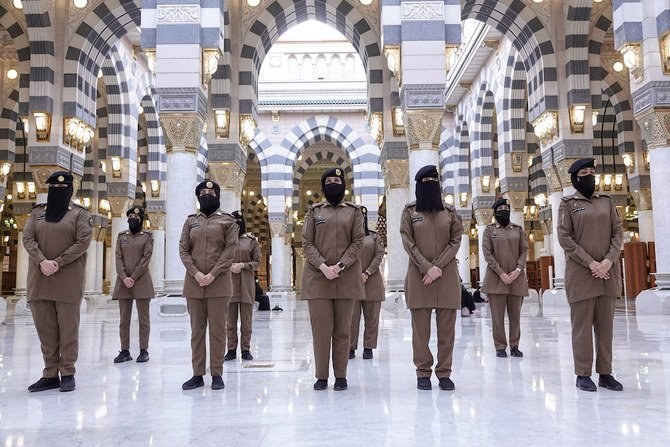
MADINAH: Few media images have captured the impressive strides Saudi Arabia has made toward the empowerment of women and gender equality since 2016 like the recent photos of a smartly uniformed female security officer guiding Umrah pilgrims in Makkah during Ramadan.
Dozens of female officers are currently deployed both in Makkah and Madinah, where they are providing security and managing worshippers at the Grand Mosque and the Prophet’s Mosque. The fact that their daily work is now considered a matter of course is a signal achievement of the Kingdom’s five-year-old Vision 2030.
The 113-strong all-female batch of military-trained officers stationed at the Prophet’s Mosque was created six months ago. It is part of the homeland security branch of Saudi Arabia’s Special Security Forces. The officers work round the clock in four teams of nearly 18 members each. Their job, according to a statement by Major-General Abdul Rahman Al-Mashhan, director of the Madinah Police, is to watch over and assist pilgrims performing Umrah.
Dressed in mocha-colored uniforms, black berets and with their faces partially veiled, the young officers oversee a section of the mosque to guide and assist female worshippers and enforce the government’s COVID-19 protocols.
They exude the confidence that comes from succeeding in a demanding career that was closed to them until recently. As part of their professional training, they learned self-defense, first aid and how to use firearms. They also had to enroll for courses in Arabic and English (to improve their communication skills), computer education and fitness.
Hanan Al-Rashidi, 27, who has been a soldier for all of eight months, said she accepted the job because it is a form of humanitarian service. “I am full of joy. It is an honor to work at the Prophet’s Mosque and serve the guests of Allah,” she told Arab News.
Al-Rashidi expresses pride in flying the flag for Saudi Vision 2030 and regards the current era as one of female empowerment.
”I am grateful to be working in this position. Our leadership has given us so many opportunities. From driving to working in any field, women are equal to men. There is no difference,” she said.
Reem Al-Mahjoob, 27, who has been performing security duties in Madinah for the past six months, echoed Al-Rashidi’s sentiments. She pointed out that Vision 2030 has empowered Saudi women to take up jobs in such diverse fields as the military, aviation and government.
”This is the era of women,” Al-Mahjoob told Arab News. “Women are now able to join the military among many other sectors they have always wanted to enter.”
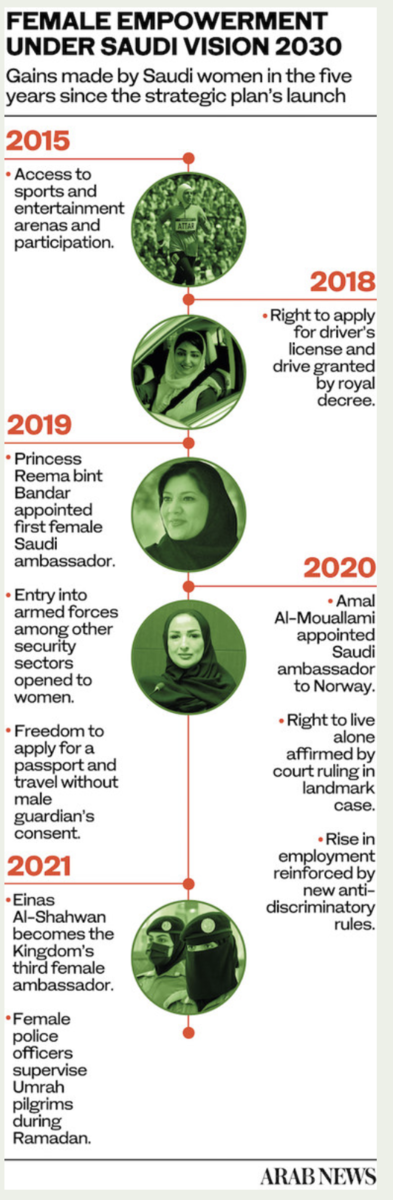
From a historical perspective, the deployment of female officers in the two holy cities is one of the many remarkable changes that Saudi Arabia has witnessed since Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman launched the Vision 2030 plan in April 2016.
Empowerment of women — including their economic inclusion and workforce participation — is one of the key objectives of the Vision 2030 programs.
As part of the strategy, Saudi Arabia has not only introduced legal reforms but also funded projects and initiatives in a number of sectors — including tourism, investment and culture — that have created opportunities for women.
Along with these initiatives, government sectors have committed to guaranteeing and protecting women’s rights in the workplace. The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development has worked to reduce gender-based discrimination and find ways to create safe work environments that foster growth and innovation.
Women have also played their part in creating legislation and opening businesses and have taken a leading role in private-sector investment. Saudi Arabia now has its first female professional racing driver, female ambassadors, female judges, and award-winning female filmmakers.
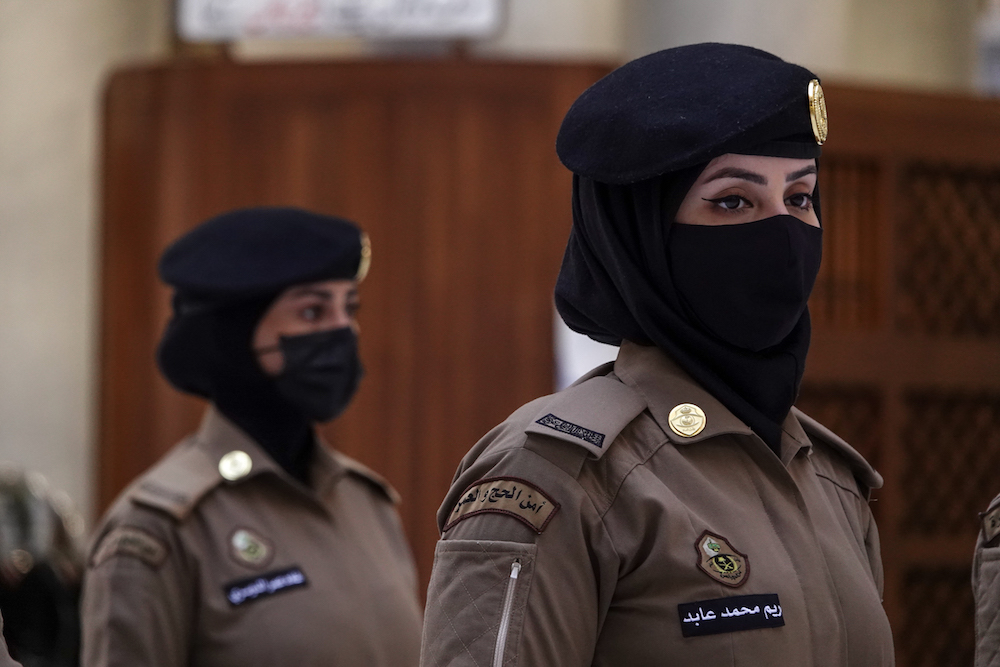

The 113-strong all-female batch of military-trained officers stationed at the Prophet’s Mosque was created six months ago. (AN Photo/Huda Bashatah)
The pace of progress towards gender equality in the defense sector has been particularly impressive. Saudi Arabia decided three years ago to allow women to join the military.
In 2020, the first military wing for women in Saudi Arabia’s armed forces was launched. In February this year, the Ministry of Defense announced that men and women in the Kingdom could apply for positions in the military through a unified admission portal.
Among the positions now open to women are lance corporal, corporal, sergeant and staff sergeant, with a long line of prospective employers, including the Royal Saudi Land Forces, Royal Saudi Air Force, Royal Saudi Naval Forces, Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces, Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force and Armed Forces Medical Services.
Female police officers joined the ranks of Makkah’s security force for the first time during last summer’s Hajj season, amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
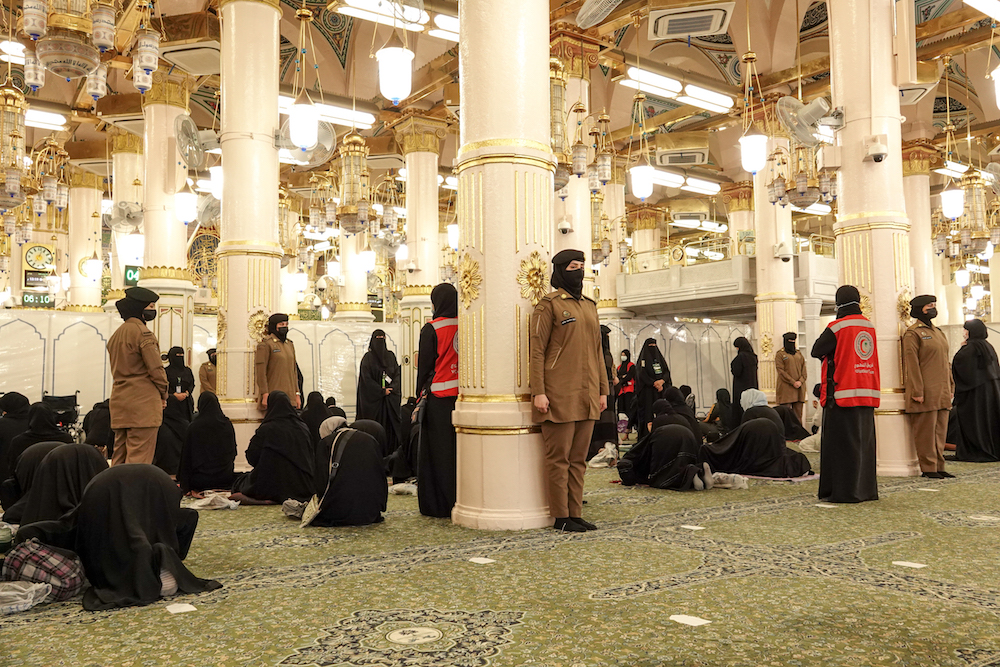

The freshly minted officers in Madinah look out for hawkers and beggars while making sure that measures to curb the spread of COVID-19 are respected by visitors. (AN Photo/Huda Bashatah)
Like them, the all-female contingent stationed at the Prophet’s Mosque in Madinah proves that anything Saudi men can do, Saudi women can do too, and that no matter how masculine a job may seem to traditionalists, it can always benefit from a woman’s touch.
The freshly minted officers in Madinah look out for hawkers and beggars while making sure that measures to curb the spread of COVID-19 are respected by visitors. Al-Hanouf Al-Gomzi, 29, who comes from a family with a defense background, said she finds her posting in the holy city hugely rewarding.
“The feeling is completely indescribable,” she told Arab News. “I’m at the Prophet’s Mosque watching over the visitors. I’m very proud of myself and my colleagues.”
As a case in point, she cited a situation that required her to be quick on her feet. “A 50-year-old woman fainted here at the mosque. I called the ambulance team right away and the woman was very well taken care of,” she recalled.
To be able to work in the military is a source of immense pride for Al-Gomzi. “I was able to join my brothers in this field. I wanted to join this sector more than any other,” she told Arab News.
Speaking about Saudi Arabia today, she said: “We now find women working in many fields. They are almost equal to men.”
-----------------
Twitter: @DeemaAlkhudair














