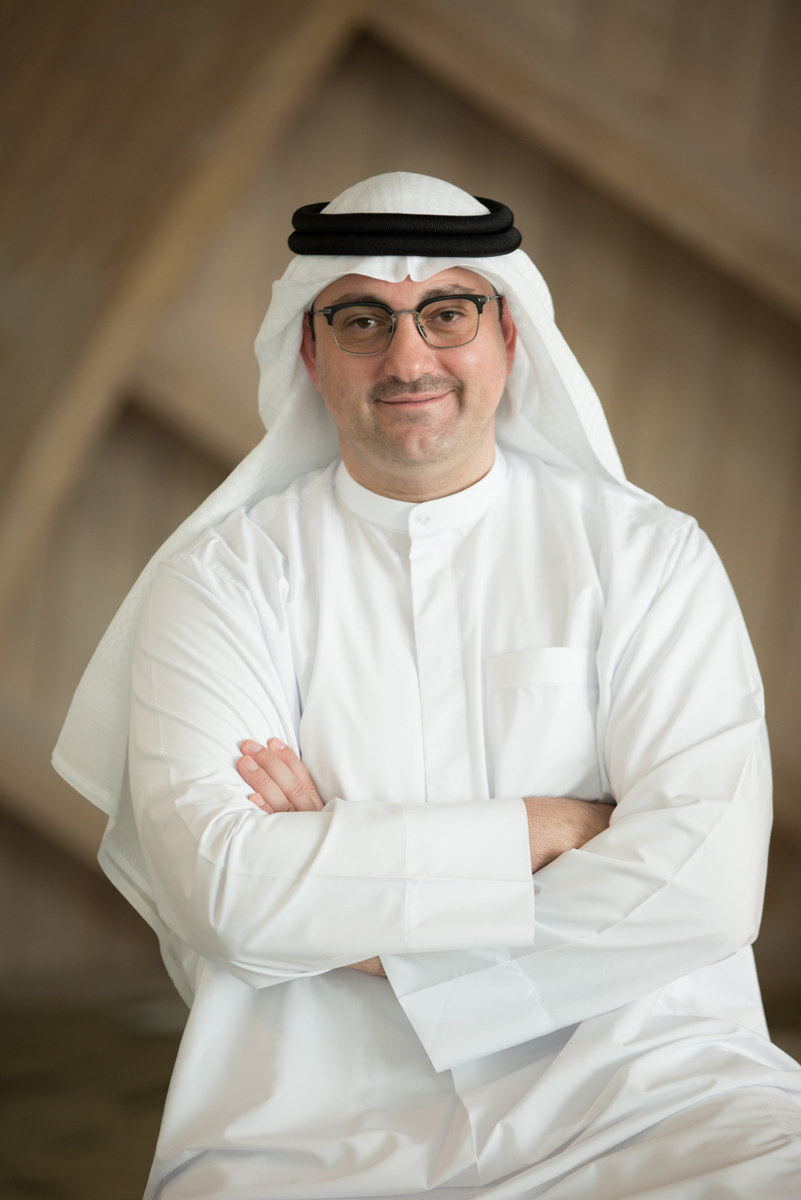

Mohamed Jameel Al-Ramahi, CEO of Masdar, a renewable energy company based in Abu Dhabi. (Supplied)
Additionally, major economies accounting for 70 percent of global CO2 emissions now have targets for carbon neutrality by 2050, and markets are now pricing in energy transitions. More than 80 percent of all new power added in 2020 was renewable — a 50-percent increase on the previous year.
For Francesco La Camera, IRENA’s director-general, these are all positive signs. But the urgency required cannot be overstated. “2030 is really the crucial time by which we need to align our energy system with near-term development goals and longer-term climate goals,” he told Arab News.
“We need a fundamental transformation of our energy system, and we need it in every country, and fast.”
In La Camera’s view, expectations are high for all countries, including those in the Arab region. He stressed that this is a crucial COP meeting that must move the world from dialogue to action.
“Many countries in this region have already shown how serious they are about the renewable energy transition,” he said.
“The announcement of a $4 billion green hydrogen project in Egypt, the ambitious plan to build the world’s largest green hydrogen plant in Saudi Arabia, and the inauguration of the region’s first industrial-scale green hydrogen facility in the UAE all point to a forward-looking region that is increasingly embracing the energy transition. But there is much work to be done.”

To address climate change, Mohamed Jameel Al-Ramahi believes the region’s young people will have a vital role to play in spreading the message and taking action. (AFP)
Renewables have become the world’s main and cheapest source of power generation, he said. “This is a fact, and it will drive the uptake of renewables significantly. Our latest data suggests most new renewables outcompete existing coal on costs — this is game changing, and it can be used to ramp up ambition.
“Now is the time to translate ambition into action through some of the steps that the IRENA has outlined in its World Energy Transitions Outlook road map to a 1.5-degree future.”
Establishing the policy, regulatory, technical and economic frameworks to enable states to scale up renewables will be indispensable to the world’s collective success.
“The real challenge today is not about technology, costs or investment flows. The main thing that holds us back from moving faster is vested interests and political will,” La Camera said. “Policy and investment decision-making must reflect the urgency of the task at hand.”
Twitter: @CalineMalek















