SAO PAULO: As the number of Muslims in Latin America increases and Islamic communities gain visibility, more and more cases of Islamophobia are being reported in the region. Community leaders, most of them women, are striving to tackle the issue.
With a Muslim population estimated at between 800,000 and 1.5 million, Brazil is the only nation in Latin America where a comprehensive study on Islamophobia has been conducted.
The issue has been in the spotlight after a copy of the holy Qur’an was burned on June 28 outside Stockholm’s central mosque in an offensive act tolerated by the authorities in Sweden. Although South America has not witnessed such crude display of intolerance, Islamophia is believed to exist just under the surface in many countries.

Swedish police watch as Salwan Momika, who fled from Iraq to Sweden several years ago, prepares to deface the Muslim holy book outside a mosque in Stockholm on June 28, 2023, during the Eid al-Adha holiday. (JAFP)
Led by anthropologist Francirosy Barbosa, a professor at the University of Sao Paulo and herself a Muslim convert, the research involved a survey of 653 Muslims that showed most of them having already suffered some kind of Islamophobia.
“Women were the majority of the respondents, something that already demonstrates that they’re the ones who suffer the most,” Barbosa told Arab News.
About 54 percent of the men who took part in the study — both those born to Islam and converts — said they have faced some sort of embarrassment due to their religion. Most cases happened on the street, in the workplace or at school.
The proportions are higher among women, with 66 percent of those born to Islam reporting that they have been offended or attacked due to their faith, and 83 percent of converts reporting the same.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Many incidents involve subtle comments and jokes, like a work colleague who discovers that somebody in the office is Muslim and begins to call him or her a “suicide bomber,” or a person who insists that her friend should not wear a headscarf because it is a symbol of male domination.
But the study also reports serious cases of physical violence, such as an unknown attacker spraying insecticide in the eyes of a woman wearing a hijab, and a girl who left her mosque and was hit by a man on the street.
Female converts “are the major victims of Islamophobia because they’re more vulnerable. Many of them come from poor neighborhoods and have to use public transportation,” Barbosa said.
Female converts also have to deal with pressures from their own families. The result is that many of them give up wearing a headscarf after being attacked, something “that brings suffering because they feel they’re failing to attend a divine commandment,” Barbosa said.

Cases of harassment particularly targeting female adherents of the faith in Brazil are on the rise. (Supplied photo)
She added that Islamophobia grew in Brazil under former President Jair Bolsonaro (2019-2022), when different anti-Muslim groups became more powerful.
“In that period, there was a boom in pro-Zionist evangelical churches, for instance,” she said. The survey’s respondents said evangelical Christians are the religious segment that discriminates against them the most.
Barbosa was invited earlier this year to take part in a workshop organized by the Ministry of Human Rights and Citizenship to discuss hate speech.
Her study on Islamophobia was presented to the group and will be part of its final report, which will orientate the government’s policies to combat intolerance.
“In our research, we included some guidelines for the struggle against Islamophobia, like the need to invest in education about religions and Islam. Now, those suggestions may finally come to light with the new government (of President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva),” Barbosa said.
In Argentina, activists against Islamophobia have been counting on partnerships with governmental institutions as well.
FASTFACTS
Recent survey found women suffer higher rate of Islamophobia than men.
Majority of incidents occurred on the street, in the workplace or at school.
Female respondents said they are often targeted for wearing the hijab.
In 2022, Islam para la Paz (Islam for Peace) celebrated a deal with the National Institute against Discrimination, Xenophobia and Racism — known by the Spanish acronym INADI — with the goal of promoting cooperation against religious discrimination.
Melody Amal Khalil Kabalan, who heads Islam para la Paz, said many press outlets were spreading misinformation about Qatar when it hosted the FIFA World Cup last year, so her organization and INADI promoted a workshop on the country for journalists.
“This year, we’ll organize a program called School without Discrimination, which will include workshops about Islamic habits for students,” she told Arab News.
While Islamophobia in Argentina is not comparable to what happens in European nations, there has been a growing number of cases lately, she said. Most cases involve women, like in Brazil.
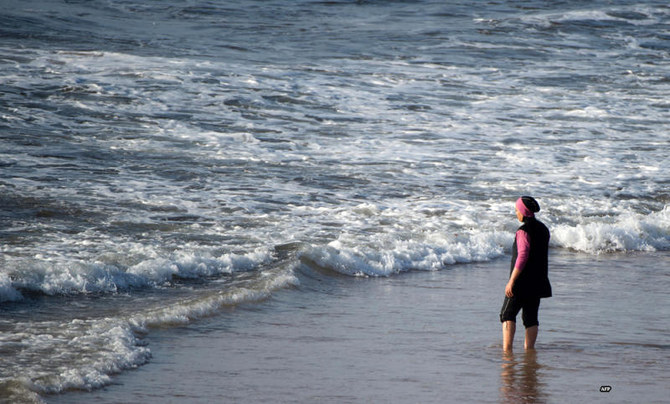

In Argentina, even the modest burkini swimwear in public places could elicit hate as it is associated with being Muslim. (Supplied
“In a notorious incident, a woman was forbidden to get into a swimming pool in (the city of) Mendoza wearing her burkini,” Khalil said.
“In other cases, women were impeded by government officials to take pictures for documents wearing a hijab, which is their right.”
Victims of Islamophobia can report incidents to INADI, but many fail to do so “because they think the authorities won’t defend Muslims as they defend other groups,” Khalil said.
“We realized that this perception is connected to the fact that our communities aren’t so organized to resist discrimination as other communities in Argentina.”
She said it is up to Muslims to inform and educate Argentinian society about their needs and specificities.
“We have a responsibility to tell people about our way of life. It’s not only a problem for the government,” she added.
Islam para la Paz recently created an observatory of Muslim issues and is gathering information on the communities’ problems.
In Colombia, a group of women led by Maria Jose Acevedo Garcia established five years ago the Islamic Foundation Assalam of Colombian Muslim Women, whose goal is to protect Muslim women and prevent Islamophobia.
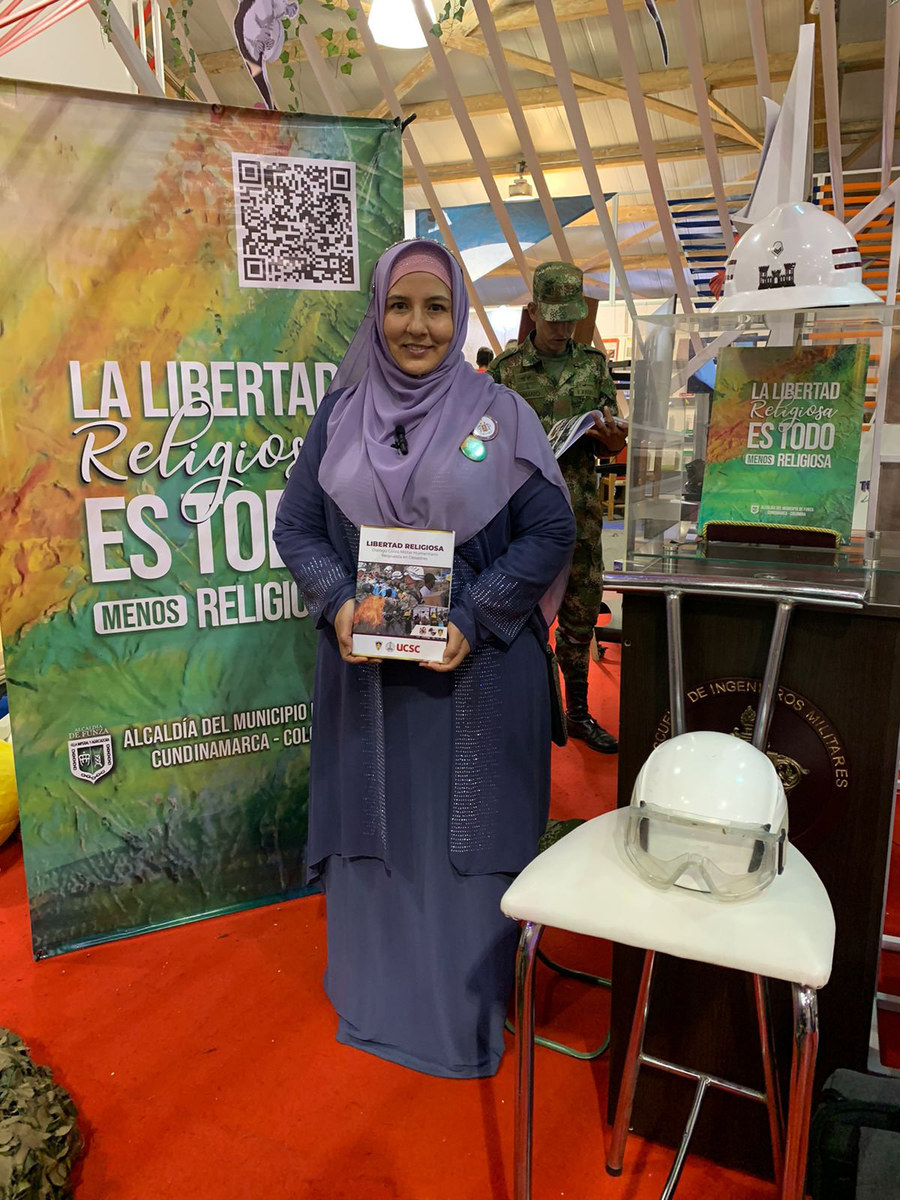

Maria Jose Acevedo during an event on religious freedom in Colombia. (Supplied)
She said the most common incidents involve discrimination at school, the workplace and in government agencies.
“Women at times are discriminated against for wearing a hijab at work. In those cases, I send a letter to the person in charge and schedule a visit to the company in order to inform people about Islam,” Acevedo told Arab News.
Raised in a Catholic family, she converted to Islam 20 years ago. At first, she would commonly hear offensive comments and get angry, but over time she “learned how to react calmly and educate people.”
She said: “Assalam frequently visits schools and universities to offer workshops against discrimination. That’s the only way to change things.”
Acevedo added that during crises in Muslim nations — such as the war in Syria and the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan — Islamophobia usually increases.
“We still haven’t experienced a great number of physical attacks, but incidents in which people tried to take off the hijab of a woman on public transportation have already been reported,” she said.

Caption
Assalam recently met with governmental authorities in order to present to them the needs of Muslim women in Colombia.
Problems commonly arise at the airport, for instance, when women coming from Muslim nations are told to take off the headscarf during inspection.
Acevedo expressed hope that more government employees will understand the nature of Islam in the future.
In Mexico, where the Muslim community has been growing over the past years, Islamophobia is noticeable in the arts, books and the news, where “negative expressions are commonly employed when it comes to Islam,” anthropologist Samantha Leyva Cortes told Arab News.
In her studies about Muslim communities in Mexico City and San Cristobal de las Casas, Leyva was told by many women that they are treated as foreigners due to their hijab.
“Shopkeepers frequently assume they aren’t from Mexico and charge them more than they should for a product,” she said.

Sonia Garcia, a Mexican convert to Islam, has partnered with Mayte Gutierrez, another Latina convert to Islam, to help build and operate an entirely new center to help Muslims feel more at home while in Tijuana. (Photo: The Latina Muslim Foundation)
Women wearing headscarves have to face all kinds of sexist remarks on the street and on public transportation, Leyva said.
“People generally think they’re passive, disenfranchised women. They don’t consider that wearing a hijab is their choice,” she added.
But the younger generations have been opening new paths lately. Many Muslim women are expanding their presence on social media and making themselves visible in the public arena.
“Many conversions have been happening online, so the internet is an important space for them,” Leyva said.
Barbosa said most Muslim leaders have been dealing with Islamophobia inadequately. “In general, they’re concerned only about spreading the religion and think that talking about discrimination and violence is something negative that can raise more problems,” she added.
Her goal now is to apply the same survey in other Latin American countries so the problem of Islamophobia in the whole region will be known, and communities and governments will be able to act.