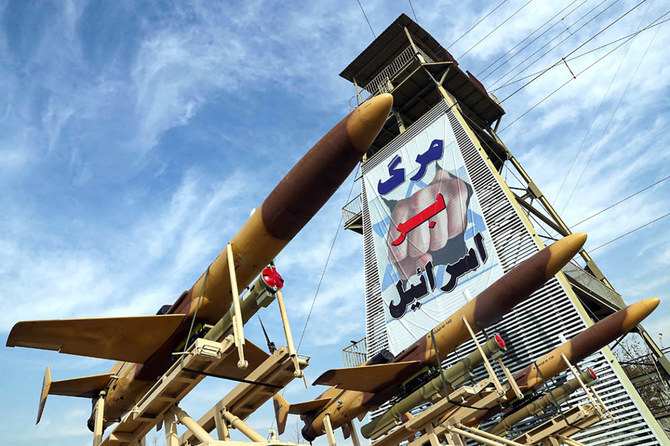
LONDON: In July 2018, a senior Iranian official made an announcement that raised eyebrows around the Middle East.
The Islamic Republic, said Manouchehr Manteqi, head of the Headquarters for Development of Knowledge-Based Aviation and Aeronautics Technology and Industry, was now capable of producing drones self-sufficiently, without reliance on foreign suppliers or outside technical know-how.
International sanctions restricting imports of vital technology had effectively crippled Iran’s ability to develop sophisticated conventional military aircraft.
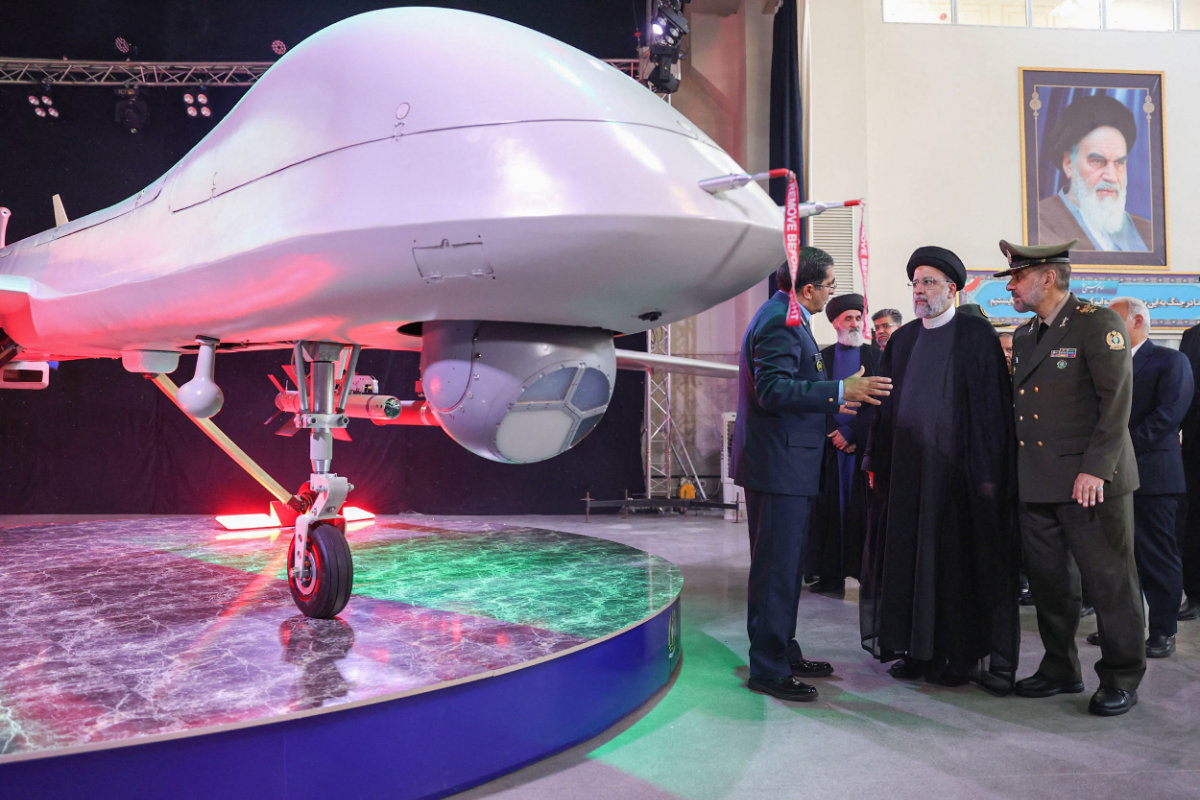

Iran's President Ebrahim Raisi (C) and Defense Minister Mohammad Reza Gharaei Ashtiani (R) attend an unveiling ceremony of the new drone "Mohajer 10" in Tehran on August 22, 2023. (Iranian Presidency photo handout/AFP)
But now, said Manteqi, “designing and building drone parts for special needs (is) done by Iranian knowledge-based companies.”
In developing its own drone technology, Iran had found a way to build up its military capabilities regardless of sanctions.
Iran had already come a long way in the development of unmanned aerial vehicles, having first embarked on the creation of surveillance drones during the Iran-Iraq War.
Speaking in September 2016, Maj. Gen. Mohammed Hossein Bagheri, chief of staff of the Iranian armed forces, credited the tactical demands of the eight-year conflict as having been “pivotal in the production of modern science and technology for future use.”
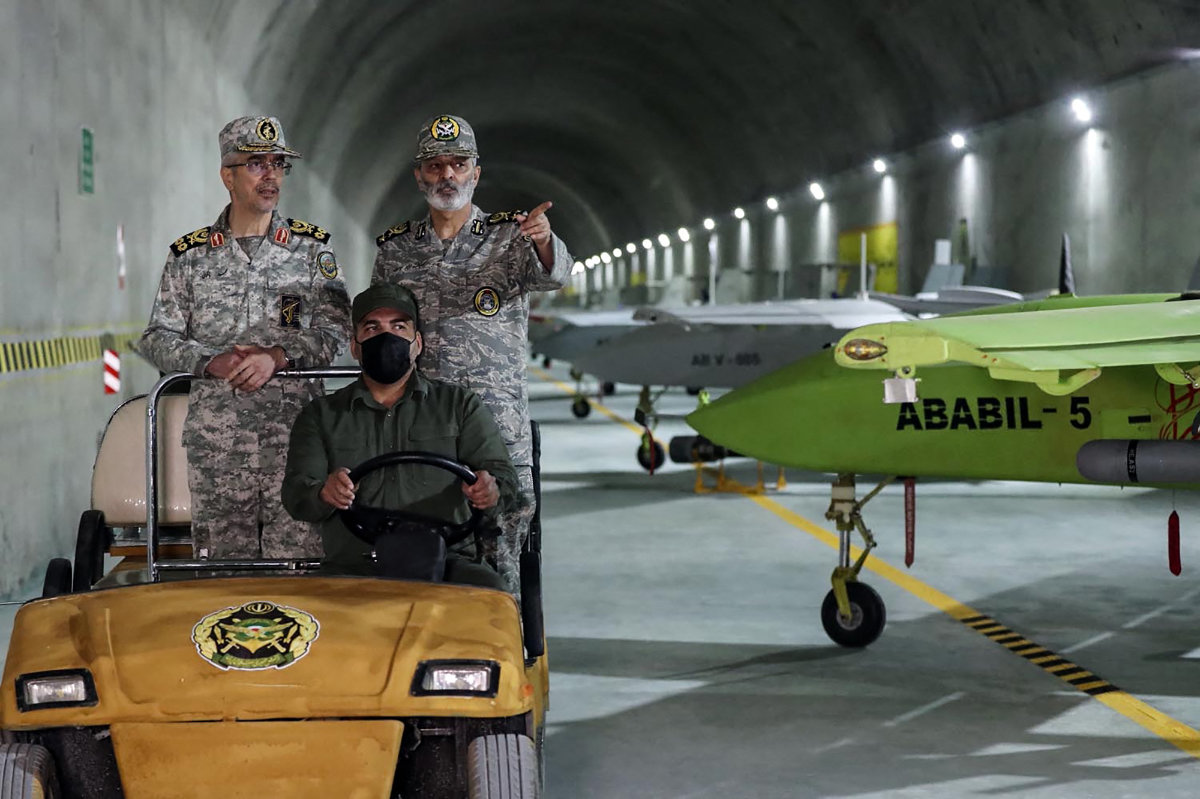

This handout picture provided by the Iranian Army on May 28, 2022, shows Major General Abdolrahim Mousavi (R), Iran commander-in-chief, and Major General Mohammad Bagheri, armed forces chief of staff, visiting an underground drone base in an unknown location in Iran. (Handout via AFP)
This, he said, had led to the development of “Iranian-manufactured long-range drones (that) can target terrorists’ positions from a great distance and with a surface of one meter square.”
Iran’s first UAV was the Ababil, a low-tech surveillance drone built in the 1980s by the Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Co. It first flew in 1985 and was quickly joined by the Mohajer, developed by the Quds Aviation Industry Co.
Although initially both of these drones were fairly primitive, over the years both platforms have been steadily developed and have become far more sophisticated.
According to a report in state newspaper Tehran Times, the current Ababil-5, unveiled on Iran Army Day in April 2022, has a range of about 480 km and can carry up to six smart bombs or missiles.
But the Mohajer 10, launched last year on Aug. 22, appears to be an even more capable, hi-tech UAV, closely resembling America’s MQ-9 Reaper in both looks and capabilities.
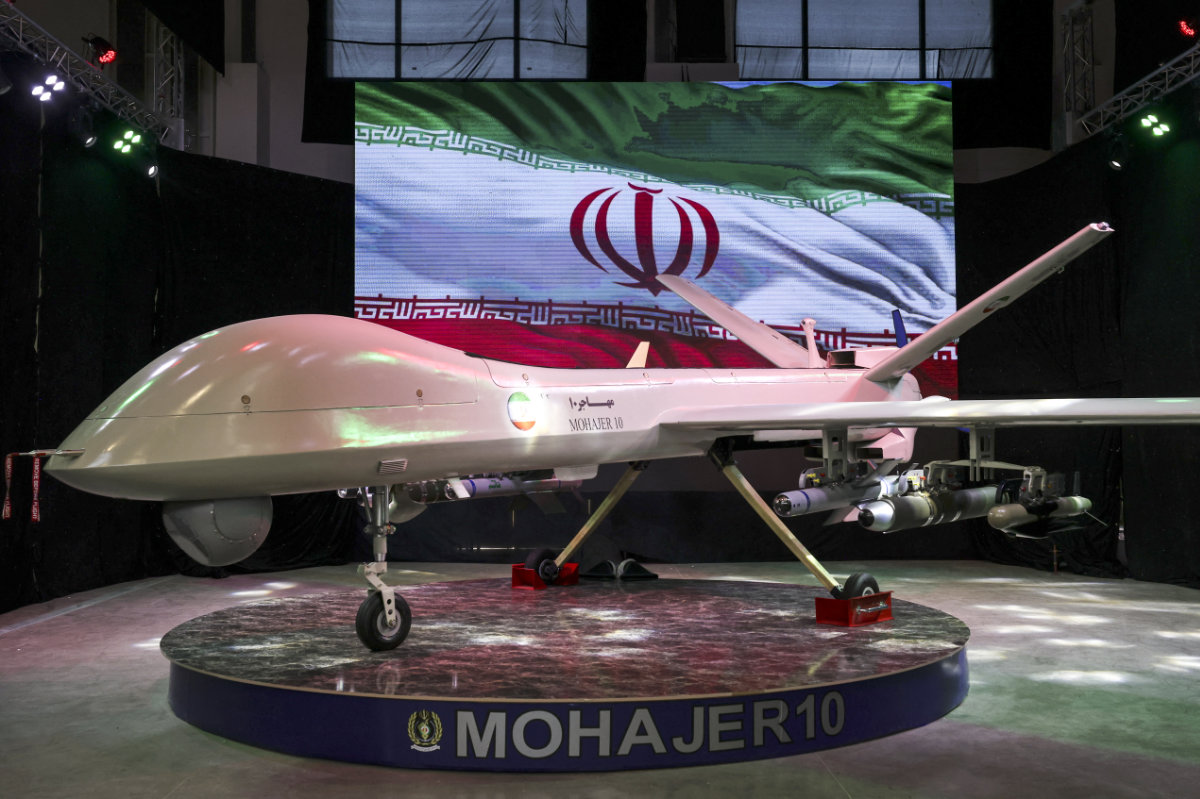

Iranian drone "Mohajer 10" is displayed Iran's defense industry achievements exhibition on August 23, 2023 in Tehran. (AFP)
Armed with several missiles and able to remain aloft for 24 hours at an altitude of up to 7 km, it has a claimed range of 2,000 km. If true, this means it is capable of hitting targets almost anywhere in any country in the Middle East.
This appeared to be confirmed in July 2022, when Javad Karimi Qodousi, a member of the Iranian parliament’s National Security and Foreign Policy Committee, told Iran’s state news agency IRNA that “Iran’s strategy in building drones is to maintain the security of the country's surrounding environment up to a depth of 2,000 kilometers.”
He added: “According to the declared policy of the Leader of the Revolution, any person, group or country who stands up against the Zionist regime, the Islamic Republic will support him with all its might, and the Islamic Republic can provide them with knowledge in the field of drones.”
By 2021, following a rash of attacks in the region, it was clear that Iranian drone technology was in the hands of non-state actors and militias throughout the Middle East.
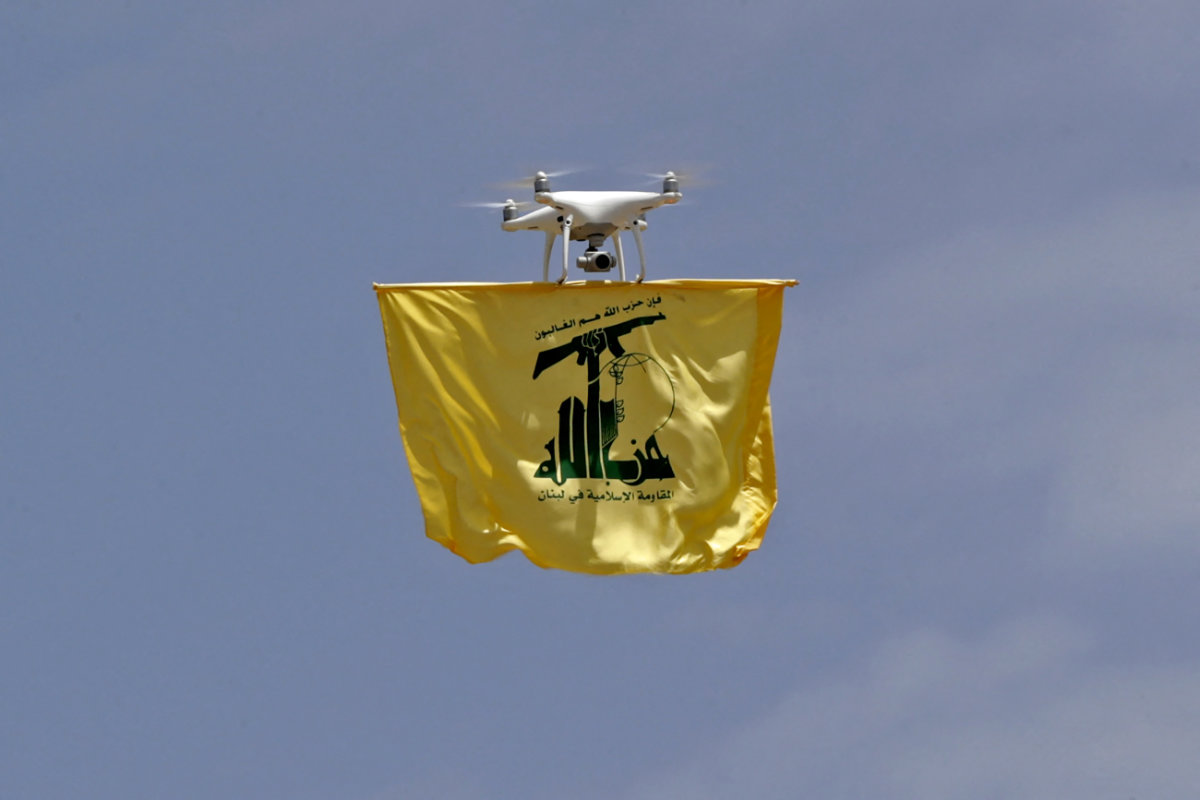

An Iran-made drone carries a flag of Lebanon's Hezbollah movement above Aaramta bordering Israel on May 21, 2023. Hezbollah simulated cross-border raids into Israel in a show of its military might, using live ammunition and an attack drone. (AFP/File)
Speaking during a visit to Iraq in May 2021, Marine Gen. Frank McKenzie, commander of US Central Command, said the Iranian drone program “has innovated with sophisticated, indigenously produced drones, which it supplies to regional allies.”
This “broad diffusion of Iranian drone technologies makes it almost impossible to tell who conducted a lethal drone strike in the region, and thus who should be held responsible and accountable.”
This, he added, “is only going to get more difficult.”
As it has raced to supply proxies and allies throughout the region and the wider world with these weapons, Iran has developed a second, cheaper class of UAV — the so-called “loitering munition,” or suicide drone.
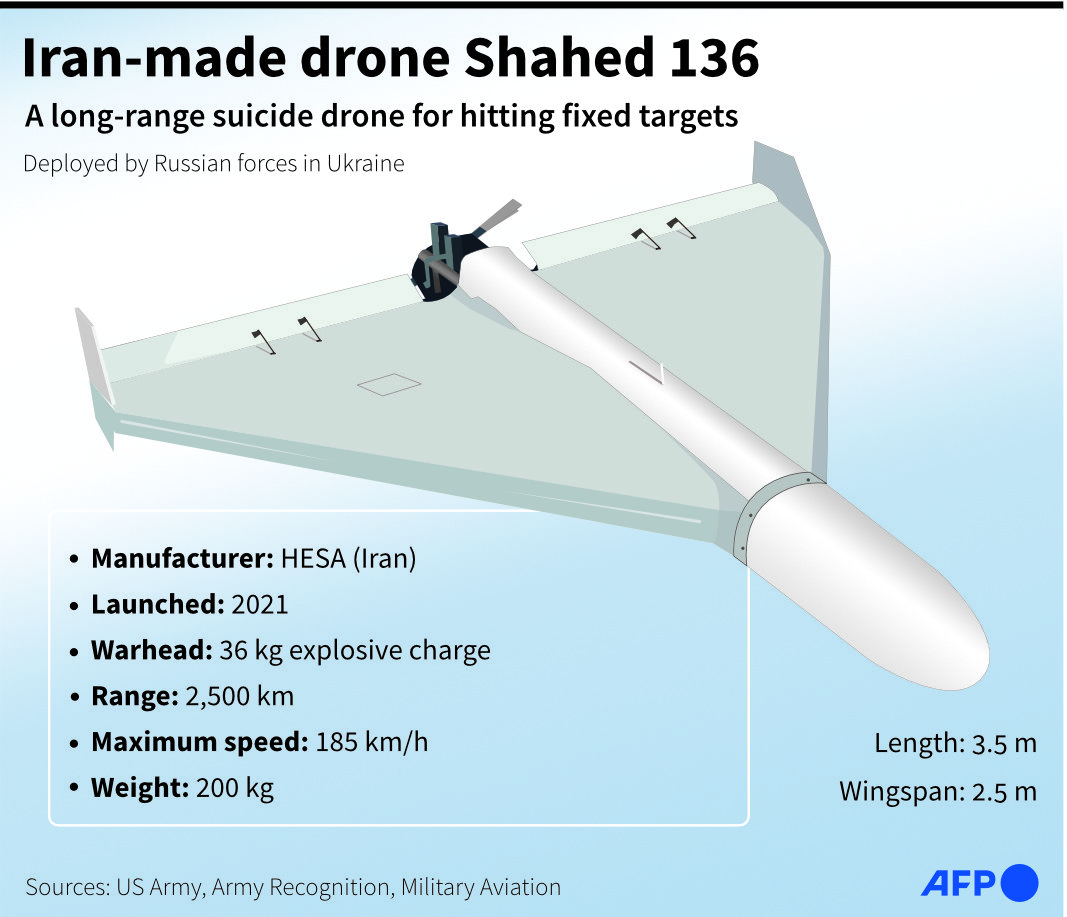
Variations of these weapons, relatively cheap to produce but capable of carrying a significant explosive payload over hundreds of kilometers, have been produced in large numbers by the IRGC-linked Shahed Aviation Industries Research Center.
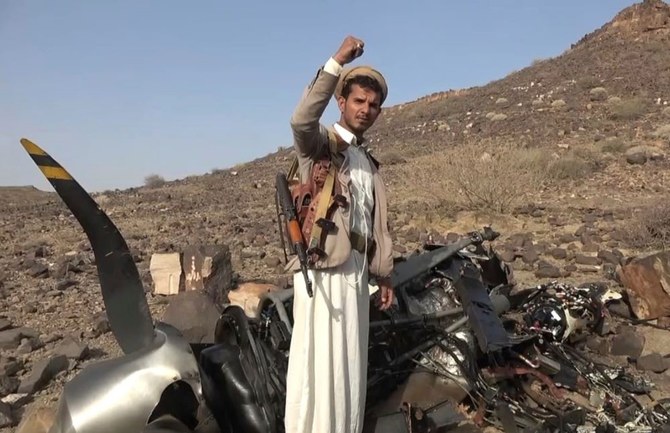
In September 2019, the Houthi rebels in Yemen claimed responsibility for an attack by 25 drones and other missiles on Saudi Aramco oil sites at Abqaiq and Khurais in eastern Saudi Arabia.
Afterward, the Kingdom’s Defense Ministry displayed wreckage that revealed delta-winged Shahed 136 drones were among the weapons that had been fired at the Kingdom.
The Houthis have claimed responsibility for other attacks by Iranian-made drones. In 2020, another Saudi oil facility was hit, at Jazan near the Yemen border; the following year, four drones targeted a civilian airport at Abha in southern Saudi Arabia, setting an aircraft on fire; and in January 2022 drones struck two targets in Abu Dhabi — at the international airport and an oil storage facility, where three workers were killed.
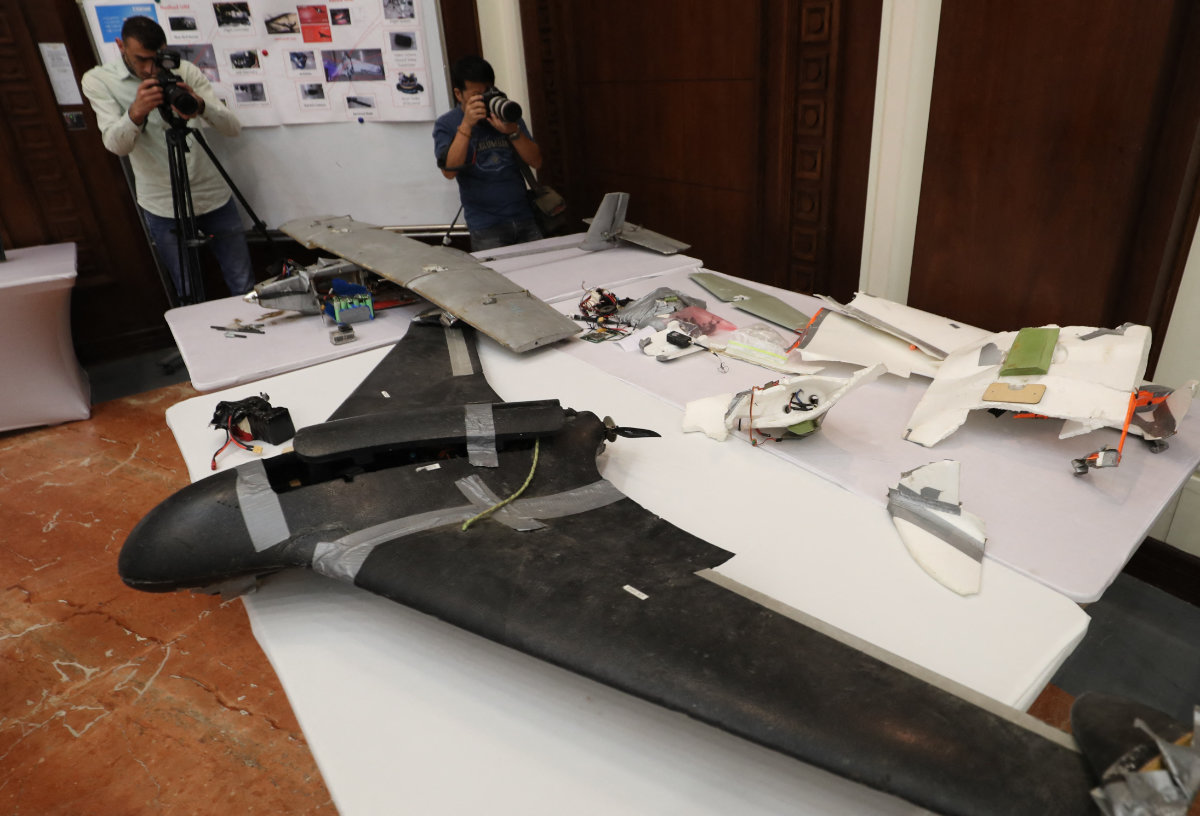

A picture taken on June 19, 2018 in Abu Dhabi shows the wreckage of a drone used by Yemen's Houthi militia in battles against the coalition forces led by Saudi Arabia and the UAE. The coalition was assembled in 2014 to help restore the UN-recognized Yemeni government that was ousted by the Iran-backed Houthis. (AFP)
In addition to supplying non-state actors with its drones, Iran is also developing a lucrative export market for the technology.
In November 2022, analysis by the Washington Institute for Near East Policy concluded that Iran “may be outsourcing kamikaze drone production to Venezuela,” a country sanctioned by the US in part because of its ties with Tehran, and in July 2023, Forbes reported that Bolivia had also expressed interest in acquiring Iranian drone technology.
Iran is not alone in developing markets for such weapons in South America. In December 2022, military intelligence and analysis organization Janes reported that Argentina had signed a contract with the Israeli Ministry of Defense to buy man-portable anti-personnel and anti-tank loitering munitions, produced by Israeli arms company Uvision.
Only four days ago, it was reported that Iranian-made armed drones have been used by the Sudanese army to turn the tide of conflict in the country’s civil war and halt the progress of the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces.
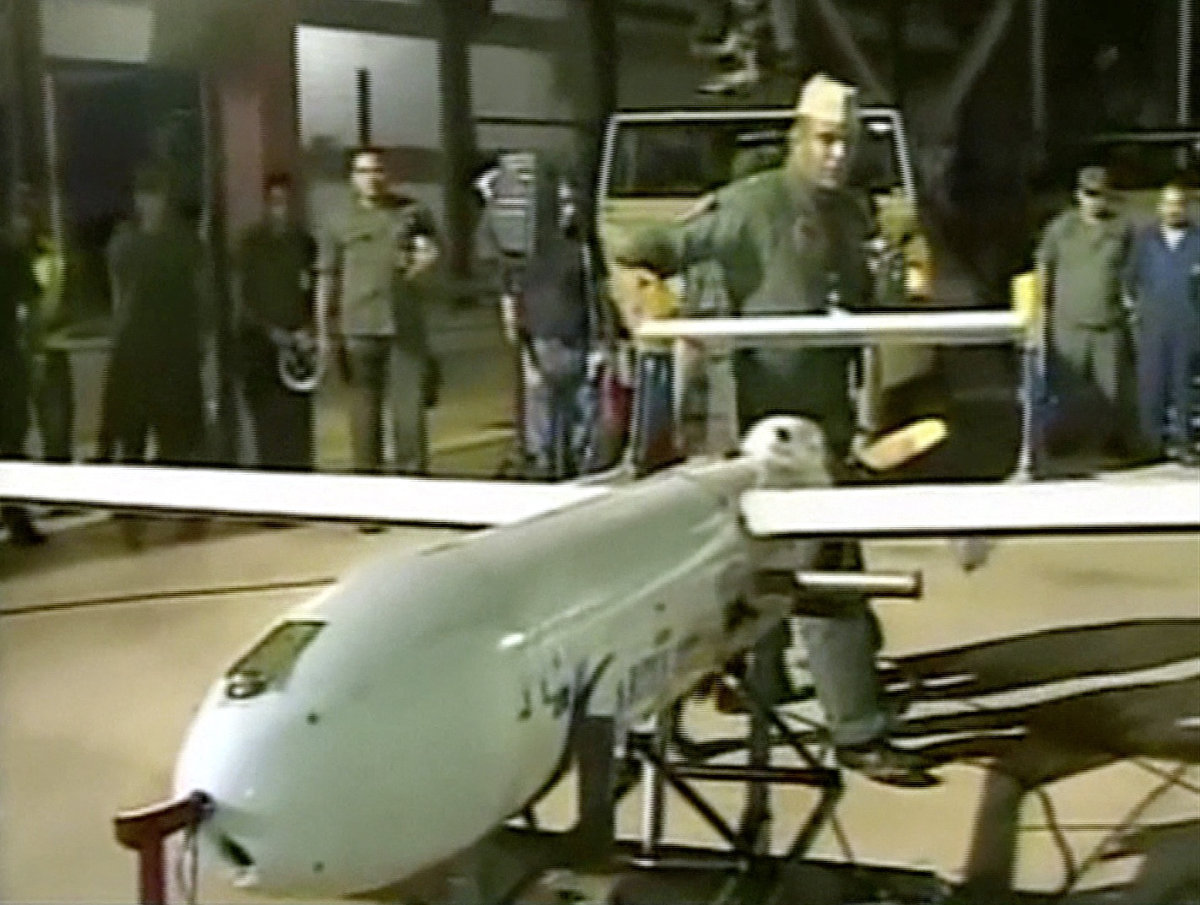

TV grab showing a UAV made in Venezuel, with help from Iran, China and Russia in 2012. Iran is thought to be outsourcing UAV production to Venezuela. (VTA handout via AFP)
According to Reuters, Sudan’s acting Foreign Minister Ali Sadeq denied his country had obtained any weapons from Iran. But the news agency cited “six Iranian sources, regional officials and diplomats,” who confirmed that Sudan’s military “had acquired Iranian-made unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) over the past few months.”
Iran’s interest in Sudan is strategic, according to an unnamed Western diplomat quoted by Reuters: “They now have a staging post on the Red Sea and on the African side.”
But Iran’s most significant state customer for its deadly drone technology to date is Russia.
In September 2022, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky expelled Iranian diplomats from the country after several downed drones were found to have been made in Iran.
“We have a number of these downed Iranian drones, and these have been sold to Russia to kill our people and are being used against civilian infrastructure and peaceful civilians,” Zelensky told Arab News at the time.
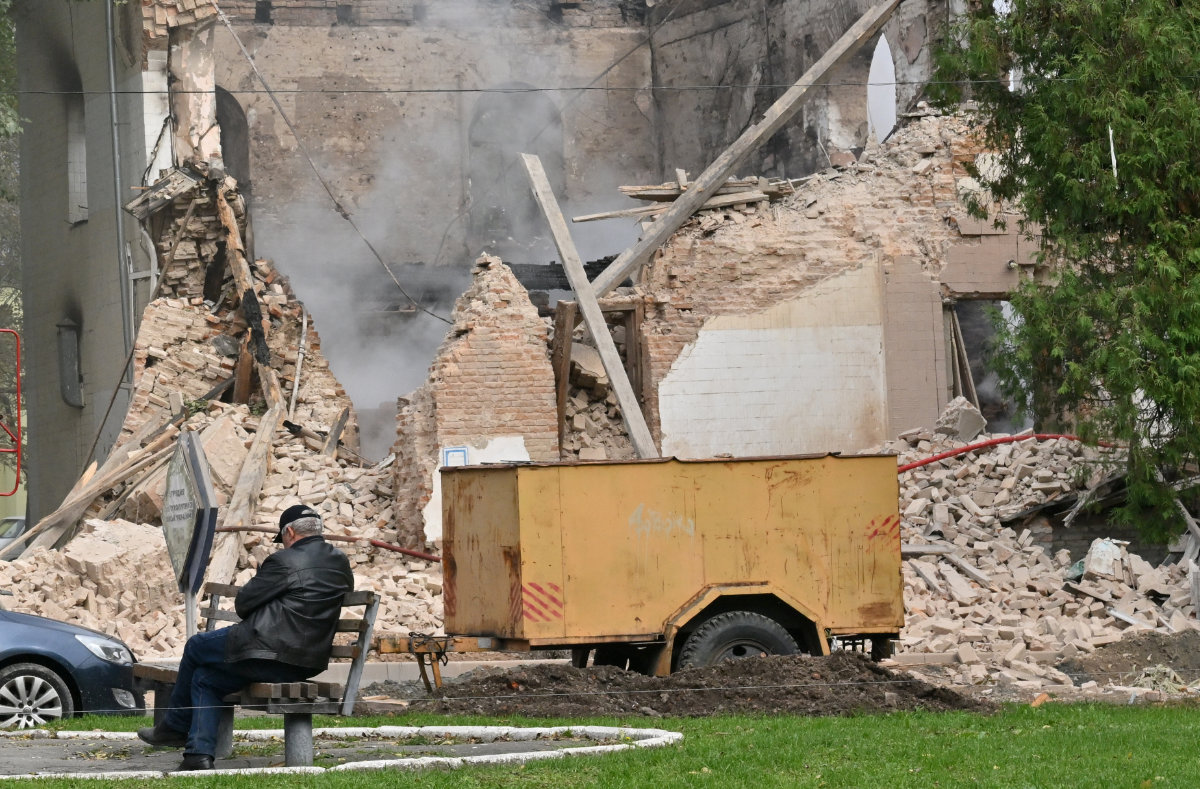

A local resident sits outside a building destroyed by Iranian-made drones after a Russian airstrike on Bila Tserkva, southwest of Kyiv, on October 5, 2022. (AFP/File)
Since then, drone use on both sides in the conflict has escalated, with Russia procuring many of its weapons and surveillance systems from Iran, in violation of UN resolutions.
At a meeting in New York on Friday the UK’s deputy political coordinator told the UN Security Council that “Russia has procured thousands of Iranian Shahed drones and has used them in a campaign against Ukraine’s electricity infrastructure, which is intended to beat Ukraine into submission by depriving its civilians of power and heat.”
But although Iran has successfully exported its drones, and drone technology, to several countries and non-state actors, its own use of the weapons has not been particularly auspicious.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
As initially developed, drones were intended first for surveillance, and then as armed platforms for tactical use against single targets.
It is not known what Iran hoped to achieve by unleashing a swarm of 170 drones at once against Israel on Saturday night, in its first openly direct attack against the country. But all the reportedly failed attack has done is demonstrate that slow-moving drones deployed en masse in a full-frontal assault are extremely vulnerable to sophisticated air defense systems.
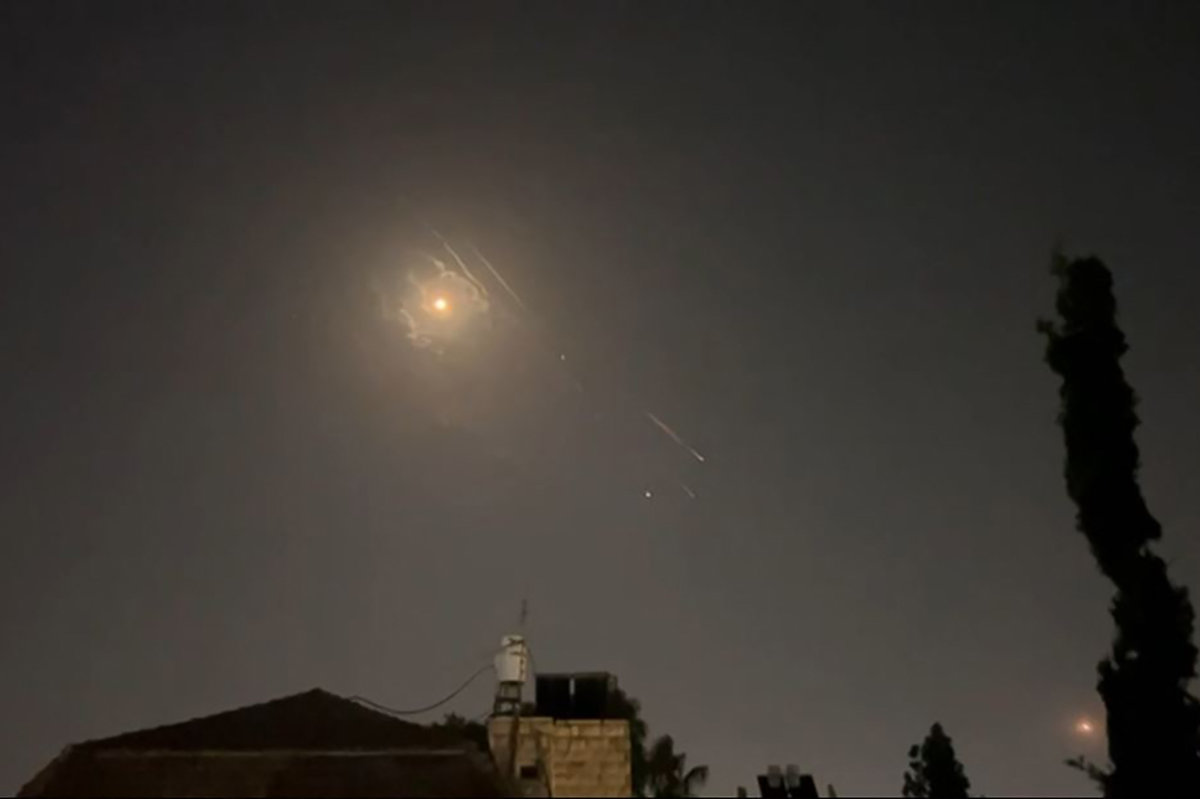

This video grab from AFPTV taken on April 14, 2024 shows explosions lighting up Jerusalem sky as Israeli air defenses intercept an Iranian drone. (AFPTV/AFP)
The vast majority of the drones, and the 30 cruise and 120 ballistic missiles fired at Israel in retaliation for the Israeli airstrike on the Iranian consulate in Damascus on April 1, were shot down, either intercepted by American warships and aircraft or downed by Israel’s multi-layered anti-missile systems.
Drone warfare through the years
The word “drone” used to describe an unmanned aerial vehicle was first coined during the Second World War, when the British converted a Tiger Moth biplane to operate as an unmanned, radio-controlled target for anti-aircraft gunnery training. Codenamed Queen Bee, between 1933 and 1943, hundreds were built. Purpose-built drones as we know them today first took to the skies over Vietnam in the 1960s in the shape of the Ryan Aeronautical Model 147 Lightning Bug. Radio-controlled, the jet-powered aircraft was launched from under-wing pylons fitted to converted C-130 Hercules transport aircraft. After its reconnaissance mission was over, the Lightning Bug parachuted itself back to Earth, where it could be recovered by a helicopter. It was Israel that developed what is considered to be the world’s first modern military surveillance drone, the propellor-driven Mastiff, which first flew in 1973. Made by Tadiran Electronic Industries, it could be launched from a runway and remain airborne for up to seven hours, feeding back live video.
• • • • • •

The Mastiff was acquired by the US military, which led to a collaboration between AAI, a US aerospace company, and the government-owned Israel Aerospace Industries. The result was the more sophisticated AAI RQ-2 Pioneer, a reconnaissance drone used extensively during the 1991 Gulf War. The breakthrough in drones as battlefield weapons was made thanks to Abraham Karem, a former designer for the Israeli Air Force who emigrated to the US in the late 1970s. His GNAT 750 drone was acquired by General Atomics and operated extensively by the CIA over Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1993 and 1994. This evolved into the satellite-linked RQ-1 Predator. First used to laser-designate targets and guide weapons fired by other aircraft, by 2000 it had been equipped with AGM-114 Hellfire missiles, and the first was fired in anger less than a month after the 9/11 terrorist attacks on America.
• • • • • •

The first strike, against a convoy carrying a Taliban leader in Afghanistan, missed. But on Nov. 14, 2001, a Predator that had taken off from a US air base in Uzbekistan fired two Hellfire missiles into a building near Kabul, killing Mohammed Atef, Osama bin Laden’s son-in-law, and several other senior Al-Qaeda personnel. Since then, silent death from the air has become the signature of American military power, thanks to a remotely operated weapons system from which no one is safe, no matter where they are. This was made clear by the audacious attack on the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corp’s Quds Force commander Qassem Soleimani, killed by a drone strike as he left Baghdad airport on Jan. 3, 2020. The MQ-9 Reaper drone that killed him had been launched from a military base in the Middle East and was controlled by operators at a US airbase over 12,000 km away in Nevada. — Jonathan Gornall