LONDON: On Friday, Sept. 29, Daniel Seidemann, an Israeli lawyer who specializes in Israeli-Palestinian relations in Jerusalem, made the finishing touches to a research paper he had been commissioned to write by the Research & Studies Unit of Arab News.
The subject was the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound on the Haram Al-Sharif, known to Jews and Christians as the Temple Mount, which holds such significance for all three Abrahamic faiths, but where only Muslims may pray and other faiths may only visit.
That, at least, is the status quo that has prevailed at the site since 1967.

A general view of East Jerusalem and the Dome of the Rock at the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound, Islam’s third holiest site on October 15, 2023. (AFP)
But as the founder of Terrestrial Jerusalem, a nongovernmental organization focused on finding a resolution to the question of the city consistent with the two-state solution, in recent months Seidemann had become increasingly aware, and concerned, that the delicate balance that has been maintained at the site for the past 56 years was in danger of being torn apart.
That, he understood, was a recipe for disaster and in the hope of averting it he was anxious “to familiarize both leadership and the public at large with the relevant facts.”
Just over a week later, Seidemann awoke on the morning of Saturday, Oct. 7, to the news that the Palestinian militant group Hamas had launched its devastating attack on Israel from Gaza.
As he listened to the news unfolding, it came as no surprise to him when he heard that Hamas commander Mohammed Deif had described the assault as “Operation Al-Aqsa Deluge,” which he claimed had been launched in retaliation for Israel’s “desecration” of the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound.
Whether or not the attack had been motivated solely by recent events at the mosque — and Hamas had certainly issued previous warnings about the increasingly frequent breaches of the long-established status quo at the site — Seidemann knew one thing was certain.

Israeli minister and Jewish Power party chief Itamar Ben-Gvir (C) walking through the courtyard of Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa mosque compound, known to Jews as Temple Mount, early on January 3, 2023. (AFP)
“The Al-Aqsa was a contributing factor, no doubt,” he said. “It always comes back to Al-Aqsa, and Jerusalem always has the last word.
“We have to familiarize both the Israeli public and the Arab world with the idea of a Jerusalem which will allow for cohabitation of these conflicting narratives. It isn’t utopia, but Jerusalem knows how to do this.
“And whether this comes to fruition or not, we will always be dealing with the question of Al-Aqsa, and nobody in the Arab or Muslim world can afford to ignore it.”
The sensitivity of the site was highlighted on Sept. 27 when Nayef Al-Sudairi, the newly appointed Saudi ambassador to the Palestinians, was reported to have agreed to postpone a planned visit to Al-Aqsa Mosque out of deference to unspecified Palestinian concerns.
These are thought to relate to the unwelcome rise in the Israeli security presence at the site, which has aided a series of provocative visits by Jewish religious extremists who are dedicated ultimately to building a Jewish temple on the site.
The extremists have the support of many in Israel’s Cabinet. On Oct. 3, Itamar Ben-Gvir, Israel’s right-wing national security minister, called on the Knesset and the state security cabinet to urgently consider “opening the Temple Mount to Jews 24/7.”

A Palestinian man prays as Israeli security forces escort a group of Jewish settlers visiting the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound on June 2, 2019. (AFP)
That day, 500 members of the Israeli settler movement entered the site. The following day, the fifth day of the Jewish holiday of Sukkot, more than 1,000 forced their way into the compound, repeating a performance that in recent months has been seen more and more often.
This time the incursion, not only witnessed but assisted by members of Israel’s security forces, earned a rebuke for the Israeli government from Jordan, which since 1924 has been the universally recognized custodian of the site through the auspices of the Jordanian-appointed Jerusalem Waqf and Al-Aqsa Mosque Affairs Department.
In a letter of protest to the Israeli Embassy in Amman the Jordanian Foreign Ministry condemned “incursions by hardliners, settlers and Knesset members into the Holy Al-Aqsa Mosque under police protection” and “the restriction of access for worshippers to the mosque, the desecration of Islamic graves and the increasing attacks on Christians in occupied Jerusalem.”
Seidemann said the ideological thinking behind the incursions into Al-Aqsa by “what began as a small, perhaps lunatic fringe, has become more mainstream.”
He added: “The National Religious Party, the ideological right, including cabinet ministers, see Israel as a continuation of ancient biblical history. For them, this is ‘the third Jewish Commonwealth,’ after the first and second temples.”
The “first temple” is the Temple of Solomon, believed by Jews to have existed on the site of the Temple Mount from the 10th to the 6th century BCE, when it was destroyed by the Babylonian King Nebuchadnezzar II in 587 BCE. The “second temple,” its replacement, was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE.
“From the perception of the religious right, the greatest blunder that Israel has made since 1967 was (Israel’s then defense minister) Moshe Dayan’s decision to take down the Israeli flags on the Temple Mount and hand the keys over to the Waqf,” said Seidemann.

Israeli Border police stand guard by newly-installed security metal detectors at the entrance to Al-Aqsa compound in Jerusalem’s Old City, on July 16, 2017. (AFP)
After victory in the Six Day War in 1967, Israel occupied East Jerusalem, including the Haram Al-Sharif, and has held it ever since.
On June 7, 1967, shortly after Israeli paratroopers stormed the compound, their commander, Col. Motta Gur, radioed a message to headquarters that has struck a controversial chord with right-wing Israelis ever since: “The Temple Mount is in our hands.”
Controversial, because it would not be in their hands for long.
The story goes that Dayan was watching the scene unfold through binoculars when, to his horror, he saw that one of the paratroopers had climbed to the top of the Dome of the Rock and raised the Israeli flag.
Dayan, keenly aware of how the crass symbolism would play across the Islamic world, ordered the flag to be taken down immediately. Later, standing by the Western Wall, at Israel’s moment of victory, Dayan made a remarkably conciliatory statement.
“To our Arab neighbors we extend, especially at this hour, the hand of peace,” he said. “To members of the other religions, Christians and Muslims, I hereby promise faithfully that their full freedom and all their religious rights will be preserved.
“We did not come to Jerusalem to conquer the holy places of others.”

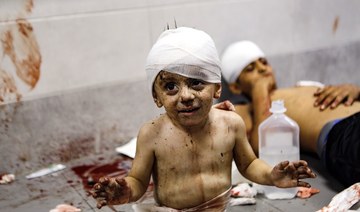
People stand over bodies of Palestinians killed in an Israeli strike on the Ahli Arab hospital in central Gaza after they were transported to Al-Shifa hospital, on October 17, 2023. (AFP)
The keys to the gates and responsibility for the policing and control of the Al-Aqsa compound were returned to the Waqf.
Over the following decades Jews were allowed into the compound on certain days, entering through the Mughrabi Gate. This was the only entrance through which non-Muslims could reach the esplanade.
All that started to change, said Seidemann, after 2003, when the Israeli government unilaterally imposed new arrangements that increasingly sidelined the Waqf.
Today, it is Israeli police who decide who can and cannot visit the compound, which is now seeing increasing numbers of settlers and other activists laying claim to the site.
“They believe it is the raison d’etre of this government to reverse the decision of Dayan because it thwarts the unfolding of the divine plan that is Israel,” said Seidemann. “This has now become mainstream.”
It has also become an article of faith for many in the Israeli Cabinet, despite (current Prime Minister) Benjamin Netanyahu’s statement in 2015, at the urging of US Secretary of State John Kerry, that “Israel will continue to enforce its longstanding policy: Muslims pray on the Temple Mount; non-Muslims visit the Temple Mount.”
At the time, PLO Secretary-General Saeb Erekat rejected Netanyahu’s assurances.

Israeli soldiers are positioned outside kibbutz Beeri near the border with the Gaza Strip on October 17, 2023. (AFP)
“Before the year 2000, tourists used to enter the Haram Al-Sharif under the guard of the employees of the Waqf department and non-Muslims were not allowed to pray there,” Erekat was quoted as saying in the Jerusalem Post.
“But now the Israelis have changed the regulations and tourists visit the site after receiving permits from Israeli authorities and under protection of the Israel police.”
Since then, provocations have escalated. In January this year a visit to the Al-Aqsa compound by Israel’s extreme right-wing national security minister Ben-Gvir was described as “just one more irresponsible provocation” by Israeli newspaper Haaretz.
It was, said Seidemann, a “triumphal visit, showing them who’s boss.”
Encouraged by politicians like Ben-Gvir, members of settler groups, the Temple Mount movement and the National Religious Party have increasingly thronged Al-Aqsa, even though under a long-established Rabbinic law related to concepts of ritual purity Jews are forbidden from entering the site.
“Last May, thousands of young ultra-right religious Israelis celebrating the victory in 1967 marched through the Muslim Quarter shouting ‘Death to the Arabs.’ It was just horrible. I think that was the worst day that I can remember in Jerusalem,” said Seidemann.
Prior to the march, hundreds of ultranationalists entered the Al-Aqsa compound.
“They could have gone by all sorts of other routes, but they went through the Muslim Quarter, to show them: ‘This is our place, we’re the landlord, you’re the tenant’.”

An Israeli border guard intervenes as participants of an Israeli annual far-right, flag-waving rally, beat Palestinian men during the event in the Old City of Jerusalem, on May 18, 2023. (AFP)
And it is not just Muslims who are on the receiving end of the new wave of religious intolerance, he said.
“In recent months there has also been a serious spike in hate crimes against Christians, inspired, I believe, by some of the people in the government, which only condemned it last week, for the first time after eight months. Meanwhile, the mayor of Jerusalem has not condemned it, and the city council has not condemned it.”
Extremists are also pressing for the building of a national park on the Mount of Olives, a site of central importance to the Christian faith.
“It’s a mirror image of what’s happening at Al-Aqsa,” said Seidemann. “A Christian holy site is being transformed by settlers into a shared Christian-Jewish holy site in a way that the Temple Mount movement wants to transform Al-Aqsa from a Muslim site into a shared Jewish-Muslim site.”
It is not that the politicians who are attempting to sabotage the status quo in Jerusalem “are necessarily inherently racist,” Seidemann believes.
“It’s that they understand that speaking with empathy and respect to the equities of others, Muslims, Arabs, or Christians, is an electoral liability and they’ll lose votes among their base.
“Personally, I would prefer them being racist, because otherwise this is a reflection on what has become of us.
“In 1967 Israel annexed Jerusalem. Every Israeli prime minister until Netanyahu has said ‘Let’s not force the issue, especially on the religious sites. We are also custodians of the most important sites in Christianity and Islam, we will deal with it with sensitivity and respect’.”

The family of a Palestinian child killed in an Israeli air strike mourn outside a hospital in Khan Yunis in the southern Gaza Strip, on October 17, 2023. (AFP)
Now, Seidemann says he fears that Israel, increasingly in the grip of extremist religious groups and politicians, is in danger of losing its way.
“Occupation is not what we do,” he said. “Occupation is who we became, and it is undermining the moral foundations of Israeli society.”
Al-Aqsa, he added, “is becoming the quintessential arena of conflict for Israelis and Palestinians, Jews and Muslims. It is not ennobling the souls of any of us and to a certain extent has defiled a very sacred spot.”
On Sept. 6, Tamir Pardo, a former head of Mossad, Israel’s intelligence agency, told the Associated Press that Israel was enforcing an apartheid system in the West Bank. “He said that before the war started, but I think he would still say it now,” said Seidemann.
“He said there is only one existential threat to Israel in this generation. It’s not the Iranian nuclear threat — we can handle that. It’s not 100,000 Hezbollah rockets — horrible, but we can deal with it.
“But Israel cannot survive as a perpetually occupying power. Israel will end occupation, or occupation will be the end of us.”