LONDON: Iran dialed up tensions in the Gulf this week when its troops stormed a South Korean-flagged tanker as it transited through the strategic Strait of Hormuz — a choke point through which a fifth of world oil output passes. The incident is only the latest in a long line of Iranian acts of “state piracy” in the flashpoint region.
The MT Hankuk Chemi was en route from Saudi Arabia’s Jubail to the UAE’s Fujairah on Monday when members of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) navy boarded the vessel and brought it to the port of Bandar Abbas in southern Iran, placing its multinational crew of 20 under arrest.
Iranian authorities alleged the tanker, carrying 7,200 tons of ethanol, was seized for infringing maritime environmental laws — claims the vessel’s owner denies.
Observers suspect the ship was in fact taken hostage as part of an ongoing row with Seoul over $7 billion in revenue from oil sales that remain frozen in South Korean banks under US sanctions imposed against Iran by the Trump administration.
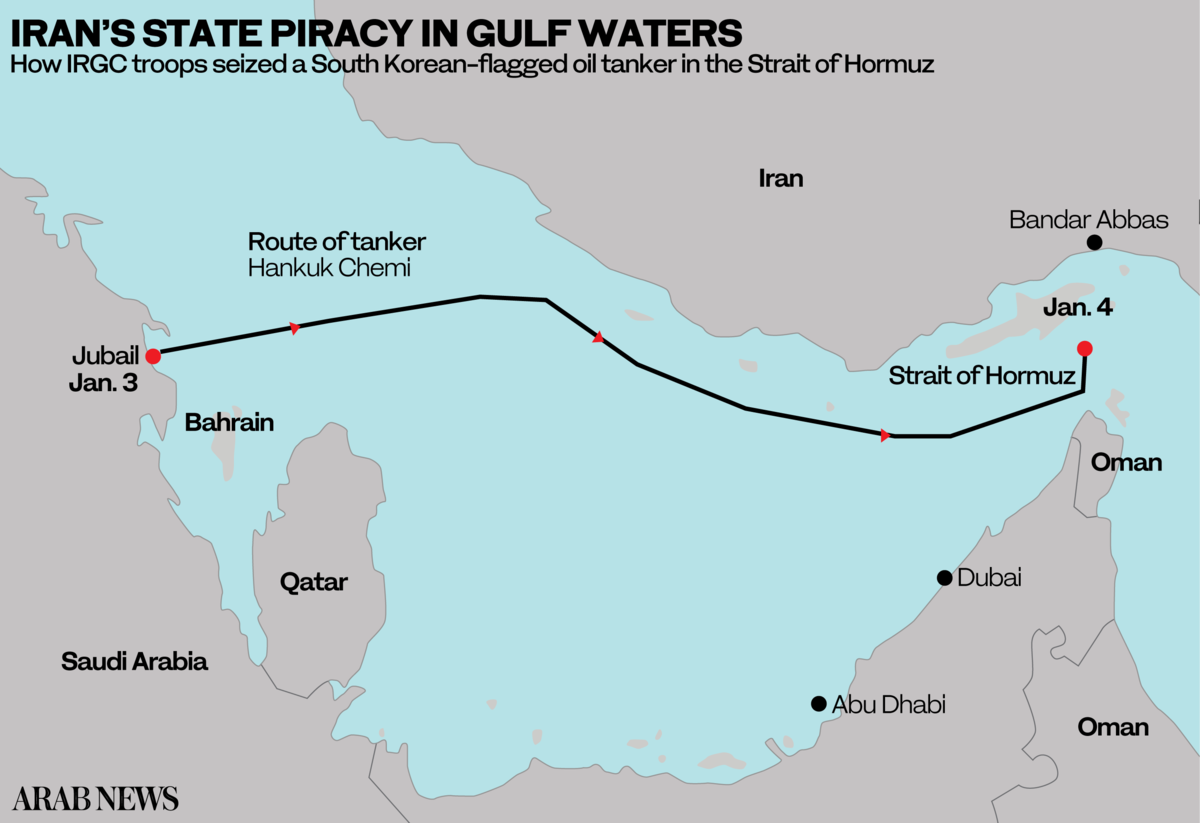
Although the MT Hankuk Chemi is the first major vessel to be seized by Iran in more than a year, incidents of this kind have become all too common in the Strait of Hormuz and nearby shipping lanes. Several vessels have been boarded or mysteriously attacked since President Donald Trump ramped up his “maximum pressure” campaign, with Iran named as the likely culprit.
The IRGC navy has long used its fleet of speedboats to harass commercial shipping and military vessels in the region, seizing at least six ships in 2019 over alleged fuel smuggling. Iran has also repeatedly threatened to blockade the strait if it is attacked.
Several incidents pre-date the current tensions. In January 2016, the IRGC seized two US Navy riverine command boats after they entered Iranian territorial waters near Iran’s Farsi Island. After a flurry of phone calls between then-US secretary of state John Kerry and Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif, the sailors were released unharmed 15 hours later.
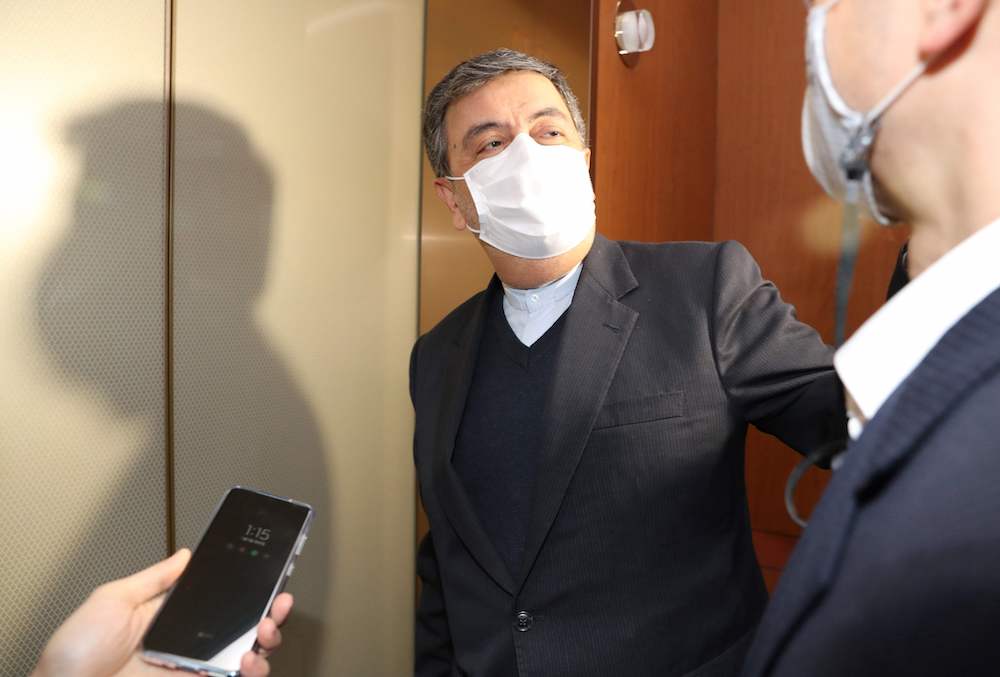

Iran's ambassador to South Korea Saeed Badamchi Shabestari arrives at the Foreign Ministry in Seoul on January 5, 2021, after he was summoned over a South Korean oil tanker being seized by Iran. (AFP/YONHAP)
In March 2007, the IRGC detained 15 British navy personnel from HMS Cornwall as they were searching a merchant vessel off the Iran-Iraq coast. They were released 13 days later. A similar incident occurred in 2004 when six Royal Marines and two Royal Navy sailors were captured by the IRGC in the Shatt al-Arab waterway. They were released three days later.
The Iran-backed Houthi militia in Yemen has also launched repeated attacks on ports and ships in recent years, routinely planting marine mines in the southern Red Sea and in the Bab Al-Mandab Strait in the path of commercial shipping.
The militia has repeatedly rebuffed UN pleas to allow an inspection team to enter the FSO Safer, a 45-year-old oil tanker abandoned off the port of Hodeidah with 1.1 million barrels of crude on board, to conduct urgent repairs. In an extraordinary session, the UN expressed fears on July 15, 2020, of "catastrophe" if the vessel ruptured into the Red Sea.
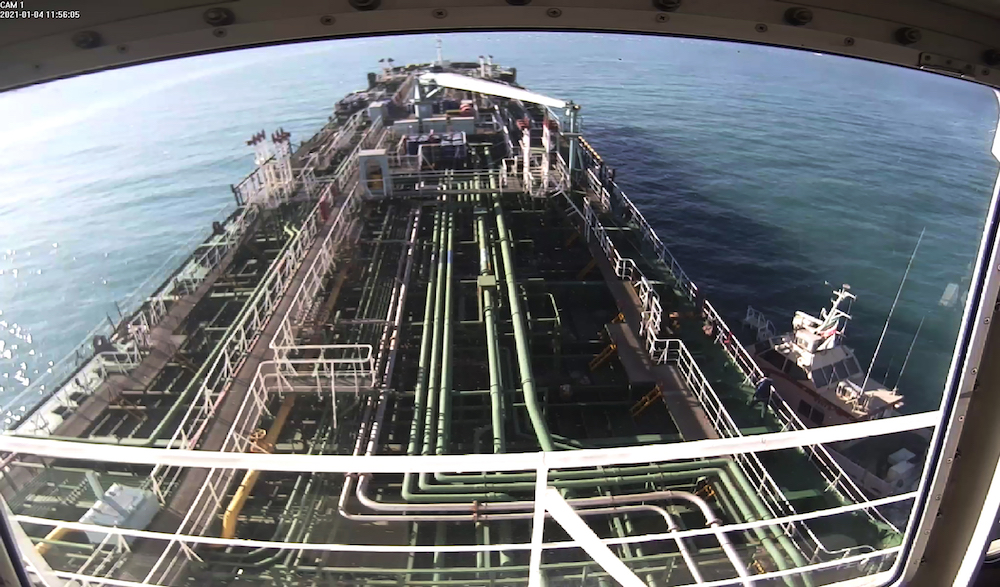

This CCTV image provided by South Korea's Taikun Shipping Co. shows the moment a South Korean tanker was captured by an Armed Iranian Revolutionary Guard speedboat, right, on the waters of the Persian Gulf and the Strait of Hormuz Monday, Jan. 4, 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
In May 2019, Washington deployed the USS Abraham Lincoln carrier strike group and four B-52 bombers to the Middle East, citing unspecified Iranian threats. A matter of days later, on May 12, four commercial ships, including two Saudi Aramco oil tankers, were damaged near the port of Fujairah in the Gulf of Oman in what the UAE called a “sabotage attack.”
On June 13, the oil tankers Front Altair and Kokuka Courageous were also both rocked by explosions, thought to have been caused by limpet mines or flying objects. Days later, on June 20, Iran shot down an American RQ-4A surveillance drone flying over the Strait of Hormuz, raising tensions further.
At the time, US President Donald Trump said Iranian boats harassing the US navy “will be shot out of the water.”
INNUMBERS
Iranian Piracy
* 20 - Civilian sailors aboard South Korean-flagged Hankuk Chemi.
* $7bn - Amount claimed by Iran to be in a South Korean bank.
The following month, the IRGC held the British-flagged oil tanker Stena Impero for two months for allegedly ramming a fishing boat. The move was widely seen as an act of retaliation after British Royal Marines detained an Iranian tanker, the Grace 1, in the Strait of Gibraltar on suspicion of violating EU sanctions on Syria.
In the wake of the incident, US Central Command established Operation Sentinel, invited nations to coordinate on surveillance and provide escorts to their flagged commercial vessels in the Gulf, the Strait of Hormuz, the Bab el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Oman.
After European powers voiced qualms about the possibility of being dragged into a war with Iran, the US rebranded Operation Sentinel as the “International Maritime Security Construct” in Sept. 2019, headquartered in Bahrain.
The world’s eyes are once again on Iran as it uses the capture of the Hankuk Chemi to win concessions from South Korea. Seoul has confirmed it is in talks with Tehran and Washington to use the frozen Iranian money to purchase coronavirus vaccines for the country.
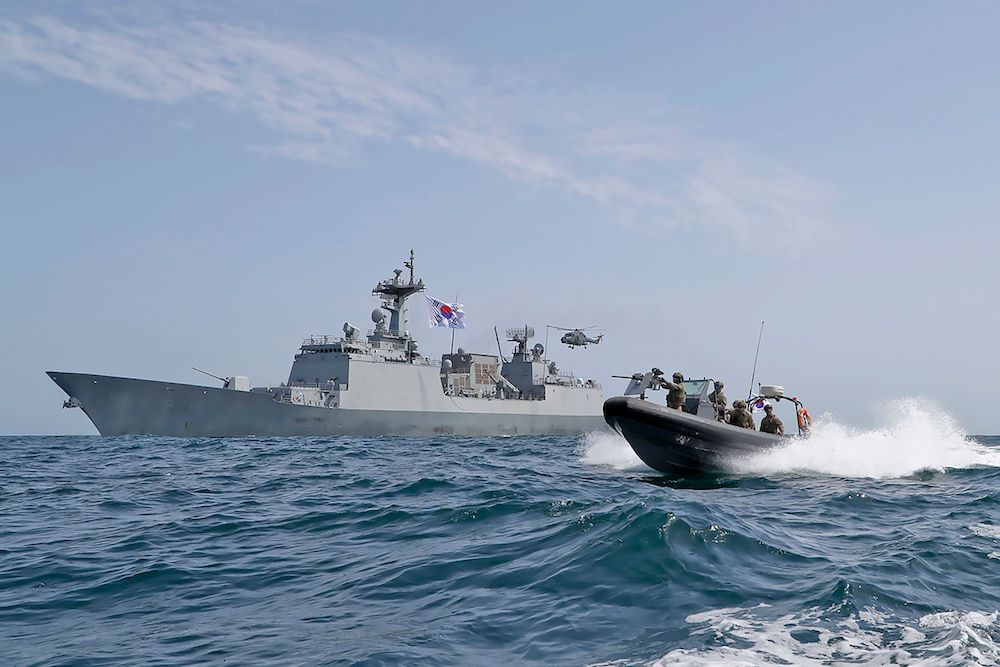

This undated picture taken in an unknown location and released on January 5, 2021 by Yonhap news agency in Seoul shows South Korean Navy's destroyer ROKS Choi Young. South Korea will send a government delegation to Iran "at the earliest possible date" to negotiate the release of a seized oil tanker and its crew, Seoul's foreign ministry said on January 5. (AFP/File Photo)
At the same time, South Korea’s foreign ministry said it is launching legal action to demand the ship’s release. Its defense ministry has also deployed its 300-strong Cheonghae anti-piracy unit to the Strait of Hormuz aboard the destroyer Choi Young to “ensure the safety” of South Korean nationals.
Shin Beom-chul, chief researcher at the Korea Research Institute for Economy and Society, told Arab News that the Iranian move is a desperate bid to get recognition from the incoming Biden administration in the US, which is expected to take a relatively softer stance vis-a-vis Iran.
“Tehran is sending a clear message that it can ratchet up aggression in the region any time, while the issue of frozen money in South Korea is just part of the Trump administration’s financial sanctions,” Shin said.
Iran is reeling from sanctions reintroduced after the Trump administration withdrew from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), better known as the Iran nuclear deal, in May 2018. Iran’s economic woes have been compounded by one of the worst coronavirus outbreaks in the region.
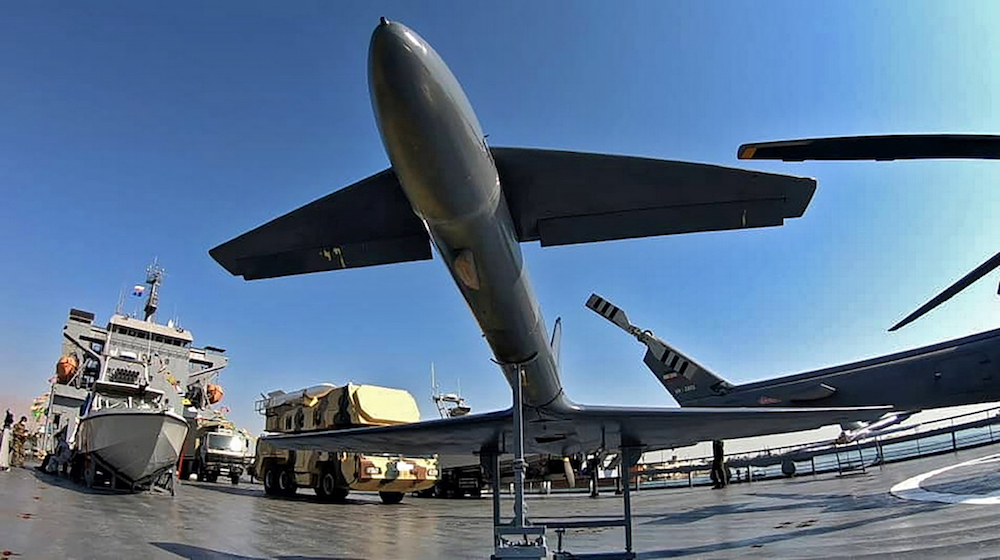

This handout photo provided by Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) official website via SEPAH News on November 19, 2020, shows a military drone parked on a warship named after slain Naval commander Abdollah Roudaki, sailing through the waters in the Gulf during it's inauguration. (AFP/File Photo)
European powers, meanwhile, are scrambling to salvage the JCPOA, just as Iran announced on Monday it has stepped up its uranium enrichment to 20 percent purity — far beyond the limits set by the deal.
Tehran’s successive breaches of the nuclear deal are widely interpreted as a means of pressuring European signatories to provide sanctions relief — a move that Washington has branded “nuclear extortion.”
Also fresh in Tehran’s mind this week is the killing of Qassem Soleimani, the IRGC’s extraterritorial Quds Force commander, who was eliminated with a US drone strike near Baghdad airport one year ago.
Struggling with sanctions and COVID-19, and bruised by strategic setbacks, Iran appeared to rein in its extra-legal naval activities in 2020. But now the IRGC seems to be reasserting itself in the waning days of the Trump administration.
With little sign of de-escalation in the Gulf, the Hankuk Chemi may not be the last commercial ship to be targeted by Iran in 2021.
-------------------
Twitter: @RobertPEdwards










